Decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to give users full control over their personal data, eliminating reliance on centralized authorities, while Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) depends on trusted certificate authorities to manage digital certificates and encryption keys for secure communication. Decentralized identity enhances privacy and security by enabling verifiable credentials without sharing unnecessary information, whereas PKI remains a foundational framework for encryption and authentication in many internet protocols. Explore the key differences and benefits of these identity management systems to understand their impact on future digital security.
Why it is important
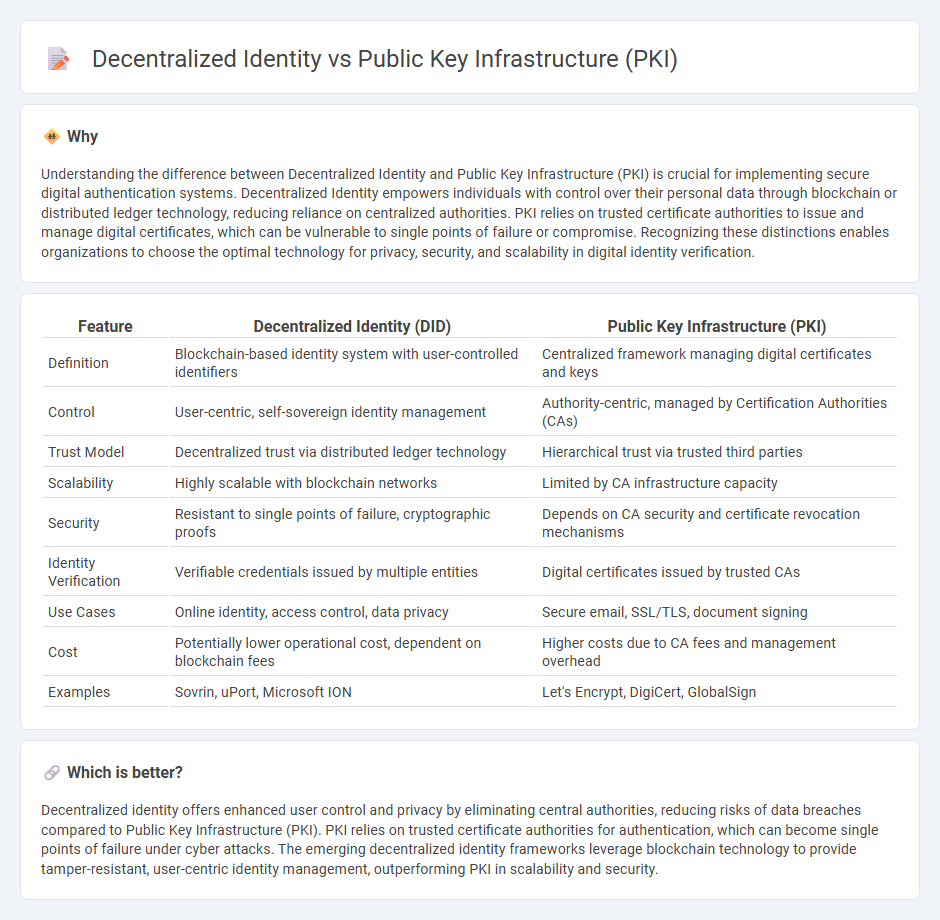
Understanding the difference between Decentralized Identity and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is crucial for implementing secure digital authentication systems. Decentralized Identity empowers individuals with control over their personal data through blockchain or distributed ledger technology, reducing reliance on centralized authorities. PKI relies on trusted certificate authorities to issue and manage digital certificates, which can be vulnerable to single points of failure or compromise. Recognizing these distinctions enables organizations to choose the optimal technology for privacy, security, and scalability in digital identity verification.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Identity (DID) | Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blockchain-based identity system with user-controlled identifiers | Centralized framework managing digital certificates and keys |
| Control | User-centric, self-sovereign identity management | Authority-centric, managed by Certification Authorities (CAs) |
| Trust Model | Decentralized trust via distributed ledger technology | Hierarchical trust via trusted third parties |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with blockchain networks | Limited by CA infrastructure capacity |
| Security | Resistant to single points of failure, cryptographic proofs | Depends on CA security and certificate revocation mechanisms |
| Identity Verification | Verifiable credentials issued by multiple entities | Digital certificates issued by trusted CAs |
| Use Cases | Online identity, access control, data privacy | Secure email, SSL/TLS, document signing |
| Cost | Potentially lower operational cost, dependent on blockchain fees | Higher costs due to CA fees and management overhead |
| Examples | Sovrin, uPort, Microsoft ION | Let's Encrypt, DigiCert, GlobalSign |
Which is better?
Decentralized identity offers enhanced user control and privacy by eliminating central authorities, reducing risks of data breaches compared to Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). PKI relies on trusted certificate authorities for authentication, which can become single points of failure under cyber attacks. The emerging decentralized identity frameworks leverage blockchain technology to provide tamper-resistant, user-centric identity management, outperforming PKI in scalability and security.
Connection
Decentralized identity leverages Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to establish secure and verifiable digital identities without relying on centralized authorities. PKI provides the cryptographic foundation for managing public and private keys, enabling users to authenticate and control their identity data autonomously. This synergy enhances privacy, reduces identity fraud, and supports user-centric identity management in the digital ecosystem.
Key Terms
Certificate Authority (CA)
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) relies heavily on Certificate Authorities (CAs) as trusted third parties that issue and manage digital certificates to authenticate identities and secure communications. In contrast, decentralized identity frameworks minimize or eliminate the role of CAs by using blockchain and cryptographic proofs to enable users to control their own identity credentials without central intermediaries. Explore the evolving dynamics between PKI and decentralized identity to understand their impact on digital trust and security.
Blockchain
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) relies on centralized Certificate Authorities to validate digital identities, whereas decentralized identity uses blockchain technology to enable secure, tamper-proof verification without relying on a single trusted entity. Blockchain-based decentralized identity enhances user control over personal data and reduces the risk of identity theft by storing credentials across a distributed ledger. Explore how blockchain transforms identity management by providing scalable, transparent, and privacy-preserving solutions.
Cryptographic Keys
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) relies on centralized certificate authorities to issue and manage cryptographic keys, ensuring trust through hierarchical validation and digital certificates. Decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to enable users to control their cryptographic keys directly, enhancing privacy and reducing reliance on third-party authorities. Explore the differences between PKI and decentralized identity to understand how cryptographic keys empower digital security.
Source and External Links
What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)? - IBM - PKI is a comprehensive framework combining software, hardware, policies, and procedures that create, distribute, manage, and revoke digital certificates to securely verify identities and enable trustworthy digital communications using public-key cryptography.
Public key infrastructure - Wikipedia - PKI consists of roles, policies, hardware, software, and procedures to manage digital certificates and public-key encryption, facilitating secure electronic information transfer and binding public keys to identities through certificates issued by certificate authorities.
What Is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) & How Does It Work? - Okta - PKI secures and authenticates digital communications by issuing digital certificates from trusted certificate authorities that verify identities and enable encryption between users and servers or within organizations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com