Biosignal decoding focuses on interpreting physiological data such as brainwaves, heart rate, and muscle activity to enable advanced health monitoring and brain-computer interfaces. Natural language processing (NLP) specializes in analyzing and generating human language to enhance communication technologies, sentiment analysis, and automated translation. Explore how these two cutting-edge technologies intersect and revolutionize human-computer interaction.
Why it is important
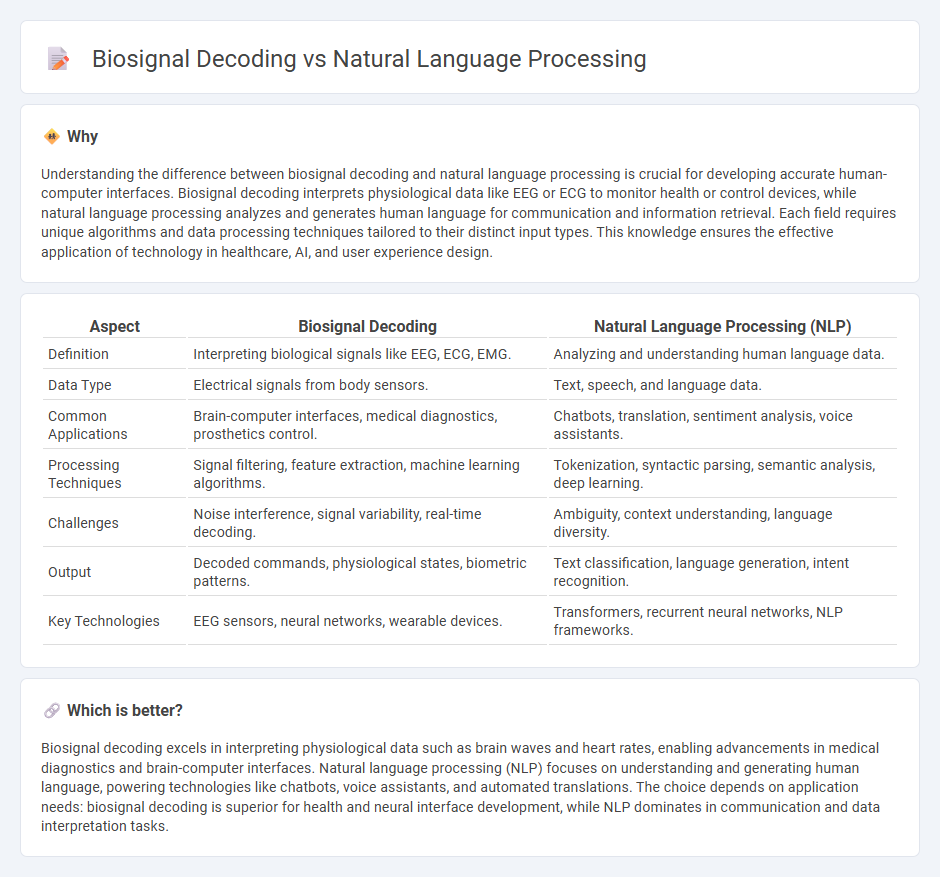
Understanding the difference between biosignal decoding and natural language processing is crucial for developing accurate human-computer interfaces. Biosignal decoding interprets physiological data like EEG or ECG to monitor health or control devices, while natural language processing analyzes and generates human language for communication and information retrieval. Each field requires unique algorithms and data processing techniques tailored to their distinct input types. This knowledge ensures the effective application of technology in healthcare, AI, and user experience design.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biosignal Decoding | Natural Language Processing (NLP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpreting biological signals like EEG, ECG, EMG. | Analyzing and understanding human language data. |
| Data Type | Electrical signals from body sensors. | Text, speech, and language data. |
| Common Applications | Brain-computer interfaces, medical diagnostics, prosthetics control. | Chatbots, translation, sentiment analysis, voice assistants. |
| Processing Techniques | Signal filtering, feature extraction, machine learning algorithms. | Tokenization, syntactic parsing, semantic analysis, deep learning. |
| Challenges | Noise interference, signal variability, real-time decoding. | Ambiguity, context understanding, language diversity. |
| Output | Decoded commands, physiological states, biometric patterns. | Text classification, language generation, intent recognition. |
| Key Technologies | EEG sensors, neural networks, wearable devices. | Transformers, recurrent neural networks, NLP frameworks. |
Which is better?
Biosignal decoding excels in interpreting physiological data such as brain waves and heart rates, enabling advancements in medical diagnostics and brain-computer interfaces. Natural language processing (NLP) focuses on understanding and generating human language, powering technologies like chatbots, voice assistants, and automated translations. The choice depends on application needs: biosignal decoding is superior for health and neural interface development, while NLP dominates in communication and data interpretation tasks.
Connection
Biosignal decoding translates physiological signals such as EEG or EMG into interpretable data, enabling machines to understand human intentions or emotional states. Natural language processing (NLP) leverages these decoded signals to improve communication interfaces, allowing more accurate speech recognition, sentiment analysis, or command execution. Combining biosignal decoding with NLP enhances human-computer interaction by bridging neural activity and language comprehension.
Key Terms
Natural Language Processing:
Natural Language Processing (NLP) leverages computational algorithms to analyze, interpret, and generate human language, enabling applications such as machine translation, sentiment analysis, and chatbots. NLP employs techniques like tokenization, syntactic parsing, and deep learning models, including transformers and recurrent neural networks, to process textual data efficiently. Explore the latest advancements in NLP architectures and their impact on enhancing human-computer interaction.
Tokenization
Tokenization in natural language processing (NLP) involves breaking down text into meaningful units like words, subwords, or characters to enhance model understanding and performance. In biosignal decoding, tokenization refers to segmenting continuous physiological signals--such as EEG or ECG--into discrete, analyzable segments or events for pattern recognition and classification. Explore further to understand how tokenization techniques differ and impact processing efficiency in both domains.
Semantic Analysis
Natural language processing (NLP) excels in semantic analysis by interpreting context, sentiment, and meaning from textual data using techniques like word embeddings and transformer models. Biosignal decoding focuses on translating physiological signals such as EEG or ECG into meaningful information, often leveraging machine learning for pattern recognition but with distinct challenges in semantic interpretation. Explore more to understand how semantic analysis techniques differ and intersect in NLP and biosignal decoding applications.
Source and External Links
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)? - TechTarget - Natural language processing (NLP) is the ability of a computer program to understand, interpret, and manipulate human language as it is spoken and written, using techniques like parsing, word segmentation, and morphological analysis to make sense of text.
What is Natural Language Processing? - NLP Explained - AWS - NLP is a machine learning technology that enables computers to interpret, manipulate, and comprehend human language through methods such as supervised and unsupervised learning, as well as natural language understanding and generation.
What Is NLP (Natural Language Processing)? - IBM - NLP is an artificial intelligence subfield that uses machine learning and computational linguistics to help computers recognize, understand, and generate human language, powering applications like chatbots, voice assistants, and automated document processing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com