Self-healing networks automatically detect and repair faults to maintain seamless connectivity, leveraging advanced algorithms and real-time monitoring. Resilient networks focus on robust architecture and redundancy to withstand and recover from failures without service disruption. Explore more to understand how these technologies enhance network reliability and performance.
Why it is important
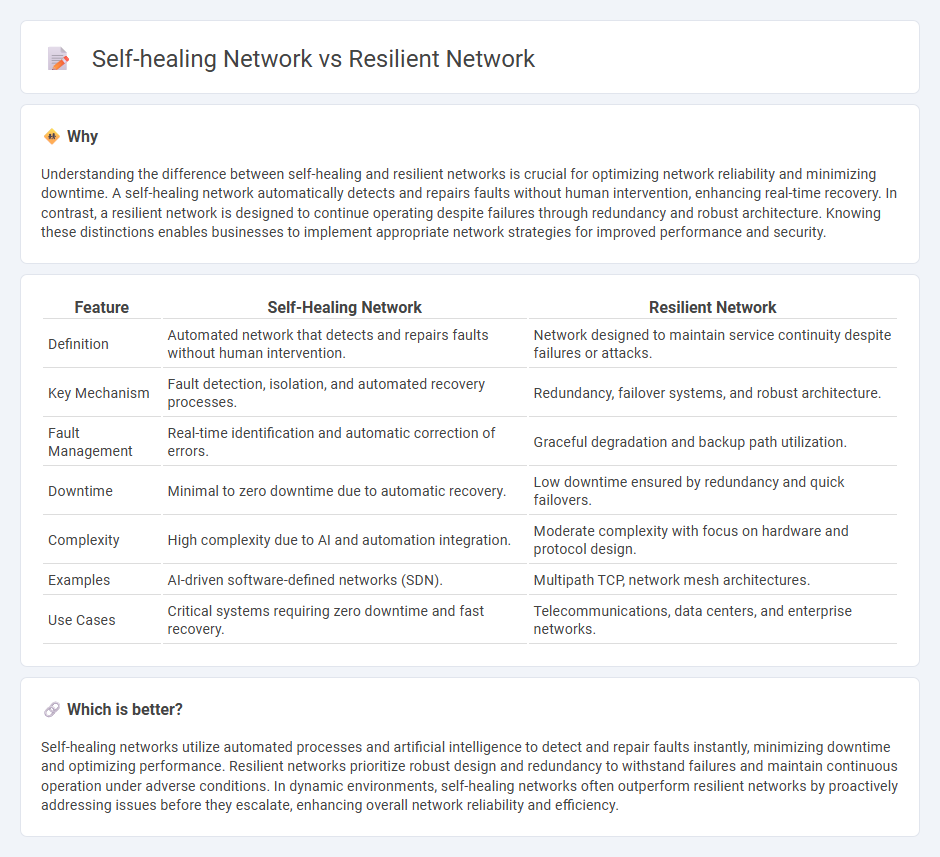
Understanding the difference between self-healing and resilient networks is crucial for optimizing network reliability and minimizing downtime. A self-healing network automatically detects and repairs faults without human intervention, enhancing real-time recovery. In contrast, a resilient network is designed to continue operating despite failures through redundancy and robust architecture. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to implement appropriate network strategies for improved performance and security.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Self-Healing Network | Resilient Network |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated network that detects and repairs faults without human intervention. | Network designed to maintain service continuity despite failures or attacks. |
| Key Mechanism | Fault detection, isolation, and automated recovery processes. | Redundancy, failover systems, and robust architecture. |
| Fault Management | Real-time identification and automatic correction of errors. | Graceful degradation and backup path utilization. |
| Downtime | Minimal to zero downtime due to automatic recovery. | Low downtime ensured by redundancy and quick failovers. |
| Complexity | High complexity due to AI and automation integration. | Moderate complexity with focus on hardware and protocol design. |
| Examples | AI-driven software-defined networks (SDN). | Multipath TCP, network mesh architectures. |
| Use Cases | Critical systems requiring zero downtime and fast recovery. | Telecommunications, data centers, and enterprise networks. |
Which is better?
Self-healing networks utilize automated processes and artificial intelligence to detect and repair faults instantly, minimizing downtime and optimizing performance. Resilient networks prioritize robust design and redundancy to withstand failures and maintain continuous operation under adverse conditions. In dynamic environments, self-healing networks often outperform resilient networks by proactively addressing issues before they escalate, enhancing overall network reliability and efficiency.
Connection
Self-healing networks utilize automated mechanisms to detect and recover from faults, enhancing overall network resilience by minimizing downtime and maintaining service continuity. Resilient networks are designed to withstand, adapt to, and rapidly recover from disruptions through strategies such as redundancy, failover protocols, and real-time monitoring. The integration of self-healing capabilities directly supports network resilience by enabling proactive fault management and ensuring robust, uninterrupted connectivity.
Key Terms
Fault Tolerance
A resilient network maintains continuous operation during faults by incorporating redundancy, fault isolation, and rapid recovery mechanisms to minimize downtime. Self-healing networks automatically detect, diagnose, and repair faults through adaptive algorithms and real-time monitoring, ensuring seamless service restoration without manual intervention. Explore the differences and benefits of each approach to enhance your network's fault tolerance.
Automated Recovery
A resilient network is designed to maintain essential functions during disruptions through redundancy and failover mechanisms, while a self-healing network specifically emphasizes automated recovery by detecting faults and autonomously rerouting traffic or repairing issues without human intervention. Automated recovery in self-healing networks reduces downtime and operational costs by quickly restoring connectivity through advanced algorithms and real-time monitoring. Explore detailed comparisons and implementations of automated recovery in network infrastructures to enhance your understanding.
Redundancy
Resilient networks emphasize redundancy by incorporating multiple pathways and backup systems to maintain connectivity during failures. Self-healing networks enhance redundancy through automated detection and rapid reconfiguration, minimizing downtime by dynamically rerouting traffic. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand how redundancy shapes network reliability.
Source and External Links
How To Build Resilient Community Networks - This article provides tips on building resilient community networks, including fostering diversity, promoting redundancy, and enhancing connectivity.
What is Network Resilience? - A resilient network is one that can respond and recover quickly from disruptions, incorporating redundancy and adaptability for operational continuity.
Six Ways to Get a More Resilient Network in 2025 - This post outlines strategies for improving network resilience, including virtualizing connectivity with Network as a Service (NaaS) and dynamic resource scaling.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com