Blockchain oracles serve as trusted data bridges between decentralized networks and external information sources, ensuring secure and reliable off-chain data integration. API gateways manage and route requests between clients and backend services, focusing on scalability, security, and traffic control within centralized architectures. Explore the key differences and use cases to understand how these technologies optimize data flow in modern applications.
Why it is important
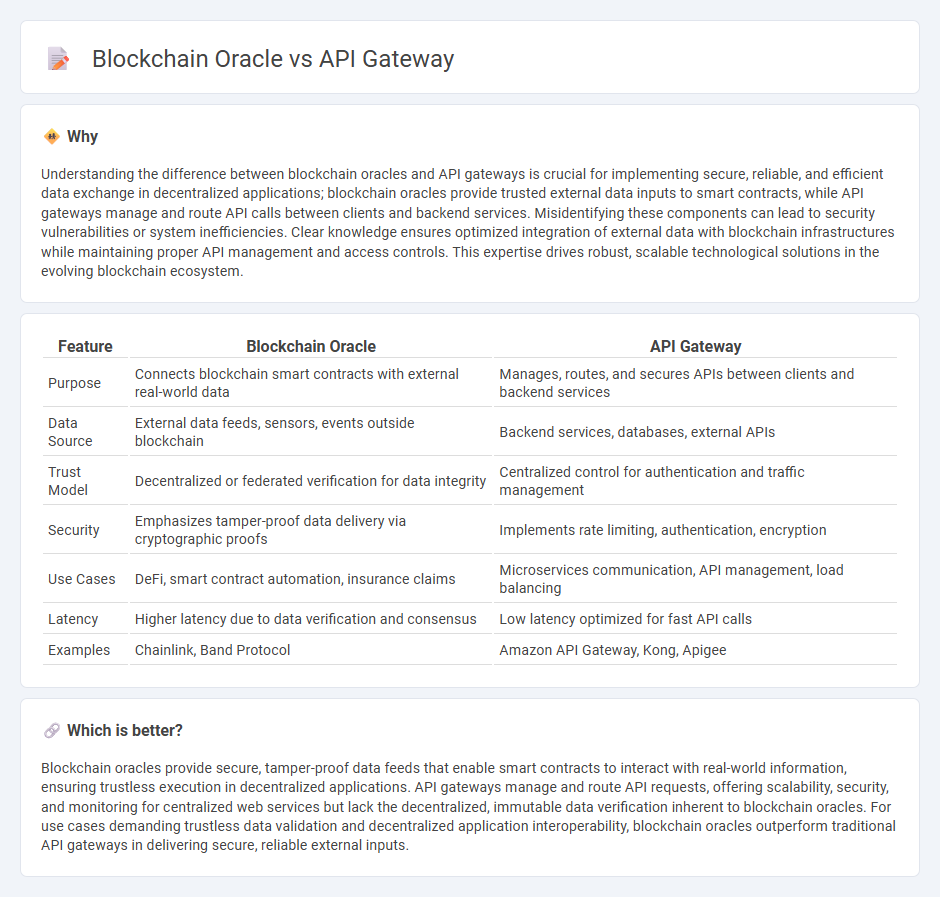
Understanding the difference between blockchain oracles and API gateways is crucial for implementing secure, reliable, and efficient data exchange in decentralized applications; blockchain oracles provide trusted external data inputs to smart contracts, while API gateways manage and route API calls between clients and backend services. Misidentifying these components can lead to security vulnerabilities or system inefficiencies. Clear knowledge ensures optimized integration of external data with blockchain infrastructures while maintaining proper API management and access controls. This expertise drives robust, scalable technological solutions in the evolving blockchain ecosystem.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Oracle | API Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects blockchain smart contracts with external real-world data | Manages, routes, and secures APIs between clients and backend services |
| Data Source | External data feeds, sensors, events outside blockchain | Backend services, databases, external APIs |
| Trust Model | Decentralized or federated verification for data integrity | Centralized control for authentication and traffic management |
| Security | Emphasizes tamper-proof data delivery via cryptographic proofs | Implements rate limiting, authentication, encryption |
| Use Cases | DeFi, smart contract automation, insurance claims | Microservices communication, API management, load balancing |
| Latency | Higher latency due to data verification and consensus | Low latency optimized for fast API calls |
| Examples | Chainlink, Band Protocol | Amazon API Gateway, Kong, Apigee |
Which is better?
Blockchain oracles provide secure, tamper-proof data feeds that enable smart contracts to interact with real-world information, ensuring trustless execution in decentralized applications. API gateways manage and route API requests, offering scalability, security, and monitoring for centralized web services but lack the decentralized, immutable data verification inherent to blockchain oracles. For use cases demanding trustless data validation and decentralized application interoperability, blockchain oracles outperform traditional API gateways in delivering secure, reliable external inputs.
Connection
Blockchain oracles serve as trusted data feeds that bridge external real-world information with blockchain smart contracts, enabling accurate and reliable data integration. API gateways manage and secure the interactions between blockchain networks and off-chain systems by routing external API requests to the appropriate oracle services. This connection ensures seamless, authenticated data flow between decentralized applications and external data sources, enhancing blockchain functionality and interoperability.
Key Terms
Request Routing
API gateways specialize in request routing by managing, filtering, and directing client requests to appropriate backend services, ensuring efficient traffic control and load balancing. Blockchain oracles, however, focus on securely fetching and delivering external data to smart contracts, enabling trustless interaction between off-chain sources and on-chain environments without traditional routing mechanisms. Explore how request routing functionalities differ fundamentally between API gateways and blockchain oracles for optimized application design.
Smart Contract
API gateways serve as intermediaries that manage and secure external API calls for smart contracts, enabling efficient data flow between on-chain and off-chain systems. Blockchain oracles provide trusted, real-time external data inputs directly to smart contracts, ensuring accuracy and authenticity for executing predefined conditions. Explore how combining API gateways with blockchain oracles can enhance smart contract functionality and reliability.
Data Validation
API gateways efficiently manage and authenticate data requests between clients and services, ensuring secure and validated data flow within centralized systems. Blockchain oracles validate and bridge external real-world data to decentralized applications, maintaining trustworthiness by cryptographic proofs and consensus mechanisms. Explore the technical differences in data validation between API gateways and blockchain oracles to optimize your application's integrity.
Source and External Links
What Is an API Gateway? A Quick Learn Guide - F5 Networks - An API gateway acts as a single entry point for client requests, routing them to appropriate microservices, handling request aggregation, protocol translation, and enforcing security policies for simplified user experience in microservices environments.
What is an API Gateway? Core Fundamentals and Use Cases - Kong - An API gateway is a software layer providing a single endpoint to manage API requests, routing, security enforcement, and protocol translation, thereby simplifying API management in microservices architectures.
API gateways - Azure Architecture Center | Microsoft Learn - An API gateway serves as a centralized entry point for client-service interactions, performing routing, authentication, SSL termination, and rate limiting to reduce complexity and improve security in microservices systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com