Vector databases store and manage high-dimensional data representations, enabling efficient similarity search and machine learning applications, while traditional file systems organize and retrieve unstructured data through hierarchical directories. Vector databases optimize tasks like image recognition and natural language processing by leveraging dense vector embeddings, contrasting with file systems' focus on file storage and access control. Explore how these technologies redefine data handling and retrieval to enhance AI-driven solutions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between vector databases and file systems is crucial for optimizing data retrieval and storage in AI and machine learning applications. Vector databases efficiently index and search high-dimensional data like embeddings, enabling faster similarity searches compared to traditional file systems. File systems primarily manage unstructured data storage without inherent search capabilities tailored for complex data types. Mastery of these distinctions enhances system performance and supports advanced analytics in technology-driven environments.
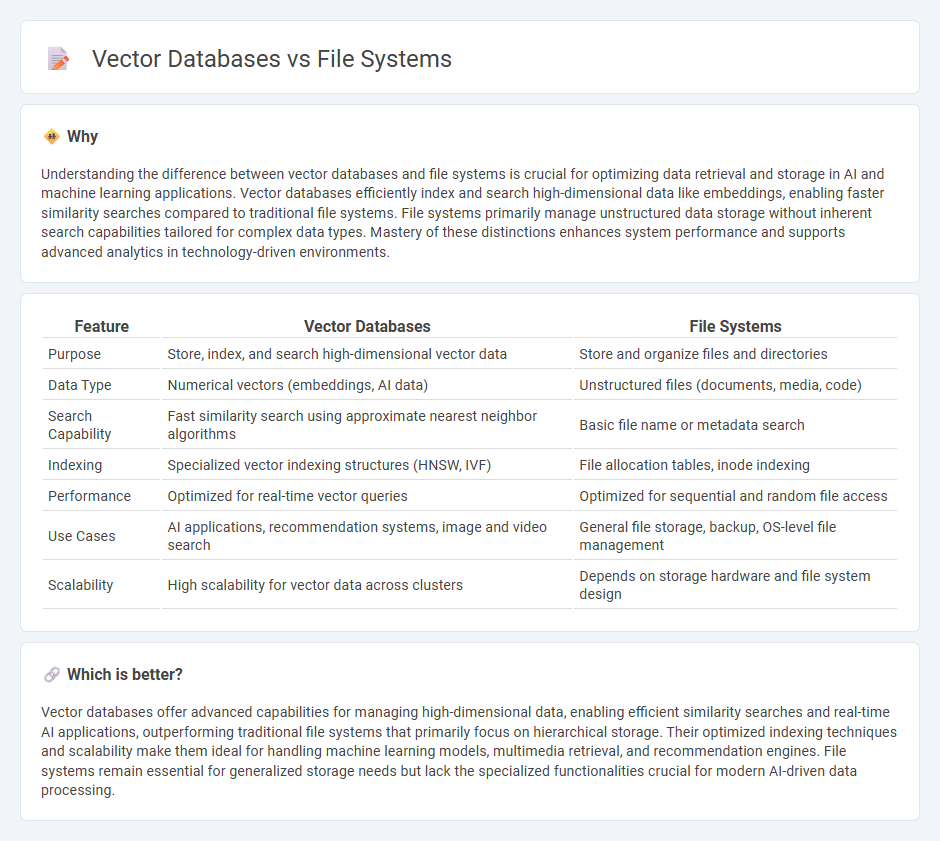
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vector Databases | File Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Store, index, and search high-dimensional vector data | Store and organize files and directories |
| Data Type | Numerical vectors (embeddings, AI data) | Unstructured files (documents, media, code) |
| Search Capability | Fast similarity search using approximate nearest neighbor algorithms | Basic file name or metadata search |
| Indexing | Specialized vector indexing structures (HNSW, IVF) | File allocation tables, inode indexing |
| Performance | Optimized for real-time vector queries | Optimized for sequential and random file access |
| Use Cases | AI applications, recommendation systems, image and video search | General file storage, backup, OS-level file management |
| Scalability | High scalability for vector data across clusters | Depends on storage hardware and file system design |
Which is better?
Vector databases offer advanced capabilities for managing high-dimensional data, enabling efficient similarity searches and real-time AI applications, outperforming traditional file systems that primarily focus on hierarchical storage. Their optimized indexing techniques and scalability make them ideal for handling machine learning models, multimedia retrieval, and recommendation engines. File systems remain essential for generalized storage needs but lack the specialized functionalities crucial for modern AI-driven data processing.
Connection
Vector databases and file systems are connected through their roles in data storage and retrieval, where vector databases manage high-dimensional data for machine learning and AI applications, and file systems organize and store the underlying files containing this data. Efficient integration between vector databases and file systems enables faster access to large-scale unstructured data, enhancing performance in similarity searches and analytics. This connection supports advanced technologies such as natural language processing, image recognition, and recommendation systems by facilitating seamless data flow and management.
Key Terms
Data Storage Structure
File systems organize data as a hierarchy of files and directories stored on physical disks, emphasizing sequential and random access to byte streams. Vector databases structure data as high-dimensional vectors indexed for efficient similarity search, optimized for AI and machine learning applications. Discover how these storage structures impact data retrieval and management in modern data ecosystems.
Indexing Methods
File systems primarily use hierarchical and B-tree indexing methods to organize and retrieve files efficiently, focusing on metadata such as filenames, timestamps, and directory structures. Vector databases utilize advanced indexing techniques like Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) algorithms, including HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) and Faiss, to handle high-dimensional vector data for similarity search and machine learning applications. Explore more to understand how these indexing methods impact data retrieval performance and use cases.
Query Efficiency
File systems organize data as blocks or files, lacking inherent indexing structures that optimize query efficiency, making searches slower for large datasets. Vector databases employ specialized indexing methods like HNSW or FAISS to facilitate rapid similarity searches over high-dimensional embeddings. Explore further to understand how vector databases outperform traditional file systems in query performance for AI-driven applications.
Source and External Links
Local File Systems - Win32 apps - Learn Microsoft - A file system organizes files and directories in a hierarchical structure, allowing applications to store and retrieve data on various storage devices, with management of volumes, directories, and files as core components.
What is a file system? | Definition from TechTarget - A file system logically and physically organizes, manages, and accesses files and directories on a device, using a directory hierarchy and maintaining metadata such as file size and creation date.
File system - Wikipedia - A file system governs file organization and access, providing data storage services to applications, and comes in various designs for different devices and use cases, including local and network file systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com