Zero-knowledge proofs enable one party to prove knowledge of information without revealing the information itself, enhancing privacy in digital transactions. Blockchain consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, ensure agreement on the network state by validating and confirming transactions collectively. Explore the intricacies of zero-knowledge proofs and blockchain consensus to discover how they revolutionize security and trust in decentralized systems.
Why it is important
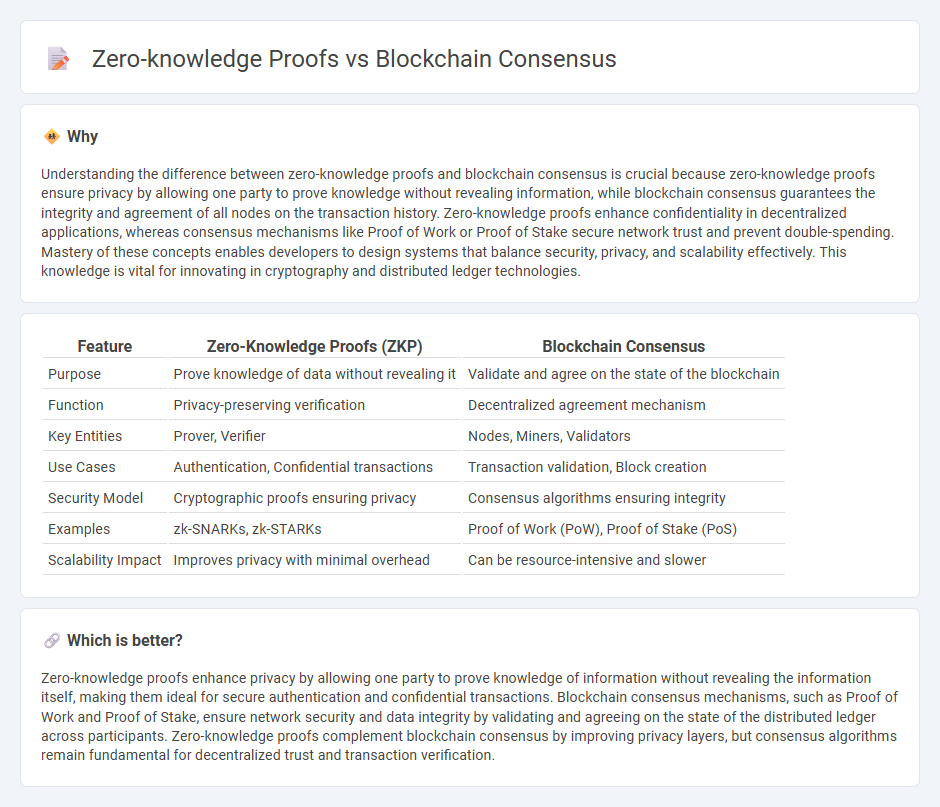
Understanding the difference between zero-knowledge proofs and blockchain consensus is crucial because zero-knowledge proofs ensure privacy by allowing one party to prove knowledge without revealing information, while blockchain consensus guarantees the integrity and agreement of all nodes on the transaction history. Zero-knowledge proofs enhance confidentiality in decentralized applications, whereas consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake secure network trust and prevent double-spending. Mastery of these concepts enables developers to design systems that balance security, privacy, and scalability effectively. This knowledge is vital for innovating in cryptography and distributed ledger technologies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) | Blockchain Consensus |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prove knowledge of data without revealing it | Validate and agree on the state of the blockchain |
| Function | Privacy-preserving verification | Decentralized agreement mechanism |
| Key Entities | Prover, Verifier | Nodes, Miners, Validators |
| Use Cases | Authentication, Confidential transactions | Transaction validation, Block creation |
| Security Model | Cryptographic proofs ensuring privacy | Consensus algorithms ensuring integrity |
| Examples | zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs | Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS) |
| Scalability Impact | Improves privacy with minimal overhead | Can be resource-intensive and slower |
Which is better?
Zero-knowledge proofs enhance privacy by allowing one party to prove knowledge of information without revealing the information itself, making them ideal for secure authentication and confidential transactions. Blockchain consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, ensure network security and data integrity by validating and agreeing on the state of the distributed ledger across participants. Zero-knowledge proofs complement blockchain consensus by improving privacy layers, but consensus algorithms remain fundamental for decentralized trust and transaction verification.
Connection
Zero-knowledge proofs enhance blockchain consensus by enabling validators to verify transactions without revealing sensitive information, ensuring privacy and security. This cryptographic method reduces data exposure during consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake or Byzantine Fault Tolerance, boosting trust and efficiency. Integrating zero-knowledge proofs into blockchain consensus protocols supports scalability while maintaining decentralization and user confidentiality.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Blockchain consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake ensure decentralization by enabling distributed validation of transactions across multiple nodes, preventing central control. Zero-knowledge proofs enhance privacy without sacrificing decentralization, allowing participants to verify transactions without revealing sensitive data, thereby maintaining trust in permissionless networks. Discover how these technologies collectively strengthen decentralized ecosystems and secure transparent, private interactions.
Privacy
Blockchain consensus mechanisms ensure agreement on the state of the ledger among distributed nodes, guaranteeing data integrity and system security through protocols like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Zero-knowledge proofs enhance privacy by allowing one party to prove knowledge of specific information without revealing the information itself, enabling confidential transactions and identity verification on blockchain networks. Explore the interplay between these technologies to understand how privacy solutions in blockchain are evolving.
Trustlessness
Blockchain consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake enable trustlessness by validating transactions through a decentralized network without relying on a central authority. Zero-knowledge proofs enhance trustlessness by allowing one party to prove the validity of information without revealing the underlying data, preserving privacy and security. Explore how these innovative cryptographic techniques redefine trust in decentralized systems.
Source and External Links
Consensus Algorithms in Blockchain - A consensus algorithm is a process through which all peers in a blockchain network agree on the current state of the distributed ledger, ensuring reliability, trust, and that each new block added is the agreed-upon version of truth among all nodes in the network.
Consensus Mechanisms In Blockchain: A Deep Dive Into ... - Consensus mechanisms enable blockchain nodes to independently agree on the ledger state and preserve the network's operational integrity without a central authority, protecting against threats like double-spending and Sybil attacks.
Consensus Mechanisms: How Blockchains Stay Secure - Consensus mechanisms allow blockchain nodes to jointly decide if data can join the chain, avoiding errors and malicious transactions while enabling decentralization by removing the need for a central authority.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com