Edge mesh technology enhances data processing by creating a decentralized network of interconnected edge devices, reducing latency and improving real-time analytics. Distributed computing allocates tasks across multiple servers or nodes to increase computational power and efficiency, often within centralized data centers. Explore the differences between edge mesh and distributed computing to optimize your technology infrastructure.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between edge mesh and distributed computing is crucial for optimizing network efficiency and data processing in technology. Edge mesh focuses on decentralized computing at the network's edge, enhancing real-time data handling and reducing latency. Distributed computing involves spreading tasks across multiple centralized or decentralized nodes to improve scalability and fault tolerance. This knowledge enables better architectural decisions for applications like IoT, cloud services, and AI deployments.
Comparison Table
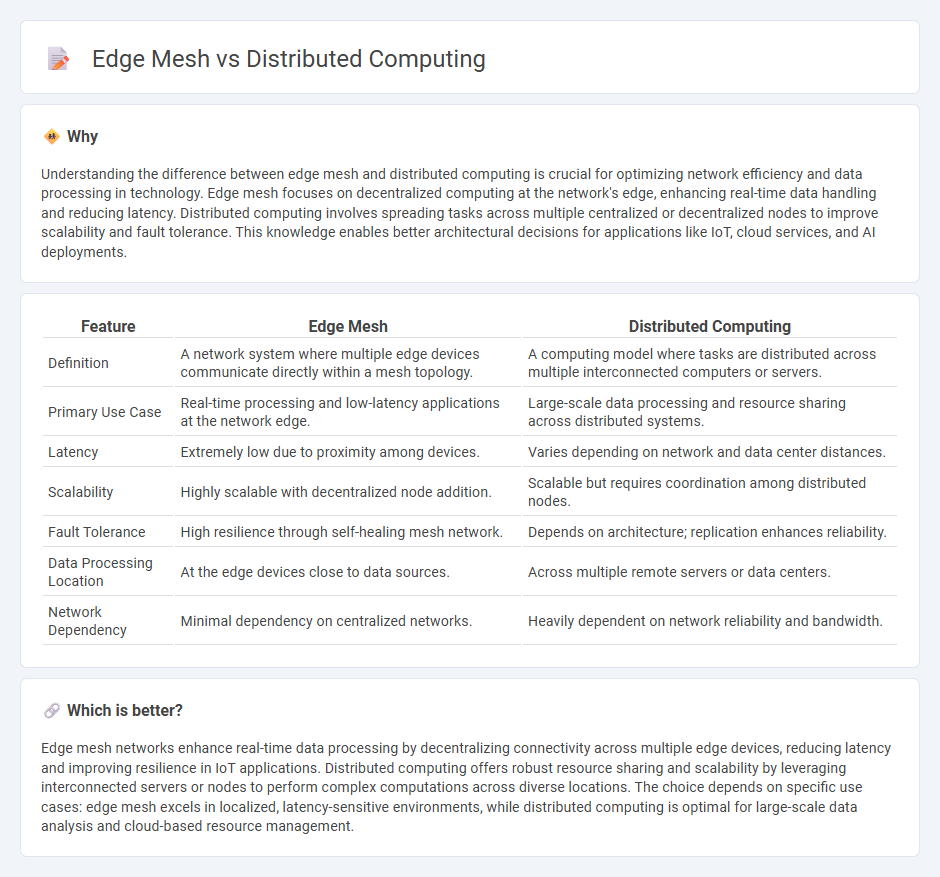
| Feature | Edge Mesh | Distributed Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A network system where multiple edge devices communicate directly within a mesh topology. | A computing model where tasks are distributed across multiple interconnected computers or servers. |
| Primary Use Case | Real-time processing and low-latency applications at the network edge. | Large-scale data processing and resource sharing across distributed systems. |
| Latency | Extremely low due to proximity among devices. | Varies depending on network and data center distances. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with decentralized node addition. | Scalable but requires coordination among distributed nodes. |
| Fault Tolerance | High resilience through self-healing mesh network. | Depends on architecture; replication enhances reliability. |
| Data Processing Location | At the edge devices close to data sources. | Across multiple remote servers or data centers. |
| Network Dependency | Minimal dependency on centralized networks. | Heavily dependent on network reliability and bandwidth. |
Which is better?
Edge mesh networks enhance real-time data processing by decentralizing connectivity across multiple edge devices, reducing latency and improving resilience in IoT applications. Distributed computing offers robust resource sharing and scalability by leveraging interconnected servers or nodes to perform complex computations across diverse locations. The choice depends on specific use cases: edge mesh excels in localized, latency-sensitive environments, while distributed computing is optimal for large-scale data analysis and cloud-based resource management.
Connection
Edge mesh networks enhance distributed computing by enabling seamless, decentralized communication among edge devices, thereby reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Distributed computing leverages this interconnected edge infrastructure to process data closer to the source, improving real-time analytics and decision-making. The synergy between edge mesh and distributed computing facilitates scalable, resilient, and efficient systems for applications like IoT, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles.
Key Terms
**Distributed Computing:**
Distributed computing leverages multiple interconnected nodes to perform complex tasks by sharing resources and processing power across vast networks, enhancing scalability and fault tolerance. It enables real-time data processing and load balancing, crucial for handling big data analytics and cloud-based applications efficiently. Explore more to understand how distributed computing transforms modern IT infrastructures and drives innovation.
Cluster
Distributed computing clusters leverage a network of interconnected nodes to process large-scale data efficiently, ensuring fault tolerance and scalability. Edge mesh clusters distribute computing resources closer to data sources, reducing latency and enhancing real-time processing capabilities at the network's periphery. Explore how cluster architectures in both systems optimize performance and reliability for various applications.
Load Balancing
Distributed computing utilizes centralized load balancing to efficiently distribute tasks across multiple servers, enhancing resource utilization and minimizing latency. Edge mesh employs decentralized load balancing by dynamically allocating workloads among edge nodes, ensuring real-time processing and reduced network congestion. Explore how innovative load balancing strategies can optimize performance in your distributed and edge mesh environments.
Source and External Links
Distributed Computing - Distributed computing is a model where software components are shared among multiple computers or nodes to improve efficiency and performance.
What is Distributed Computing - Distributed computing involves processing and data storage distributed across multiple devices or systems, allowing them to work together without a central hub.
What is Distributed Computing - Distributed computing makes multiple computers work together to solve common problems, providing large-scale resources for complex tasks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com