Vector databases excel in handling unstructured data like images and text using high-dimensional vectors, enabling efficient similarity searches and AI-driven analytics. NewSQL databases combine the scalability of NoSQL systems with the ACID compliance and structured query capabilities of traditional SQL databases, making them ideal for transactional workloads requiring consistency and speed. Explore these revolutionary database technologies to understand their distinct advantages and applications.
Why it is important
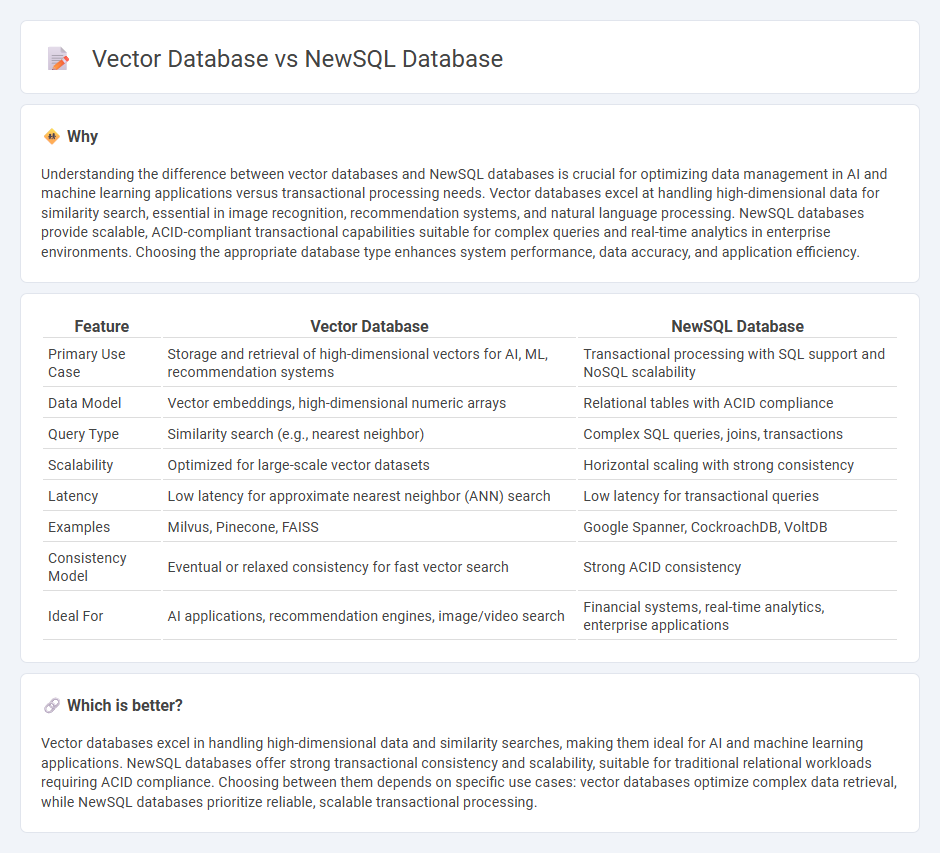
Understanding the difference between vector databases and NewSQL databases is crucial for optimizing data management in AI and machine learning applications versus transactional processing needs. Vector databases excel at handling high-dimensional data for similarity search, essential in image recognition, recommendation systems, and natural language processing. NewSQL databases provide scalable, ACID-compliant transactional capabilities suitable for complex queries and real-time analytics in enterprise environments. Choosing the appropriate database type enhances system performance, data accuracy, and application efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vector Database | NewSQL Database |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Storage and retrieval of high-dimensional vectors for AI, ML, recommendation systems | Transactional processing with SQL support and NoSQL scalability |
| Data Model | Vector embeddings, high-dimensional numeric arrays | Relational tables with ACID compliance |
| Query Type | Similarity search (e.g., nearest neighbor) | Complex SQL queries, joins, transactions |
| Scalability | Optimized for large-scale vector datasets | Horizontal scaling with strong consistency |
| Latency | Low latency for approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search | Low latency for transactional queries |
| Examples | Milvus, Pinecone, FAISS | Google Spanner, CockroachDB, VoltDB |
| Consistency Model | Eventual or relaxed consistency for fast vector search | Strong ACID consistency |
| Ideal For | AI applications, recommendation engines, image/video search | Financial systems, real-time analytics, enterprise applications |
Which is better?
Vector databases excel in handling high-dimensional data and similarity searches, making them ideal for AI and machine learning applications. NewSQL databases offer strong transactional consistency and scalability, suitable for traditional relational workloads requiring ACID compliance. Choosing between them depends on specific use cases: vector databases optimize complex data retrieval, while NewSQL databases prioritize reliable, scalable transactional processing.
Connection
Vector databases and NewSQL databases intersect through their ability to handle complex, high-dimensional data with scalable, real-time transactional processing. Vector databases specialize in managing unstructured data like embeddings for AI and machine learning applications, while NewSQL databases provide the consistency and concurrency of traditional SQL with modern scalability. Integrating vector database capabilities into NewSQL systems enhances analytics and search functionalities by combining advanced vector similarity search with strong ACID compliance.
Key Terms
Scalability
NewSQL databases offer high scalability by combining traditional SQL query capabilities with modern distributed architectures, allowing seamless horizontal scaling across multiple nodes. Vector databases specialize in managing and searching high-dimensional data efficiently, supporting scalable machine learning and AI applications with optimized nearest neighbor search algorithms. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how these databases address scalability challenges in different use cases.
ACID compliance
NewSQL databases maintain strict ACID compliance, ensuring atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability for transactional workloads, which is crucial for applications requiring reliable data integrity. Vector databases optimize for similarity search and high-dimensional data management but often sacrifice full ACID guarantees to enhance scalability and performance. Explore the trade-offs between transactional reliability and advanced data querying capabilities to determine the best fit for your data needs.
Embedding vectors
NewSQL databases excel in handling traditional relational data with ACID compliance and high transaction throughput, but they lack native support for embedding vectors used in AI and machine learning tasks. Vector databases are specifically optimized to store, index, and query high-dimensional embedding vectors, enabling efficient similarity searches crucial for applications like recommendation systems and semantic search. Explore the distinct advantages and use cases of NewSQL and vector databases to determine the best solution for embedding vector management.
Source and External Links
What is NewSQL? - Dremio - NewSQL is a modern relational database technology that combines the scalability of NoSQL with the ACID compliance of traditional SQL databases, designed for high-performance OLTP workloads using distributed architectures.
What is NewSQL? - Aerospike - NewSQL is a relational database management system that aims to deliver NoSQL-style scalability while maintaining transactional consistency through ACID compliance and supports SQL for large-scale transaction processing.
Best NewSQL Databases - NewSQL databases improve upon traditional RDBMS by offering horizontal scaling, SQL support, and ACID guarantees, combining the benefits of NoSQL with relational models, including key features like sharding, concurrency control, and crash recovery.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com