Trustless computing enables secure transactions without relying on a central authority, utilizing cryptographic algorithms to validate data integrity. Blockchain technology exemplifies trustless computing by maintaining a decentralized ledger where all participants verify and record transactions transparently. Explore the distinctions and synergies between trustless computing and blockchain to understand their impact on digital security.
Why it is important
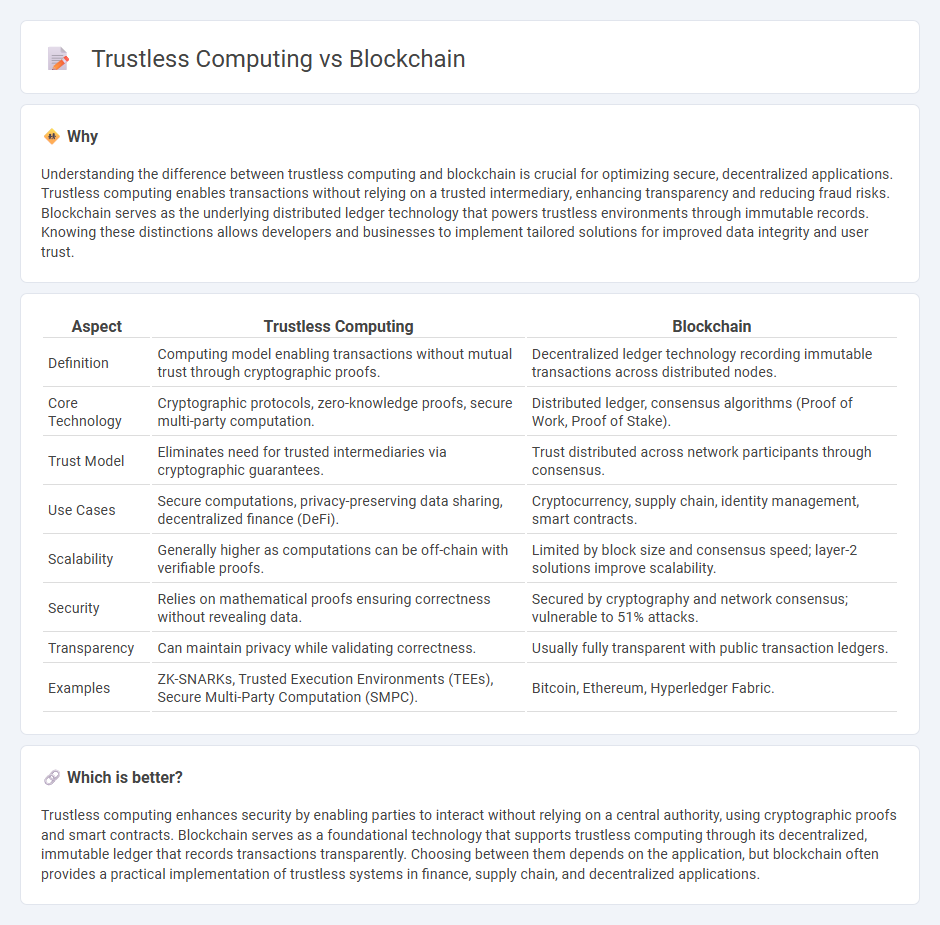
Understanding the difference between trustless computing and blockchain is crucial for optimizing secure, decentralized applications. Trustless computing enables transactions without relying on a trusted intermediary, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risks. Blockchain serves as the underlying distributed ledger technology that powers trustless environments through immutable records. Knowing these distinctions allows developers and businesses to implement tailored solutions for improved data integrity and user trust.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Trustless Computing | Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Computing model enabling transactions without mutual trust through cryptographic proofs. | Decentralized ledger technology recording immutable transactions across distributed nodes. |
| Core Technology | Cryptographic protocols, zero-knowledge proofs, secure multi-party computation. | Distributed ledger, consensus algorithms (Proof of Work, Proof of Stake). |
| Trust Model | Eliminates need for trusted intermediaries via cryptographic guarantees. | Trust distributed across network participants through consensus. |
| Use Cases | Secure computations, privacy-preserving data sharing, decentralized finance (DeFi). | Cryptocurrency, supply chain, identity management, smart contracts. |
| Scalability | Generally higher as computations can be off-chain with verifiable proofs. | Limited by block size and consensus speed; layer-2 solutions improve scalability. |
| Security | Relies on mathematical proofs ensuring correctness without revealing data. | Secured by cryptography and network consensus; vulnerable to 51% attacks. |
| Transparency | Can maintain privacy while validating correctness. | Usually fully transparent with public transaction ledgers. |
| Examples | ZK-SNARKs, Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), Secure Multi-Party Computation (SMPC). | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric. |
Which is better?
Trustless computing enhances security by enabling parties to interact without relying on a central authority, using cryptographic proofs and smart contracts. Blockchain serves as a foundational technology that supports trustless computing through its decentralized, immutable ledger that records transactions transparently. Choosing between them depends on the application, but blockchain often provides a practical implementation of trustless systems in finance, supply chain, and decentralized applications.
Connection
Trustless computing relies on decentralized networks where participants can interact and execute transactions without needing to trust a central authority. Blockchain technology underpins trustless computing by providing a transparent, immutable ledger that verifies and records transactions through consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake. This synergy ensures secure, tamper-proof operations in applications ranging from cryptocurrency to smart contracts, revolutionizing digital trust frameworks.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Blockchain technology enables decentralized data management by distributing information across a network of nodes, ensuring transparency and immutability without relying on a central authority. Trustless computing leverages cryptographic proofs and decentralized protocols to perform secure computations among mutually untrusted parties without exposing sensitive data. Explore how these innovations drive the future of decentralized systems and enable new applications by learning more.
Consensus Mechanism
Consensus mechanisms are pivotal in both blockchain and trustless computing, ensuring network agreement without centralized authority. Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) are common algorithms that validate transactions and maintain system integrity while preventing malicious attacks. Explore further to understand how these consensus protocols enable secure, decentralized operations across various applications.
Cryptographic Security
Blockchain employs decentralized ledgers secured by complex cryptographic algorithms like SHA-256 and elliptic curve signatures to ensure data integrity and immutability, eliminating the need for central authorities. Trustless computing extends beyond blockchain by leveraging advanced cryptography, such as zero-knowledge proofs and secure multiparty computation, to execute transactions or processes without requiring trust among participants. Explore how these cutting-edge cryptographic methods transform security paradigms in decentralized ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Blockchain - Wikipedia - Blockchain is a distributed ledger made of linked blocks secured by cryptographic hashes, designed to be resistant to alteration and managed by a peer-to-peer network validating transactions through consensus algorithms, first implemented for bitcoin in 2008.
What Is Blockchain? | IBM - Blockchain is a decentralized and immutable digital ledger enabling secure recording of transactions and asset tracking across a business network without relying on intermediaries, ensuring transparency and trust.
What is Blockchain Technology? - AWS - Blockchain technology creates a transparent, tamper-proof ledger by storing data in blocks linked chronologically and secured by network consensus, eliminating the need for a trusted central authority in transactions such as property sales.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com