Zero Trust Architecture eliminates implicit trust by continuously verifying every user and device, enhancing security beyond traditional perimeter models. Defense in Depth uses multiple security layers like firewalls, intrusion detection, and antivirus to protect systems from diverse threats. Discover how these approaches complement each other to safeguard modern digital environments.
Why it is important
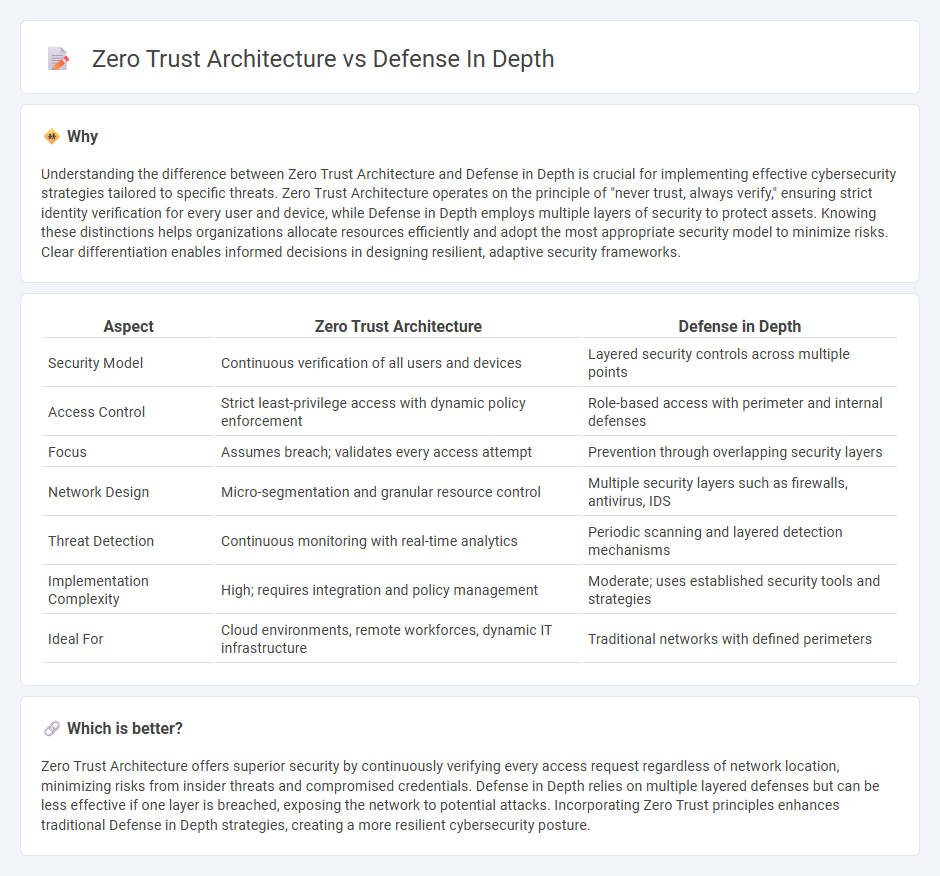
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Architecture and Defense in Depth is crucial for implementing effective cybersecurity strategies tailored to specific threats. Zero Trust Architecture operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," ensuring strict identity verification for every user and device, while Defense in Depth employs multiple layers of security to protect assets. Knowing these distinctions helps organizations allocate resources efficiently and adopt the most appropriate security model to minimize risks. Clear differentiation enables informed decisions in designing resilient, adaptive security frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust Architecture | Defense in Depth |
|---|---|---|
| Security Model | Continuous verification of all users and devices | Layered security controls across multiple points |
| Access Control | Strict least-privilege access with dynamic policy enforcement | Role-based access with perimeter and internal defenses |
| Focus | Assumes breach; validates every access attempt | Prevention through overlapping security layers |
| Network Design | Micro-segmentation and granular resource control | Multiple security layers such as firewalls, antivirus, IDS |
| Threat Detection | Continuous monitoring with real-time analytics | Periodic scanning and layered detection mechanisms |
| Implementation Complexity | High; requires integration and policy management | Moderate; uses established security tools and strategies |
| Ideal For | Cloud environments, remote workforces, dynamic IT infrastructure | Traditional networks with defined perimeters |
Which is better?
Zero Trust Architecture offers superior security by continuously verifying every access request regardless of network location, minimizing risks from insider threats and compromised credentials. Defense in Depth relies on multiple layered defenses but can be less effective if one layer is breached, exposing the network to potential attacks. Incorporating Zero Trust principles enhances traditional Defense in Depth strategies, creating a more resilient cybersecurity posture.
Connection
Zero Trust Architecture and Defense in Depth are interconnected cybersecurity strategies that enhance organizational security by implementing multiple, layered defenses to protect data and resources. Zero Trust Architecture assumes no implicit trust within the network, enforcing strict identity verification at every access point, while Defense in Depth incorporates this principle by applying diverse security controls across physical, technical, and administrative layers. Together, they create a robust security posture that minimizes potential attack surfaces and mitigates the risk of unauthorized access and breaches.
Key Terms
Layered Security
Defense in depth employs multiple, overlapping security layers to protect systems by combining physical, technical, and administrative controls, creating redundancies that deter or mitigate attacks. Zero trust architecture assumes no implicit trust within or outside the network perimeter, enforcing strict identity verification, micro-segmentation, and least-privilege access across all layers. Explore how integrating these approaches strengthens cyber resilience by visiting our detailed analysis.
Least Privilege
Defense in depth employs multiple security layers, limiting user access at each level but can still allow excessive permissions if not managed properly. Zero Trust architecture enforces the principle of Least Privilege by continuously verifying user identities and access rights, minimizing exposure and potential breaches. Explore how Zero Trust redefines access management to enhance security rigor.
Micro-Segmentation
Defense in depth employs layered security controls across the network perimeter, endpoints, and applications, while zero trust architecture assumes no implicit trust and requires continuous verification of every user and device. Micro-segmentation plays a critical role in zero trust by dividing the network into isolated segments, minimizing lateral movement for attackers and enforcing granular access policies at the workload level. Discover how micro-segmentation enhances both defense in depth and zero trust strategies to strengthen cybersecurity frameworks.
Source and External Links
Defense in depth (computing) - Wikipedia - Defense in depth is an information security approach that uses multiple, overlapping layers of security controls (physical, technical, and administrative) throughout an IT system to provide redundancy and protection if one layer fails.
What is Defense-in-Depth? - Definition - CyberArk - A defense-in-depth strategy employs several layers of security measures--covering people, technology, and operations--to reduce vulnerabilities, contain threats, and mitigate risks, ensuring that a breach in one layer does not compromise the entire system.
What is defense in depth? | Layered security - Cloudflare - Defense in depth is a cybersecurity strategy that relies on multiple security products and practices (physical, technical, and administrative controls) across various layers to protect an organization's network and resources, often referred to as "layered security".
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com