Vector databases excel in managing high-dimensional data crucial for AI and machine learning applications by enabling efficient similarity searches using vector embeddings. Object stores provide scalable, cost-effective storage solutions ideal for unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups, supporting vast amounts of information with high durability. Explore the differences between vector databases and object stores to optimize your data infrastructure strategy.
Why it is important
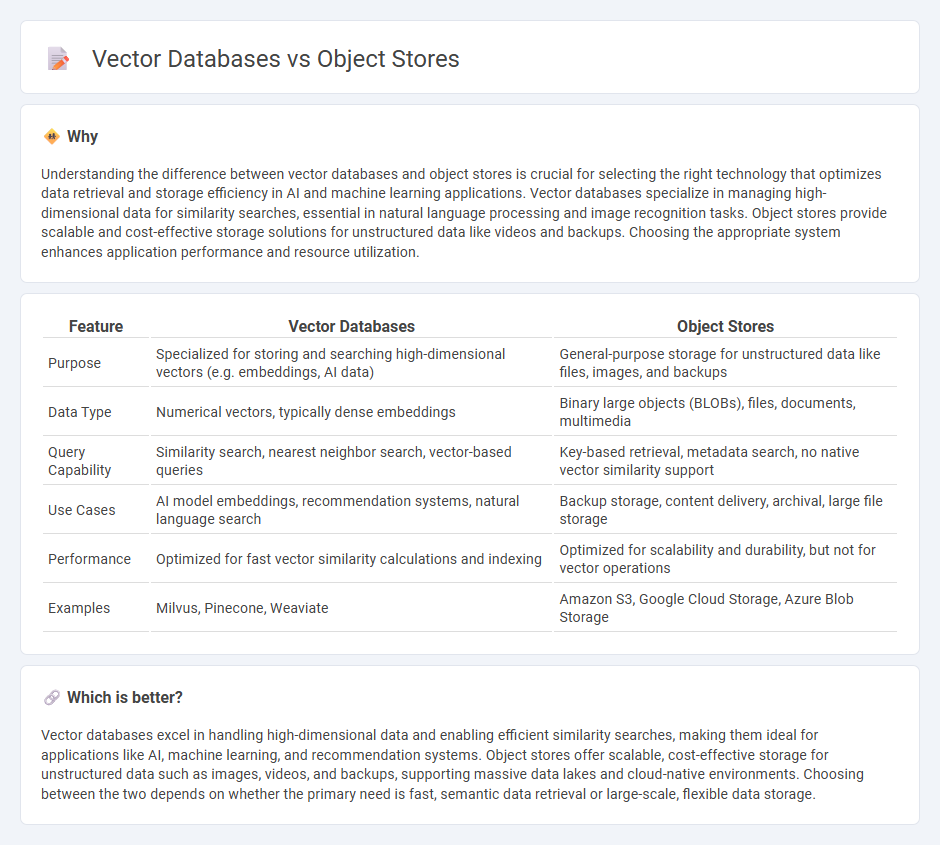
Understanding the difference between vector databases and object stores is crucial for selecting the right technology that optimizes data retrieval and storage efficiency in AI and machine learning applications. Vector databases specialize in managing high-dimensional data for similarity searches, essential in natural language processing and image recognition tasks. Object stores provide scalable and cost-effective storage solutions for unstructured data like videos and backups. Choosing the appropriate system enhances application performance and resource utilization.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vector Databases | Object Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Specialized for storing and searching high-dimensional vectors (e.g. embeddings, AI data) | General-purpose storage for unstructured data like files, images, and backups |
| Data Type | Numerical vectors, typically dense embeddings | Binary large objects (BLOBs), files, documents, multimedia |
| Query Capability | Similarity search, nearest neighbor search, vector-based queries | Key-based retrieval, metadata search, no native vector similarity support |
| Use Cases | AI model embeddings, recommendation systems, natural language search | Backup storage, content delivery, archival, large file storage |
| Performance | Optimized for fast vector similarity calculations and indexing | Optimized for scalability and durability, but not for vector operations |
| Examples | Milvus, Pinecone, Weaviate | Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage |
Which is better?
Vector databases excel in handling high-dimensional data and enabling efficient similarity searches, making them ideal for applications like AI, machine learning, and recommendation systems. Object stores offer scalable, cost-effective storage for unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups, supporting massive data lakes and cloud-native environments. Choosing between the two depends on whether the primary need is fast, semantic data retrieval or large-scale, flexible data storage.
Connection
Vector databases optimize the storage and retrieval of high-dimensional data, enabling efficient similarity searches crucial for AI and machine learning applications. Object stores provide scalable, durable storage solutions for unstructured data, such as images and multimedia, which serve as the source for vector embeddings. Integrating vector databases with object stores allows AI systems to quickly access and analyze large volumes of complex data, enhancing performance in tasks like recommendation engines and natural language processing.
Key Terms
Scalability
Object stores like Amazon S3 offer virtually unlimited scalability by distributing data across multiple servers, making them ideal for storing large amounts of unstructured data. Vector databases such as Pinecone and Weaviate are designed to scale dynamically with the growth of high-dimensional data, optimizing retrieval speed and accuracy through distributed indexing and partitioning techniques. Explore more about how scalability impacts your choice between object stores and vector databases for efficient data management.
Data Structure
Object stores manage unstructured data such as images, videos, and documents by storing objects with metadata for efficient retrieval, relying on simple key-value pair structures. Vector databases specialize in handling high-dimensional vector data generated from machine learning models, supporting complex similarity searches using structures like Annoy, HNSW, or Faiss indexes. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which data structure best suits your AI and big data applications.
Query Capability
Object stores primarily offer scalable, cost-effective storage solutions with limited query capabilities, mostly supporting basic metadata searches. Vector databases excel in advanced query capabilities, enabling similarity searches and complex data retrieval using high-dimensional vector embeddings for AI and machine learning applications. Explore our in-depth analysis to understand the strengths and ideal use cases of each technology.
Source and External Links
What is Object Storage? | IBM - Object storage is a data storage architecture ideal for storing, archiving, and managing high volumes of static unstructured data efficiently and affordably.
What is object storage or object-based storage? - NetApp - Object storage organizes and manages data as individual units called objects, each containing data, metadata, and a unique identifier, making it highly scalable and efficient.
What is Object Storage? Use cases & benefits - Google Cloud - Object storage is a data storage architecture designed to handle large amounts of unstructured data by organizing it into units with metadata and a unique identifier for easy access.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com