Liquid cooling and immersion cooling are advanced thermal management technologies designed to improve the efficiency of high-performance computing systems. Liquid cooling circulates coolant through pipes and heat exchangers to dissipate heat, while immersion cooling submerges components directly in dielectric fluids for enhanced heat transfer. Explore the differences and benefits of each cooling method to understand their impact on data center performance and energy savings.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between liquid cooling and immersion cooling is crucial for optimizing data center efficiency and thermal management. Liquid cooling uses a coolant circulated through cold plates attached to components, while immersion cooling submerges hardware directly in dielectric fluids for superior heat dissipation. Choosing the right technology impacts energy consumption, system reliability, and overall operational costs. Professionals in IT infrastructure benefit from knowledge of both to enhance performance and sustainability.
Comparison Table
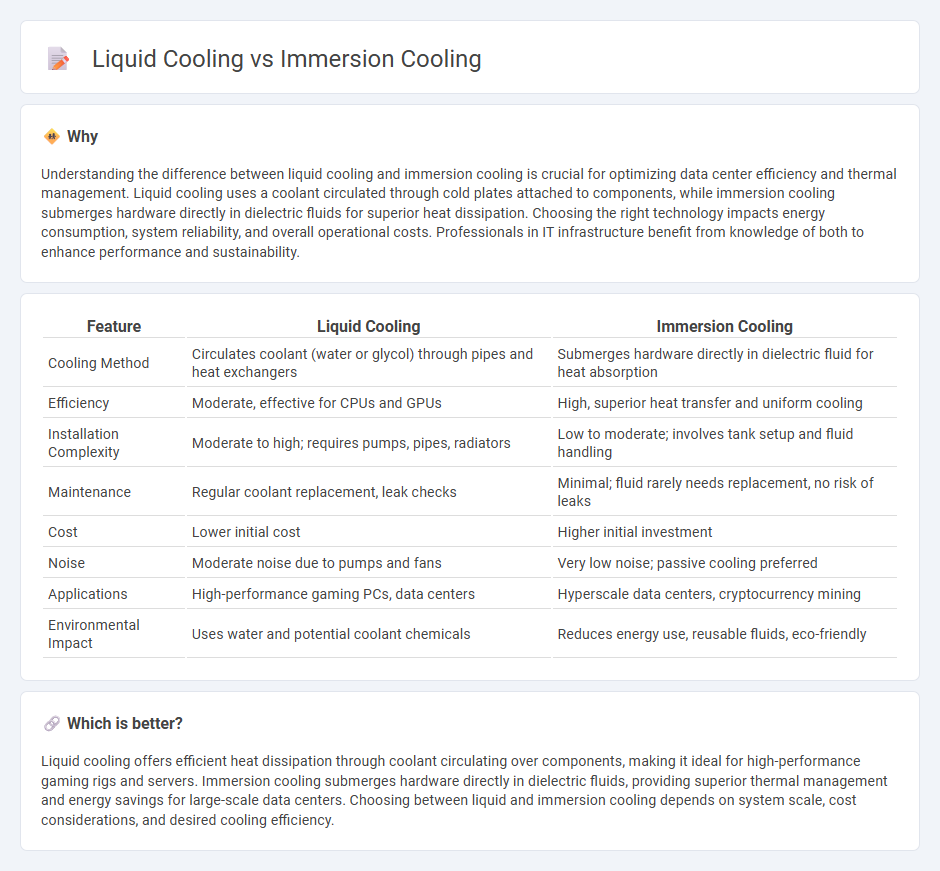
| Feature | Liquid Cooling | Immersion Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Circulates coolant (water or glycol) through pipes and heat exchangers | Submerges hardware directly in dielectric fluid for heat absorption |
| Efficiency | Moderate, effective for CPUs and GPUs | High, superior heat transfer and uniform cooling |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate to high; requires pumps, pipes, radiators | Low to moderate; involves tank setup and fluid handling |
| Maintenance | Regular coolant replacement, leak checks | Minimal; fluid rarely needs replacement, no risk of leaks |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Noise | Moderate noise due to pumps and fans | Very low noise; passive cooling preferred |
| Applications | High-performance gaming PCs, data centers | Hyperscale data centers, cryptocurrency mining |
| Environmental Impact | Uses water and potential coolant chemicals | Reduces energy use, reusable fluids, eco-friendly |
Which is better?
Liquid cooling offers efficient heat dissipation through coolant circulating over components, making it ideal for high-performance gaming rigs and servers. Immersion cooling submerges hardware directly in dielectric fluids, providing superior thermal management and energy savings for large-scale data centers. Choosing between liquid and immersion cooling depends on system scale, cost considerations, and desired cooling efficiency.
Connection
Liquid cooling and immersion cooling are advanced thermal management techniques used in data centers and high-performance computing to efficiently dissipate heat generated by electronic components. Both methods use conductive liquids to absorb and transfer heat away from critical hardware, with liquid cooling relying on coolant circulated through pipes and heat exchangers, while immersion cooling submerges components directly in dielectric fluids. These cooling solutions enable higher processing speeds and energy efficiency by maintaining optimal operating temperatures and reducing the risk of overheating.
Key Terms
Dielectric Fluid (Immersion Cooling)
Dielectric fluid in immersion cooling offers superior thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, enabling efficient heat dissipation without the risk of short circuits in high-performance computing systems. Unlike traditional liquid cooling that relies on direct contact with conductive coolants, immersion cooling submerges components in non-conductive fluids, enhancing reliability and reducing maintenance. Explore the transformative benefits of dielectric fluids in immersion cooling to optimize your data center's thermal management.
Cold Plate (Liquid Cooling)
Liquid cooling systems using cold plates efficiently transfer heat away from high-performance electronics through direct contact with a coolant, enhancing thermal management in data centers and industrial applications. Immersion cooling submerges entire components in dielectric fluids to achieve uniform cooling, but cold plate setups offer targeted heat dissipation and easier maintenance. Explore detailed comparisons of cold plate liquid cooling and immersion cooling technologies to optimize your thermal management strategy.
Direct Contact (Immersion Cooling)
Direct Contact Immersion Cooling involves submerging hardware components directly into a thermally conductive dielectric liquid, enabling efficient heat dissipation and reducing the need for traditional air-cooling systems. This method contrasts with conventional liquid cooling, where coolant circulates through tubes and cold plates without direct immersion, often resulting in less effective heat transfer. Explore the advantages and technology behind Direct Contact Immersion Cooling to understand its impact on data center efficiency.
Source and External Links
How Does Immersion Cooling Work? - Immersion cooling involves submerging electronics in a dielectric liquid to efficiently capture and dissipate heat, offering significant advantages over air cooling.
Immersion Cooling - This technology uses dielectric fluids to cool electronic components directly, enhancing thermal management and sustainability in data centers.
What is Immersion Cooling? - Immersion cooling is a method of cooling IT equipment by submerging it in a non-conductive fluid, providing energy efficiency and environmental benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com