Circular electronics promote sustainable design, reuse, and recycling to minimize environmental impact, contrasting sharply with traditional e-waste management, which often involves landfill disposal and hazardous material exposure. Efficient circular models extend product life cycles and recover valuable materials like gold and rare earth metals, significantly reducing global electronic waste, which reached over 50 million metric tons in 2019. Discover how embracing circular electronics can transform waste challenges into economic and ecological opportunities.
Why it is important
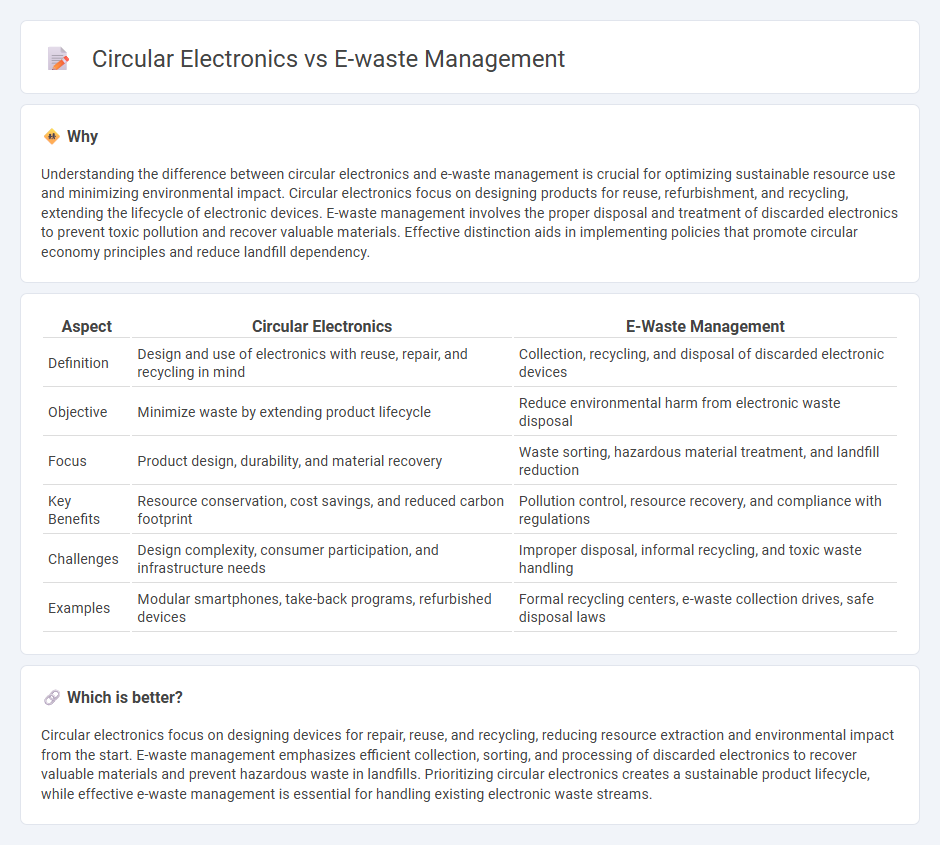
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and e-waste management is crucial for optimizing sustainable resource use and minimizing environmental impact. Circular electronics focus on designing products for reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, extending the lifecycle of electronic devices. E-waste management involves the proper disposal and treatment of discarded electronics to prevent toxic pollution and recover valuable materials. Effective distinction aids in implementing policies that promote circular economy principles and reduce landfill dependency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Electronics | E-Waste Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Design and use of electronics with reuse, repair, and recycling in mind | Collection, recycling, and disposal of discarded electronic devices |
| Objective | Minimize waste by extending product lifecycle | Reduce environmental harm from electronic waste disposal |
| Focus | Product design, durability, and material recovery | Waste sorting, hazardous material treatment, and landfill reduction |
| Key Benefits | Resource conservation, cost savings, and reduced carbon footprint | Pollution control, resource recovery, and compliance with regulations |
| Challenges | Design complexity, consumer participation, and infrastructure needs | Improper disposal, informal recycling, and toxic waste handling |
| Examples | Modular smartphones, take-back programs, refurbished devices | Formal recycling centers, e-waste collection drives, safe disposal laws |
Which is better?
Circular electronics focus on designing devices for repair, reuse, and recycling, reducing resource extraction and environmental impact from the start. E-waste management emphasizes efficient collection, sorting, and processing of discarded electronics to recover valuable materials and prevent hazardous waste in landfills. Prioritizing circular electronics creates a sustainable product lifecycle, while effective e-waste management is essential for handling existing electronic waste streams.
Connection
Circular electronics design prioritizes reuse, repair, and recycling, significantly reducing e-waste generation and its environmental impact. Efficient e-waste management systems recover valuable materials from discarded devices, supporting the circular economy by minimizing resource extraction. Integrating circular electronics principles with advanced e-waste processing promotes sustainable technology lifecycles and reduces landfill dependency.
Key Terms
**E-waste Management:**
E-waste management involves the systematic collection, recycling, and disposal of discarded electronic devices to minimize environmental impact and reduce hazardous waste. Efficient e-waste processes recover valuable materials like gold, silver, and copper, promoting resource conservation and reducing landfill pollution. Explore comprehensive strategies in e-waste management to safeguard the environment and enhance sustainable electronics use.
Recycling
E-waste management primarily emphasizes collecting, processing, and recycling discarded electronic devices to reduce environmental hazards and recover valuable materials such as gold, copper, and rare earth elements. Circular electronics extends beyond recycling by incorporating sustainable design, refurbishment, and reuse to minimize resource extraction and maximize product lifecycle efficiency. Explore innovative strategies and technologies transforming e-waste recycling and circular electronics for a sustainable future.
Hazardous Materials
E-waste management primarily addresses the safe disposal and treatment of hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium found in discarded electronics to prevent environmental contamination. Circular electronics emphasize designing products for easier disassembly and material recovery, reducing the release of toxic substances and promoting the reuse of hazardous components. Explore our detailed insights to understand how integrating circular principles drastically improves hazardous material handling in electronic waste management.
Source and External Links
The Complete E-Waste Recycling Process - Outlines the step-by-step process of e-waste management, including collection, safe storage, manual sorting, dismantling, shredding, and material separation for recycling.
Electronic waste (e-waste) - Highlights international agreements and national actions needed to protect public health from hazardous e-waste, emphasizing the role of the Basel Convention and regional treaties in regulating transboundary movements.
The benefits of e-waste management go beyond the environment - Emphasizes the importance of circular economy practices in e-waste management, noting its rapid global growth and the financial benefits of responsible recycling and reuse.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com