Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decryption, ensuring data privacy during processing. Functional encryption allows users to decrypt specific functions of encrypted data, restricting information access to only what is necessary. Explore the differences and applications of homomorphic and functional encryption to enhance your understanding of advanced cryptographic techniques.
Why it is important
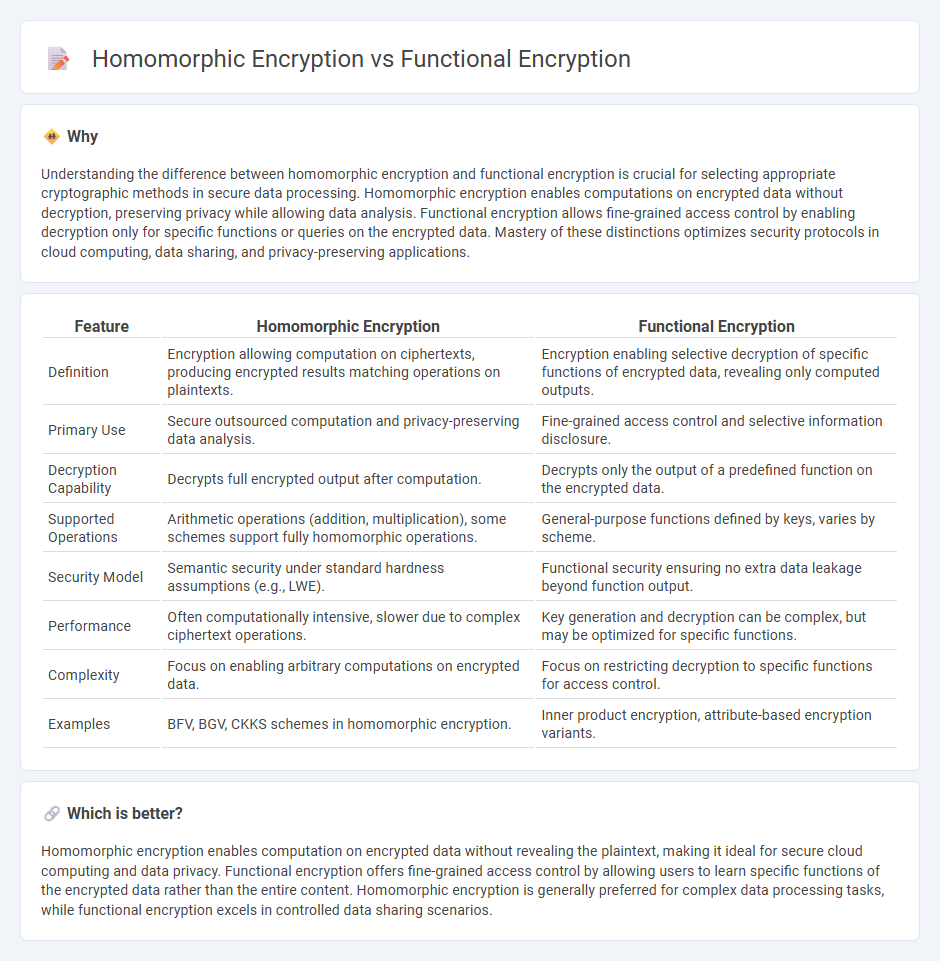
Understanding the difference between homomorphic encryption and functional encryption is crucial for selecting appropriate cryptographic methods in secure data processing. Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decryption, preserving privacy while allowing data analysis. Functional encryption allows fine-grained access control by enabling decryption only for specific functions or queries on the encrypted data. Mastery of these distinctions optimizes security protocols in cloud computing, data sharing, and privacy-preserving applications.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Homomorphic Encryption | Functional Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Encryption allowing computation on ciphertexts, producing encrypted results matching operations on plaintexts. | Encryption enabling selective decryption of specific functions of encrypted data, revealing only computed outputs. |
| Primary Use | Secure outsourced computation and privacy-preserving data analysis. | Fine-grained access control and selective information disclosure. |
| Decryption Capability | Decrypts full encrypted output after computation. | Decrypts only the output of a predefined function on the encrypted data. |
| Supported Operations | Arithmetic operations (addition, multiplication), some schemes support fully homomorphic operations. | General-purpose functions defined by keys, varies by scheme. |
| Security Model | Semantic security under standard hardness assumptions (e.g., LWE). | Functional security ensuring no extra data leakage beyond function output. |
| Performance | Often computationally intensive, slower due to complex ciphertext operations. | Key generation and decryption can be complex, but may be optimized for specific functions. |
| Complexity | Focus on enabling arbitrary computations on encrypted data. | Focus on restricting decryption to specific functions for access control. |
| Examples | BFV, BGV, CKKS schemes in homomorphic encryption. | Inner product encryption, attribute-based encryption variants. |
Which is better?
Homomorphic encryption enables computation on encrypted data without revealing the plaintext, making it ideal for secure cloud computing and data privacy. Functional encryption offers fine-grained access control by allowing users to learn specific functions of the encrypted data rather than the entire content. Homomorphic encryption is generally preferred for complex data processing tasks, while functional encryption excels in controlled data sharing scenarios.
Connection
Homomorphic encryption and functional encryption are both advanced cryptographic techniques that enable computations on encrypted data without revealing the underlying plaintext, enhancing data privacy in cloud computing and secure multi-party computations. Homomorphic encryption allows specific types of computations to be performed on ciphertexts, generating encrypted results that, once decrypted, match the outcome of operations performed on the plaintext. Functional encryption generalizes this concept by allowing the decryption key to reveal only a specific function of the encrypted data, providing fine-grained access control and data confidentiality.
Key Terms
Fine-grained access control
Functional encryption enables fine-grained access control by allowing decryption of specific functions of encrypted data without revealing the entire dataset, thereby ensuring users access only the information they are authorized to. Homomorphic encryption allows computation on encrypted data, but its access control is typically broader and less granular, as it processes encrypted inputs to produce encrypted outputs without revealing the data itself. Explore more to understand how these encryption methods balance privacy and functionality in sensitive data environments.
Computation on ciphertexts
Functional encryption enables fine-grained access control by allowing specific function outputs to be computed directly from ciphertexts without revealing the underlying data, enhancing privacy in delegated computations. Homomorphic encryption permits arbitrary computations on encrypted data, enabling cloud services to perform complex operations without decrypting the information, thereby preserving confidentiality throughout the process. Explore the distinctions and applications of these cryptographic techniques to deepen your understanding of secure data computation.
Data privacy
Functional encryption enables fine-grained access to encrypted data by allowing specific functions to be computed without revealing the underlying plaintext, enhancing data privacy through customized decryption capabilities. Homomorphic encryption supports computations on ciphertexts directly, preserving data confidentiality while producing encrypted results that can be decrypted later, making it ideal for secure data processing. Explore the distinct privacy mechanisms and use cases of functional and homomorphic encryption to deepen your understanding of advanced data protection.
Source and External Links
Functional Encryption Survey - Applied Cryptography Group - Functional encryption is a specialized encryption type allowing users to learn specific functions of encrypted data without revealing the underlying data itself, enabling fine-grained access control beyond traditional public-key encryption.
Forget Homomorphic Encryption, Here Comes Functional Encryption - Functional encryption generalizes public-key encryption by enabling different decryption keys to reveal only specific functions of encrypted data, supporting delegation of function evaluation while preserving data privacy.
A survey on functional encryption - Functional encryption expands traditional encryption by supporting fine-grained access control as well as learning particular functions of encrypted data, encompassing multiple classes and schemes with varying security properties.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com