Blockchain oracles serve as bridges connecting smart contracts to real-world data, enabling automated, trustless execution based on external inputs. Distributed ledgers, on the other hand, provide decentralized databases that record transactions across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency and security without relying on a central authority. Explore in-depth how blockchain oracles and distributed ledgers complement each other to revolutionize data integrity and automation.
Why it is important
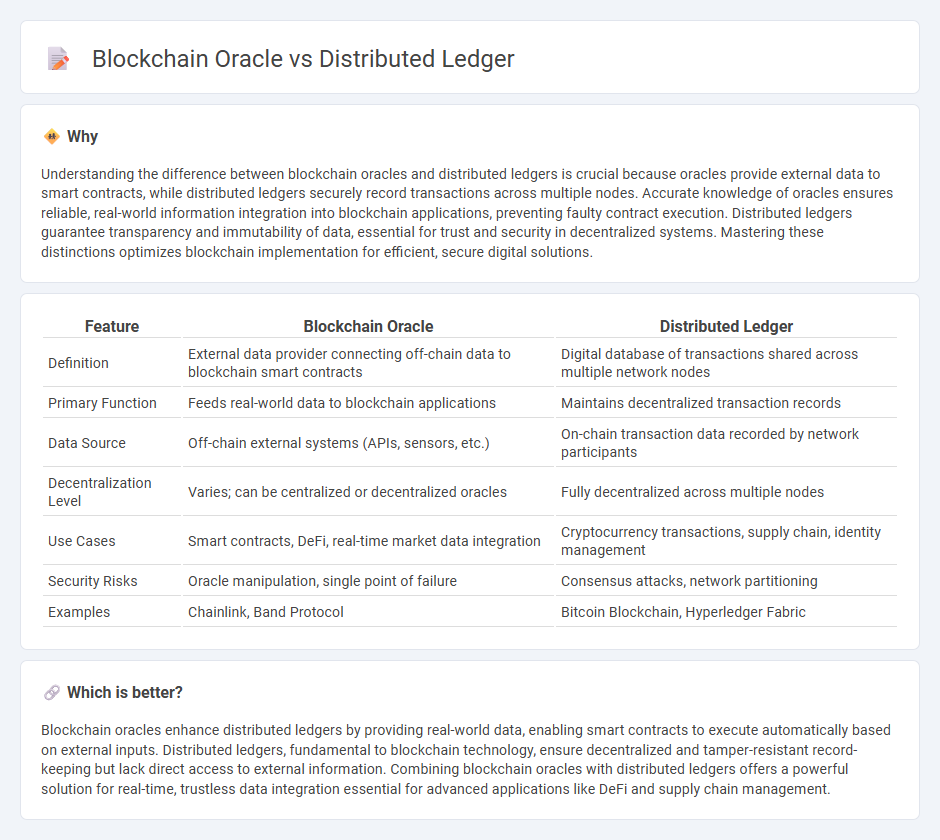
Understanding the difference between blockchain oracles and distributed ledgers is crucial because oracles provide external data to smart contracts, while distributed ledgers securely record transactions across multiple nodes. Accurate knowledge of oracles ensures reliable, real-world information integration into blockchain applications, preventing faulty contract execution. Distributed ledgers guarantee transparency and immutability of data, essential for trust and security in decentralized systems. Mastering these distinctions optimizes blockchain implementation for efficient, secure digital solutions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Oracle | Distributed Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | External data provider connecting off-chain data to blockchain smart contracts | Digital database of transactions shared across multiple network nodes |
| Primary Function | Feeds real-world data to blockchain applications | Maintains decentralized transaction records |
| Data Source | Off-chain external systems (APIs, sensors, etc.) | On-chain transaction data recorded by network participants |
| Decentralization Level | Varies; can be centralized or decentralized oracles | Fully decentralized across multiple nodes |
| Use Cases | Smart contracts, DeFi, real-time market data integration | Cryptocurrency transactions, supply chain, identity management |
| Security Risks | Oracle manipulation, single point of failure | Consensus attacks, network partitioning |
| Examples | Chainlink, Band Protocol | Bitcoin Blockchain, Hyperledger Fabric |
Which is better?
Blockchain oracles enhance distributed ledgers by providing real-world data, enabling smart contracts to execute automatically based on external inputs. Distributed ledgers, fundamental to blockchain technology, ensure decentralized and tamper-resistant record-keeping but lack direct access to external information. Combining blockchain oracles with distributed ledgers offers a powerful solution for real-time, trustless data integration essential for advanced applications like DeFi and supply chain management.
Connection
Blockchain oracles serve as bridges between external data sources and distributed ledgers, enabling smart contracts to execute based on real-world information. Distributed ledgers provide the immutable and decentralized infrastructure where blockchain oracles feed verified external data, ensuring accuracy and trustworthiness in transactions. The integration of oracles with distributed ledgers enhances the functionality and reliability of blockchain applications across various industries.
Key Terms
**Distributed Ledger:**
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a decentralized database managed across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability without relying on a central authority. Unlike blockchain, which structures data into sequential blocks, distributed ledgers can utilize various data structures, enhancing flexibility and scalability in financial, healthcare, and supply chain applications. Discover how distributed ledger technology revolutionizes data integrity and trust in modern decentralized systems.
Consensus Mechanism
Distributed ledgers use various consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance to validate and agree on transaction records across multiple nodes. Blockchain oracles, however, rely on consensus among multiple data sources or off-chain validators to ensure accurate and reliable external information feeds to smart contracts. Explore the differences in consensus approaches for secure and trustworthy decentralized applications.
Node Synchronization
Node synchronization in distributed ledgers ensures all nodes maintain a consistent and up-to-date copy of the ledger by validating and sharing transaction data continuously. Blockchain oracles, by contrast, provide external data to smart contracts, requiring robust synchronization mechanisms to align off-chain information with on-chain state accurately. Explore the critical differences in synchronization approaches to enhance your understanding of decentralized data integrity.
Source and External Links
Distributed ledger - Wikipedia - A distributed ledger is a digital system where data is replicated, shared, and synchronized across multiple nodes on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for a central authority and providing resilience against single points of failure.
What is distributed ledger technology (DLT)? - TechTarget - DLT is a decentralized system that records transactions across multiple locations simultaneously, uses cryptography for security, and achieves consensus among nodes to ensure all copies of the ledger remain synchronized and tamper-resistant.
What are distributed ledger technologies? | Hedera - A distributed ledger is a database maintained by multiple participants, each updating a synchronized copy, enabling secure, direct transactions without intermediaries like banks or brokers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com