Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices using AI algorithms for faster decision-making and reduced latency. Distributed computing spreads data and processing tasks across multiple systems, enhancing computational power and resource efficiency. Explore how these technologies transform data handling and real-time analytics.
Why it is important
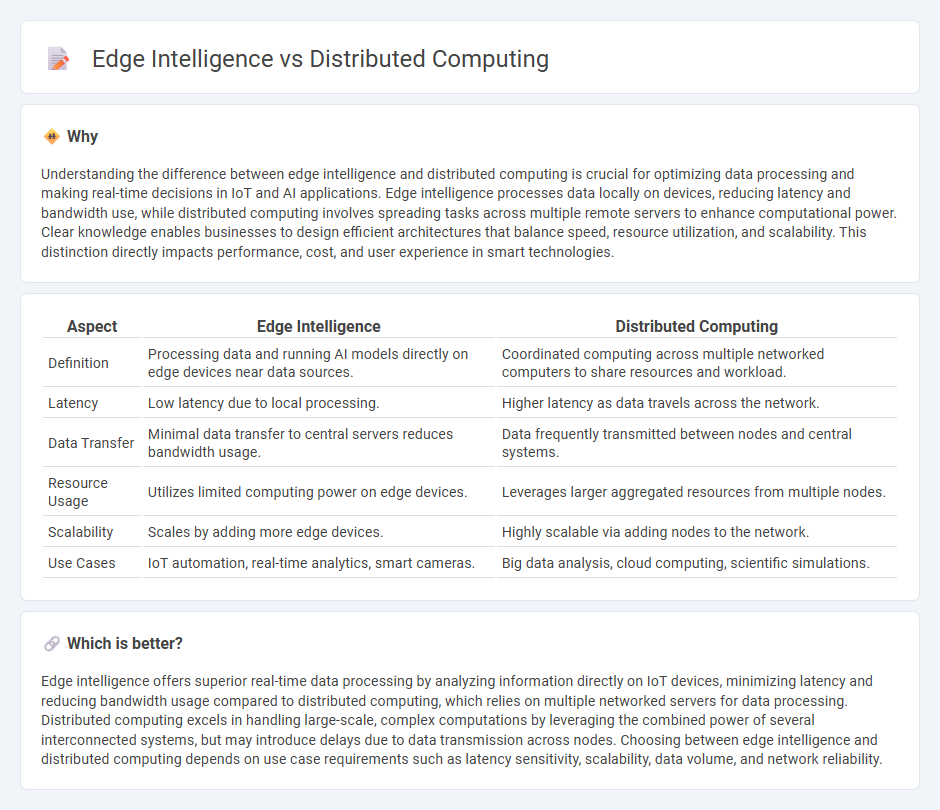
Understanding the difference between edge intelligence and distributed computing is crucial for optimizing data processing and making real-time decisions in IoT and AI applications. Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices, reducing latency and bandwidth use, while distributed computing involves spreading tasks across multiple remote servers to enhance computational power. Clear knowledge enables businesses to design efficient architectures that balance speed, resource utilization, and scalability. This distinction directly impacts performance, cost, and user experience in smart technologies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Edge Intelligence | Distributed Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processing data and running AI models directly on edge devices near data sources. | Coordinated computing across multiple networked computers to share resources and workload. |
| Latency | Low latency due to local processing. | Higher latency as data travels across the network. |
| Data Transfer | Minimal data transfer to central servers reduces bandwidth usage. | Data frequently transmitted between nodes and central systems. |
| Resource Usage | Utilizes limited computing power on edge devices. | Leverages larger aggregated resources from multiple nodes. |
| Scalability | Scales by adding more edge devices. | Highly scalable via adding nodes to the network. |
| Use Cases | IoT automation, real-time analytics, smart cameras. | Big data analysis, cloud computing, scientific simulations. |
Which is better?
Edge intelligence offers superior real-time data processing by analyzing information directly on IoT devices, minimizing latency and reducing bandwidth usage compared to distributed computing, which relies on multiple networked servers for data processing. Distributed computing excels in handling large-scale, complex computations by leveraging the combined power of several interconnected systems, but may introduce delays due to data transmission across nodes. Choosing between edge intelligence and distributed computing depends on use case requirements such as latency sensitivity, scalability, data volume, and network reliability.
Connection
Edge intelligence leverages distributed computing by processing data locally on edge devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to centralized cloud systems. Distributed computing supports edge intelligence through decentralized resource allocation and real-time data analysis across interconnected nodes. This synergy enhances autonomous decision-making capabilities in Internet of Things (IoT) networks and smart systems.
Key Terms
Scalability
Distributed computing enhances scalability by allocating tasks across multiple nodes, enabling efficient handling of large-scale data and complex processes. Edge intelligence improves scalability through localized data processing, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by performing computations near data sources. Explore more to understand how these technologies optimize scalable solutions for diverse applications.
Latency
Distributed computing enhances system performance by spreading tasks across multiple servers, minimizing processing delays but still reliant on centralized data centers, which can introduce latency. Edge intelligence processes data locally on edge devices, significantly reducing latency by bypassing the need to send data to distant servers for analysis. Explore more about how these technologies impact latency in real-time applications and optimize computing efficiency.
Data locality
Distributed computing enhances processing by spreading tasks across multiple nodes, reducing latency and bandwidth usage through data locality advantages. Edge intelligence further leverages data locality by processing data closer to the source at the edge devices, minimizing transmission delays and improving real-time decision-making. Explore how embracing data locality in edge intelligence outperforms traditional distributed computing for latency-sensitive applications.
Source and External Links
Distributed Computing - TechTarget - Distributed computing is a model where components of a software system are shared among multiple computers or nodes, improving efficiency and performance through parallel processing.
What is Distributed Computing? - GeeksforGeeks - Distributed computing involves processing and data storage distributed across multiple devices or systems, allowing them to work together to perform tasks and share resources.
What is Distributed Computing? - AWS - Distributed computing is a method where multiple computers work together to solve common problems, providing large-scale resources and benefits like scalability and fault tolerance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com