Ambient intelligence integrates AI and sensors into everyday environments to create seamless, context-aware experiences. Edge computing processes data near its source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage for real-time decision-making. Explore how these technologies transform industries and enhance digital interaction.
Why it is important
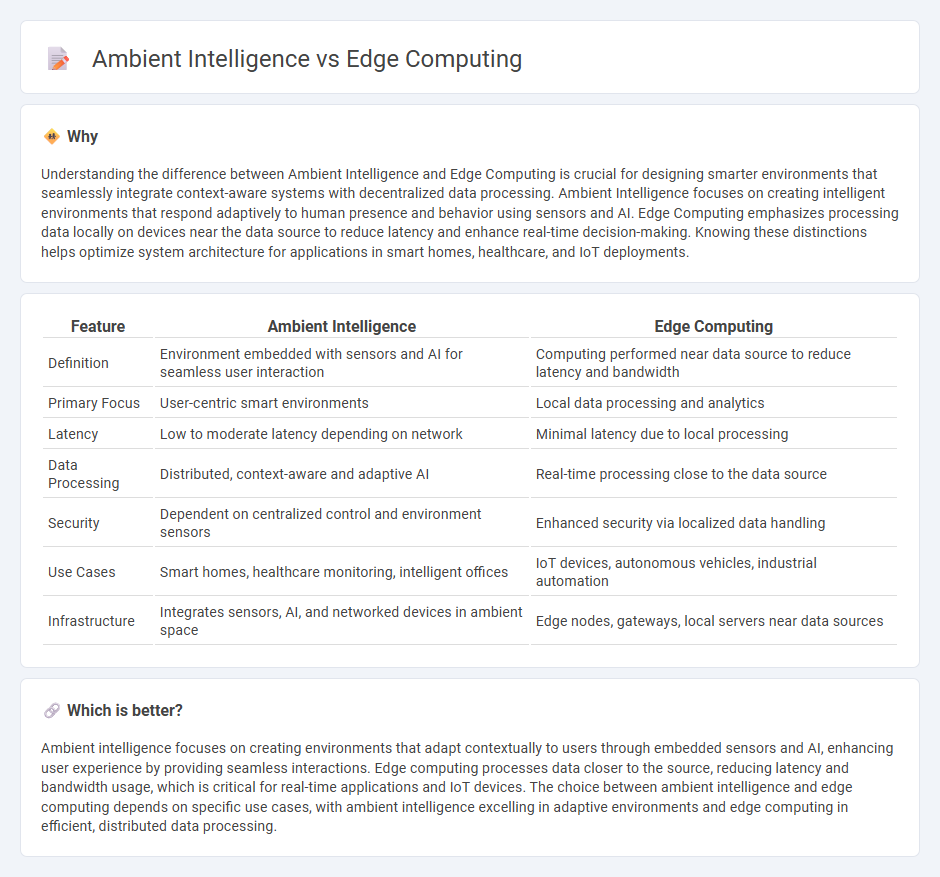
Understanding the difference between Ambient Intelligence and Edge Computing is crucial for designing smarter environments that seamlessly integrate context-aware systems with decentralized data processing. Ambient Intelligence focuses on creating intelligent environments that respond adaptively to human presence and behavior using sensors and AI. Edge Computing emphasizes processing data locally on devices near the data source to reduce latency and enhance real-time decision-making. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize system architecture for applications in smart homes, healthcare, and IoT deployments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ambient Intelligence | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Environment embedded with sensors and AI for seamless user interaction | Computing performed near data source to reduce latency and bandwidth |
| Primary Focus | User-centric smart environments | Local data processing and analytics |
| Latency | Low to moderate latency depending on network | Minimal latency due to local processing |
| Data Processing | Distributed, context-aware and adaptive AI | Real-time processing close to the data source |
| Security | Dependent on centralized control and environment sensors | Enhanced security via localized data handling |
| Use Cases | Smart homes, healthcare monitoring, intelligent offices | IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation |
| Infrastructure | Integrates sensors, AI, and networked devices in ambient space | Edge nodes, gateways, local servers near data sources |
Which is better?
Ambient intelligence focuses on creating environments that adapt contextually to users through embedded sensors and AI, enhancing user experience by providing seamless interactions. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, which is critical for real-time applications and IoT devices. The choice between ambient intelligence and edge computing depends on specific use cases, with ambient intelligence excelling in adaptive environments and edge computing in efficient, distributed data processing.
Connection
Ambient intelligence relies on edge computing to process data locally, enabling real-time context-aware interactions without relying on centralized cloud servers. Edge computing reduces latency and enhances privacy by keeping sensitive information near the data source, which is critical for ambient intelligence environments like smart homes and IoT devices. This synergy boosts adaptive systems that respond seamlessly to user behavior and environmental changes.
Key Terms
Data Processing Location
Edge computing processes data near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by analyzing information locally on devices or edge servers. Ambient intelligence integrates sensors and devices into the environment, enabling seamless, context-aware interactions through distributed data processing spread across the network. Explore the distinctions in data processing locations to understand how these technologies optimize real-time responsiveness and user experience.
Context Awareness
Edge computing processes data near the source, enabling real-time context awareness by reducing latency and bandwidth use, which enhances ambient intelligence systems that rely on understanding and reacting to user environments. Ambient intelligence integrates sensors, AI, and user interfaces to create adaptive, context-aware environments that anticipate needs and provide seamless interactions. Explore the differences and synergies between edge computing and ambient intelligence to better understand their impact on smart environments.
Real-Time Analytics
Edge computing processes data near the source to enable real-time analytics with minimal latency and reduced bandwidth usage, crucial for time-sensitive applications. Ambient intelligence integrates sensors, AI, and contextual data within environments to create adaptive systems that respond instantly to user needs. Explore how these technologies revolutionize real-time data processing and decision-making.
Source and External Links
What is edge computing? - Edge computing stores and processes data closer to the user, reducing delays and enabling real-time analysis for applications like self-driving cars and smart cities.
What Is Edge Computing? - Edge computing allows devices in remote locations to process data at the edge of the network, minimizing latency by only sending critical data to central datacenters.
What is edge computing? - Edge computing brings computation as close as possible to data sources to reduce latency and bandwidth use, supporting the growing number of IoT devices globally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com