Zero Trust and Least Privilege are core cybersecurity principles that minimize access risks by enforcing strict user verification and limiting permissions to the bare minimum necessary for tasks. Zero Trust operates on the assumption that threats exist both inside and outside the network, requiring continuous authentication and micro-segmentation. Explore the differences and strategic benefits of these models to enhance your security posture.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between zero trust and least privilege is crucial for enhancing cybersecurity frameworks by minimizing access risks and preventing unauthorized data breaches. Zero trust enforces strict identity verification for every user and device, regardless of their location within or outside the network perimeter. Least privilege restricts users' access rights to only the resources necessary for their role, reducing potential attack surfaces. Knowing these distinctions helps organizations implement resilient security policies that effectively mitigate evolving cyber threats.
Comparison Table
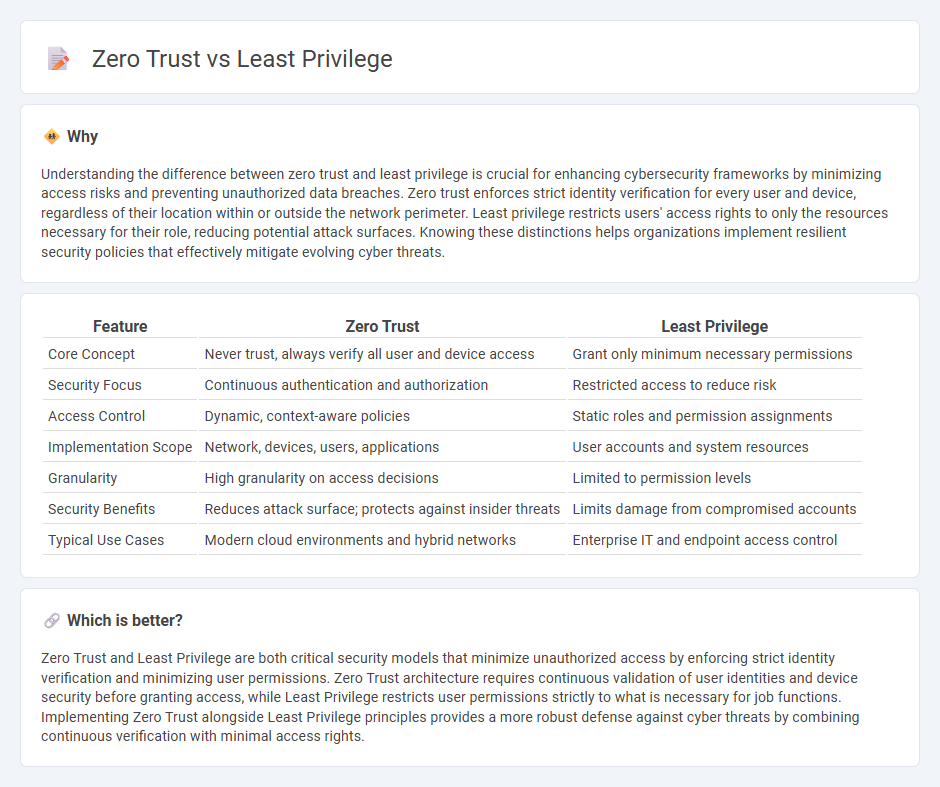
| Feature | Zero Trust | Least Privilege |
|---|---|---|
| Core Concept | Never trust, always verify all user and device access | Grant only minimum necessary permissions |
| Security Focus | Continuous authentication and authorization | Restricted access to reduce risk |
| Access Control | Dynamic, context-aware policies | Static roles and permission assignments |
| Implementation Scope | Network, devices, users, applications | User accounts and system resources |
| Granularity | High granularity on access decisions | Limited to permission levels |
| Security Benefits | Reduces attack surface; protects against insider threats | Limits damage from compromised accounts |
| Typical Use Cases | Modern cloud environments and hybrid networks | Enterprise IT and endpoint access control |
Which is better?
Zero Trust and Least Privilege are both critical security models that minimize unauthorized access by enforcing strict identity verification and minimizing user permissions. Zero Trust architecture requires continuous validation of user identities and device security before granting access, while Least Privilege restricts user permissions strictly to what is necessary for job functions. Implementing Zero Trust alongside Least Privilege principles provides a more robust defense against cyber threats by combining continuous verification with minimal access rights.
Connection
Zero trust and least privilege are interconnected security models that minimize risk by restricting access to only what is strictly necessary for users and systems. Zero trust enforces continuous verification of every access request regardless of network location, while least privilege ensures that permissions granted are limited to the minimum required for task completion. Together, they create a robust defense framework that reduces attack surfaces and limits potential damage from compromised credentials or insider threats.
Key Terms
Access Control
Least privilege enforces access control by granting users the minimal permissions necessary to perform their tasks, reducing the risk of insider threats and lateral movement within systems. Zero trust builds on this by continuously verifying user identity, device health, and contextual factors before granting access, operating under the assumption that no entity is inherently trustworthy. Explore more about how these access control models enhance cybersecurity frameworks.
Authentication
Least privilege enforces strict access controls by granting users only the minimum permissions necessary for their tasks, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Zero trust architecture enhances authentication by continuously verifying user identities and device health before granting access, regardless of network location. Explore deeper insights into how authentication strategies differ between least privilege and zero trust models.
Micro-segmentation
Least privilege restricts user and application access to only what is necessary, reducing the attack surface by minimizing unnecessary permissions. Zero trust expands this by enforcing continuous verification and micro-segmentation, isolating network segments to prevent lateral movement of threats. Explore how micro-segmentation enhances network security within zero trust frameworks for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
What Is Least Privilege & Why Do You Need It? - The principle of least privilege restricts access rights for users, accounts, and processes to only those resources essential to perform authorized functions, minimizing security risks and is fundamental to zero trust security architectures.
What is Least Privilege? - Definition - Least privilege is a security practice that grants users and non-human entities the minimum access necessary for their tasks, preventing "privilege creep" and reducing vulnerabilities from excessive permissions.
What is principle of least privilege? | Zero Trust - The principle of least privilege limits users' access strictly to what they need to perform their responsibilities, thereby minimizing the impact of account compromise or insider threats.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com