Biosignal decoding involves interpreting electrical signals from the body, such as EEG or ECG, to understand physiological states and intentions, enabling advancements in medical diagnostics and brain-computer interfaces. Object detection focuses on identifying and locating objects within images or videos using machine learning and computer vision techniques, driving innovations in automation, surveillance, and autonomous vehicles. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies transform industries and improve human-computer interaction.
Why it is important
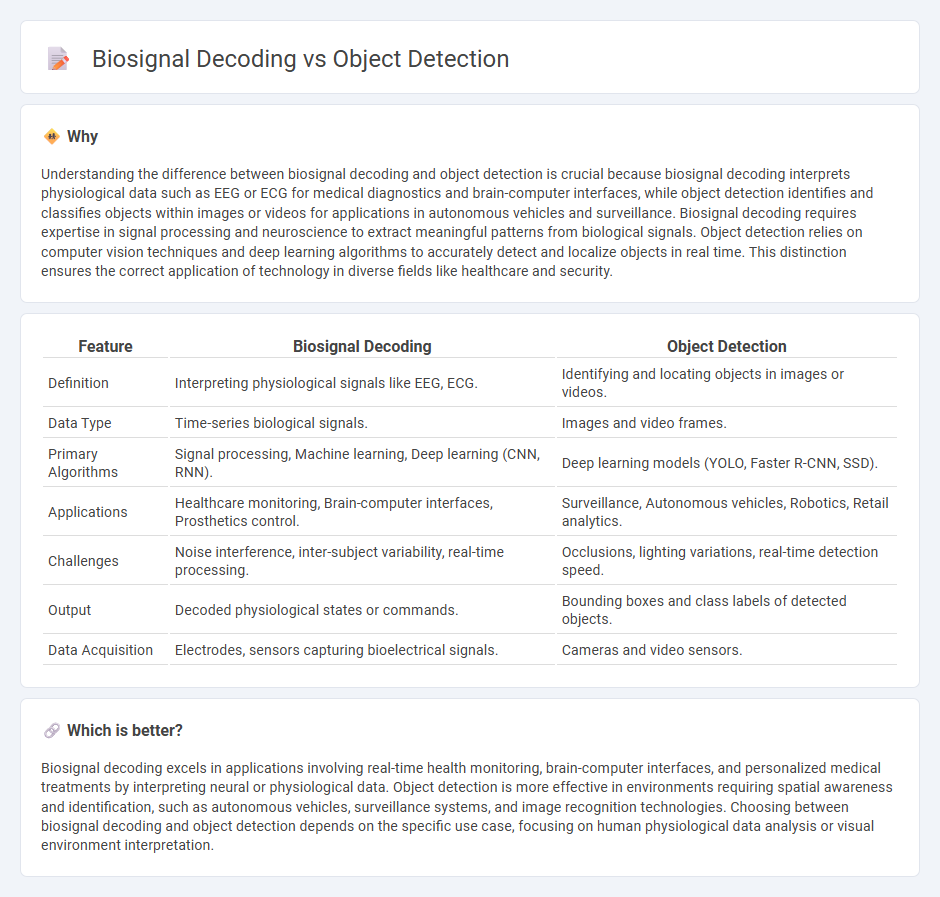
Understanding the difference between biosignal decoding and object detection is crucial because biosignal decoding interprets physiological data such as EEG or ECG for medical diagnostics and brain-computer interfaces, while object detection identifies and classifies objects within images or videos for applications in autonomous vehicles and surveillance. Biosignal decoding requires expertise in signal processing and neuroscience to extract meaningful patterns from biological signals. Object detection relies on computer vision techniques and deep learning algorithms to accurately detect and localize objects in real time. This distinction ensures the correct application of technology in diverse fields like healthcare and security.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Biosignal Decoding | Object Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpreting physiological signals like EEG, ECG. | Identifying and locating objects in images or videos. |
| Data Type | Time-series biological signals. | Images and video frames. |
| Primary Algorithms | Signal processing, Machine learning, Deep learning (CNN, RNN). | Deep learning models (YOLO, Faster R-CNN, SSD). |
| Applications | Healthcare monitoring, Brain-computer interfaces, Prosthetics control. | Surveillance, Autonomous vehicles, Robotics, Retail analytics. |
| Challenges | Noise interference, inter-subject variability, real-time processing. | Occlusions, lighting variations, real-time detection speed. |
| Output | Decoded physiological states or commands. | Bounding boxes and class labels of detected objects. |
| Data Acquisition | Electrodes, sensors capturing bioelectrical signals. | Cameras and video sensors. |
Which is better?
Biosignal decoding excels in applications involving real-time health monitoring, brain-computer interfaces, and personalized medical treatments by interpreting neural or physiological data. Object detection is more effective in environments requiring spatial awareness and identification, such as autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, and image recognition technologies. Choosing between biosignal decoding and object detection depends on the specific use case, focusing on human physiological data analysis or visual environment interpretation.
Connection
Biosignal decoding and object detection are interconnected through their reliance on advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to interpret and analyze complex data patterns. Biosignal decoding translates physiological signals like EEG or EMG into meaningful information, which can then be used to enhance object detection systems by improving accuracy in dynamic environments. Integrating biosignal inputs enables more intuitive and responsive object detection applications in fields such as augmented reality, prosthetics, and human-computer interaction.
Key Terms
Computer Vision
Object detection in computer vision involves identifying and localizing objects within images or video frames using algorithms like YOLO, SSD, and Faster R-CNN, which analyze visual patterns for accurate recognition. Biosignal decoding interprets physiological data such as EEG, EMG, or ECG by extracting relevant features for applications in brain-computer interfaces and healthcare monitoring. Explore the latest advancements and practical applications to deepen your understanding of these pivotal technologies.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Object detection involves identifying and localizing objects within images or videos using algorithms like convolutional neural networks, whereas biosignal decoding, particularly Electroencephalography (EEG), interprets brain activity signals to understand neural patterns and cognitive states. EEG biosignal decoding leverages temporal and frequency domain features to classify mental tasks, enabling applications in brain-computer interfaces and neurological diagnostics. Explore further to understand how these technologies revolutionize machine learning and neuroscience integration.
Machine Learning
Machine learning techniques in object detection analyze visual data to identify and classify objects within images or videos using convolutional neural networks and region-based algorithms. Biosignal decoding leverages machine learning models like recurrent neural networks and support vector machines to interpret physiological signals such as EEG, ECG, or EMG for applications in health monitoring and brain-computer interfaces. Explore advanced methodologies and comparative studies to deepen your understanding of machine learning applications in these diverse domains.
Source and External Links
Object detection - Object detection is a computer vision technology that identifies and locates instances of semantic objects such as people, vehicles, or buildings in images and videos, widely used in applications like face detection, video surveillance, and autonomous driving.
What is Object Detection? | IBM - Object detection combines object localization and classification using neural networks to find and categorize objects within digital images, distinguishing itself from image classification by identifying multiple individual objects within a single image.
Object Detection: The Definitive Guide - Popular object detection algorithms include CNN-based methods like R-CNN, Fast R-CNN, and single-shot detectors like YOLO and SSD, which balance accuracy and speed for applications in real-time and large-scale image analysis.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com