RISC-V is an open-source instruction set architecture known for its modular design and energy efficiency, making it popular in embedded systems and academic research. Intel's Itanium architecture, designed for enterprise servers, emphasizes high-performance computing with its explicit parallel instruction computing (EPIC) technology. Explore the fundamental differences between these architectures and their impact on modern computing.
Why it is important
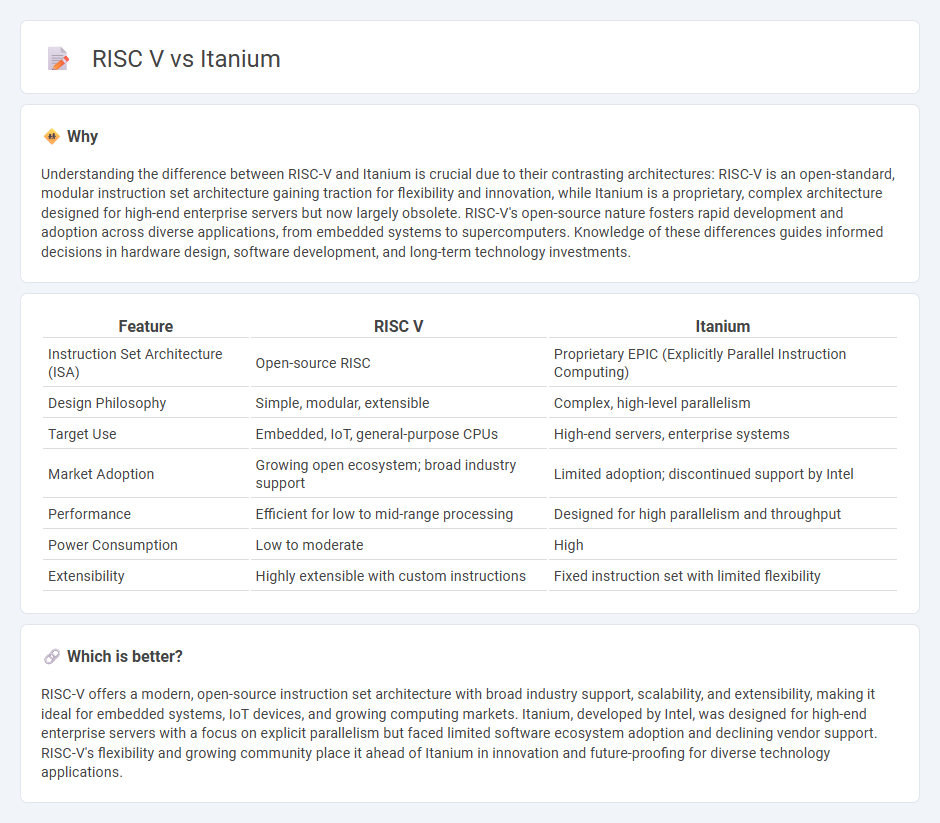
Understanding the difference between RISC-V and Itanium is crucial due to their contrasting architectures: RISC-V is an open-standard, modular instruction set architecture gaining traction for flexibility and innovation, while Itanium is a proprietary, complex architecture designed for high-end enterprise servers but now largely obsolete. RISC-V's open-source nature fosters rapid development and adoption across diverse applications, from embedded systems to supercomputers. Knowledge of these differences guides informed decisions in hardware design, software development, and long-term technology investments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | RISC V | Itanium |
|---|---|---|
| Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) | Open-source RISC | Proprietary EPIC (Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing) |
| Design Philosophy | Simple, modular, extensible | Complex, high-level parallelism |
| Target Use | Embedded, IoT, general-purpose CPUs | High-end servers, enterprise systems |
| Market Adoption | Growing open ecosystem; broad industry support | Limited adoption; discontinued support by Intel |
| Performance | Efficient for low to mid-range processing | Designed for high parallelism and throughput |
| Power Consumption | Low to moderate | High |
| Extensibility | Highly extensible with custom instructions | Fixed instruction set with limited flexibility |
Which is better?
RISC-V offers a modern, open-source instruction set architecture with broad industry support, scalability, and extensibility, making it ideal for embedded systems, IoT devices, and growing computing markets. Itanium, developed by Intel, was designed for high-end enterprise servers with a focus on explicit parallelism but faced limited software ecosystem adoption and declining vendor support. RISC-V's flexibility and growing community place it ahead of Itanium in innovation and future-proofing for diverse technology applications.
Connection
RISC-V and Itanium are connected through their roles in advancing computer processor architectures, with both focusing on optimizing instruction sets for improved performance and efficiency. Itanium, designed by Intel with an Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing (EPIC) architecture, contrasts RISC-V's open-standard Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) approach, which promotes extensibility and customization. The comparison highlights trends in processor design evolution, emphasizing RISC-V's growing adoption as an open, scalable architecture versus Itanium's proprietary, high-complexity model.
Key Terms
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
Itanium utilizes Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing (EPIC) architecture to exploit instruction-level parallelism, emphasizing complex instruction sets for high-performance computing. In contrast, RISC-V follows a reduced instruction set architecture (RISC) model prioritizing simplicity, modularity, and extensibility, enabling easier customization and scalability across diverse platforms. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how the ISA differences impact processor design and application efficiency.
Parallelism
Itanium architecture leverages Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing (EPIC) to maximize instruction-level parallelism through compiler-driven parallel execution, enhancing performance for complex workloads. RISC-V, an open-standard ISA, supports scalable parallelism with modular extensions enabling efficient multi-core and vector processing in diverse applications. Explore detailed comparisons and implementation strategies to understand their impact on parallel computing advancements.
Open Source
Itanium, developed by Intel, is a proprietary 64-bit architecture designed for high-performance enterprise servers, while RISC-V is an open-source instruction set architecture promoting innovation and collaboration across hardware developers. RISC-V's open-source model allows customization, fostering a growing ecosystem that contrasts with Itanium's limited flexibility and declining adoption. Explore the rise of open-source architectures and their impact on the future of computing hardware.
Source and External Links
Itanium - Wikipedia - Itanium is a discontinued family of 64-bit Intel microprocessors implementing the IA-64 architecture, developed jointly by HP and Intel, released in 2001 for enterprise servers, but its performance lagged behind established RISC and CISC processors, and it was eventually discontinued.
Itanium processor microarchitecture - H Sharangpani - The Itanium processor employs EPIC (Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing) architecture, designed to optimize instruction-level parallelism by shifting scheduling complexity to the compiler for high performance on 64-bit addressing and enterprise workloads.
The Itanium processor, part 1: Warming up - Microsoft Dev Blog - Itanium is a 64-bit EPIC processor architecture featuring a large number of registers (128 integer, 128 floating point, and 64 predicate registers) and relies heavily on compiler optimization to explicitly schedule instructions for parallel execution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com