Trustless computing enables secure transactions without relying on a central authority by using cryptographic proofs and decentralized protocols, enhancing data integrity and privacy. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) strengthens security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes, reducing unauthorized access risks. Explore the differences and benefits of these technologies to understand their impact on digital security.
Why it is important
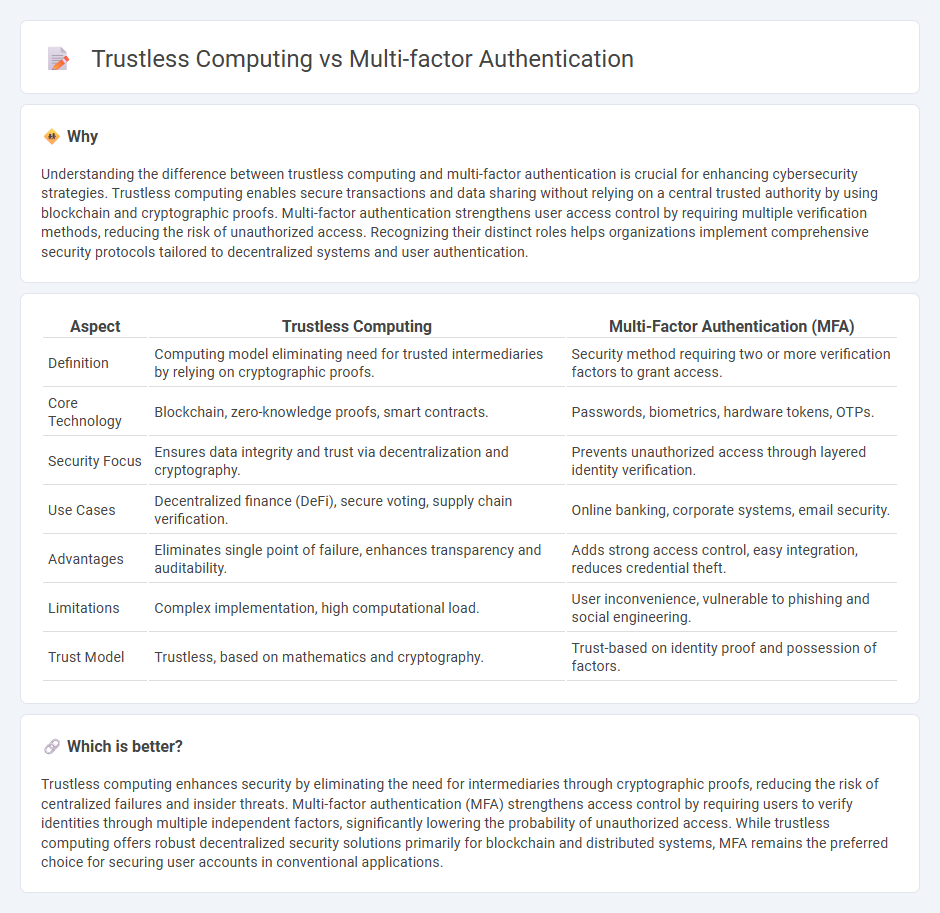
Understanding the difference between trustless computing and multi-factor authentication is crucial for enhancing cybersecurity strategies. Trustless computing enables secure transactions and data sharing without relying on a central trusted authority by using blockchain and cryptographic proofs. Multi-factor authentication strengthens user access control by requiring multiple verification methods, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Recognizing their distinct roles helps organizations implement comprehensive security protocols tailored to decentralized systems and user authentication.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Trustless Computing | Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Computing model eliminating need for trusted intermediaries by relying on cryptographic proofs. | Security method requiring two or more verification factors to grant access. |
| Core Technology | Blockchain, zero-knowledge proofs, smart contracts. | Passwords, biometrics, hardware tokens, OTPs. |
| Security Focus | Ensures data integrity and trust via decentralization and cryptography. | Prevents unauthorized access through layered identity verification. |
| Use Cases | Decentralized finance (DeFi), secure voting, supply chain verification. | Online banking, corporate systems, email security. |
| Advantages | Eliminates single point of failure, enhances transparency and auditability. | Adds strong access control, easy integration, reduces credential theft. |
| Limitations | Complex implementation, high computational load. | User inconvenience, vulnerable to phishing and social engineering. |
| Trust Model | Trustless, based on mathematics and cryptography. | Trust-based on identity proof and possession of factors. |
Which is better?
Trustless computing enhances security by eliminating the need for intermediaries through cryptographic proofs, reducing the risk of centralized failures and insider threats. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) strengthens access control by requiring users to verify identities through multiple independent factors, significantly lowering the probability of unauthorized access. While trustless computing offers robust decentralized security solutions primarily for blockchain and distributed systems, MFA remains the preferred choice for securing user accounts in conventional applications.
Connection
Trustless computing enhances security by eliminating the need for trusted third parties, relying instead on cryptographic proofs and decentralized protocols. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) complements this by requiring multiple forms of user verification, reducing the risk of unauthorized access even in trustless environments. Together, they create a robust security framework that safeguards digital transactions and user identities without relying on centralized trust.
Key Terms
Identity Verification
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances identity verification by requiring users to provide multiple forms of evidence, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Trustless computing leverages decentralized protocols and cryptographic proofs to verify identities without relying on a central authority, ensuring higher security and privacy. Explore how these technologies revolutionize identity verification in modern digital ecosystems.
Cryptographic Protocols
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring multiple cryptographic proofs, such as passwords, biometrics, or hardware tokens, to verify user identity, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Trustless computing leverages cryptographic protocols like zero-knowledge proofs and secure multiparty computation to enable secure transactions and data processing without relying on a trusted third party. Explore the latest advancements in cryptographic protocols to understand how MFA and trustless computing fortify digital security.
Decentralization
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring multiple verification steps, often involving centralized identity providers, which can limit decentralization. Trustless computing leverages blockchain and decentralized protocols to eliminate reliance on a central authority, ensuring data integrity and user control without intermediaries. Explore how combining MFA with trustless systems can strengthen decentralized security solutions.
Source and External Links
What is MFA (Multifactor Authentication)? - Multifactor authentication (MFA) requires at least two distinct forms of proof to verify a user's identity, such as a password and a code sent to a mobile device, providing extra layers of protection beyond passwords alone.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)? - OneLogin - MFA is an authentication method that requires two or more verification factors (like a password and a one-time code) to access resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication? - MFA Explained - MFA is a multi-step login process that asks users for more than just a password, such as a code sent via email or a biometric scan, to help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive accounts and systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com