Spatial computing integrates real-world environments with digital data through technologies like augmented reality, enabling immersive user experiences and advanced location-based services. Blockchain offers a decentralized ledger system ensuring secure, transparent transactions and data integrity across various applications, from finance to supply chain. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies transform industries and shape the future of digital interaction.
Why it is important
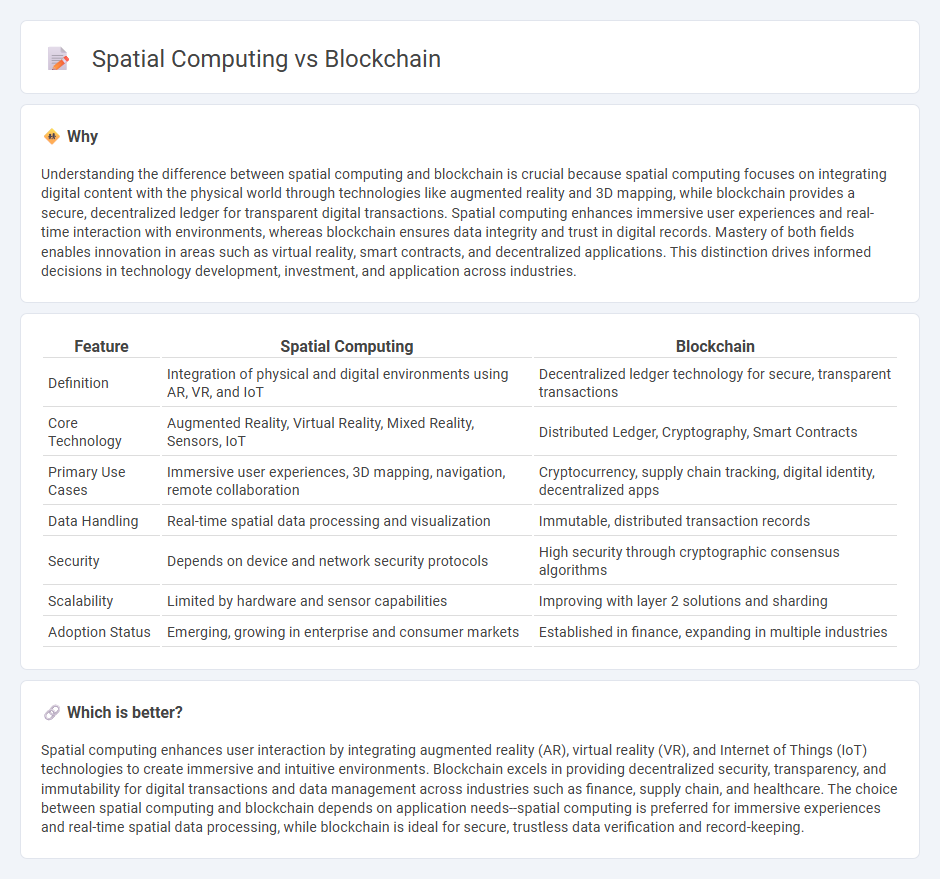
Understanding the difference between spatial computing and blockchain is crucial because spatial computing focuses on integrating digital content with the physical world through technologies like augmented reality and 3D mapping, while blockchain provides a secure, decentralized ledger for transparent digital transactions. Spatial computing enhances immersive user experiences and real-time interaction with environments, whereas blockchain ensures data integrity and trust in digital records. Mastery of both fields enables innovation in areas such as virtual reality, smart contracts, and decentralized applications. This distinction drives informed decisions in technology development, investment, and application across industries.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Spatial Computing | Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of physical and digital environments using AR, VR, and IoT | Decentralized ledger technology for secure, transparent transactions |
| Core Technology | Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, Mixed Reality, Sensors, IoT | Distributed Ledger, Cryptography, Smart Contracts |
| Primary Use Cases | Immersive user experiences, 3D mapping, navigation, remote collaboration | Cryptocurrency, supply chain tracking, digital identity, decentralized apps |
| Data Handling | Real-time spatial data processing and visualization | Immutable, distributed transaction records |
| Security | Depends on device and network security protocols | High security through cryptographic consensus algorithms |
| Scalability | Limited by hardware and sensor capabilities | Improving with layer 2 solutions and sharding |
| Adoption Status | Emerging, growing in enterprise and consumer markets | Established in finance, expanding in multiple industries |
Which is better?
Spatial computing enhances user interaction by integrating augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies to create immersive and intuitive environments. Blockchain excels in providing decentralized security, transparency, and immutability for digital transactions and data management across industries such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare. The choice between spatial computing and blockchain depends on application needs--spatial computing is preferred for immersive experiences and real-time spatial data processing, while blockchain is ideal for secure, trustless data verification and record-keeping.
Connection
Spatial computing leverages blockchain technology to enhance data security and transparency within virtual and augmented reality environments. Blockchain's decentralized ledger enables immutable tracking of digital assets and interactions in spatial platforms, fostering trust among users. Integrating these technologies supports advanced applications like secure digital identity verification and seamless asset transfers in the metaverse.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Blockchain technology excels in decentralization by distributing data across a global network of nodes, ensuring transparency, security, and resistance to censorship. Spatial computing integrates decentralized elements through edge computing and blockchain-based data sharing to enhance real-time interactions in augmented and virtual environments. Explore how decentralization shapes the future of blockchain and spatial computing advancements.
Immersive Environments
Blockchain technology ensures secure and transparent transactions in immersive environments by creating decentralized ledgers that prevent data tampering. Spatial computing leverages 3D mapping, augmented reality, and sensors to enable real-time interaction with digital content in physical spaces, significantly enhancing user experience. Explore how these technologies converge to transform immersive environments and unlock new possibilities.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts on blockchain provide secure, decentralized transaction execution, leveraging cryptographic validation to ensure trustless agreements. Spatial computing enhances smart contracts by integrating real-world, location-based data and augmented reality interfaces, enabling context-aware contract interactions and automation within physical environments. Explore further to understand how these technologies converge to revolutionize digital agreements.
Source and External Links
Blockchain Wikipedia - Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers, providing a secure and transparent way to track data.
IBM Blockchain - Blockchain operates as a decentralized digital ledger, offering a secure and transparent method for recording transactions and tracking assets within business networks.
AWS Blockchain - Blockchain technology is an advanced database mechanism that allows for transparent information sharing, creating an immutable ledger for tracking transactions across a business network.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com