Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume through renewable sources like solar panels and wind turbines, significantly reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Zero carbon buildings focus on eliminating carbon emissions by optimizing energy efficiency and incorporating sustainable materials, often relying on off-site renewable energy to balance carbon footprints. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these innovative building approaches to understand their impact on sustainable real estate development.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between energy positive buildings and zero carbon buildings is crucial for optimizing sustainability strategies and reducing environmental impact in real estate. Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, contributing excess clean energy back to the grid. Zero carbon buildings focus on eliminating carbon emissions through energy efficiency and the use of renewable energy sources. This distinction guides developers and investors in choosing appropriate technologies and certifications to meet regulatory requirements and market demands.
Comparison Table
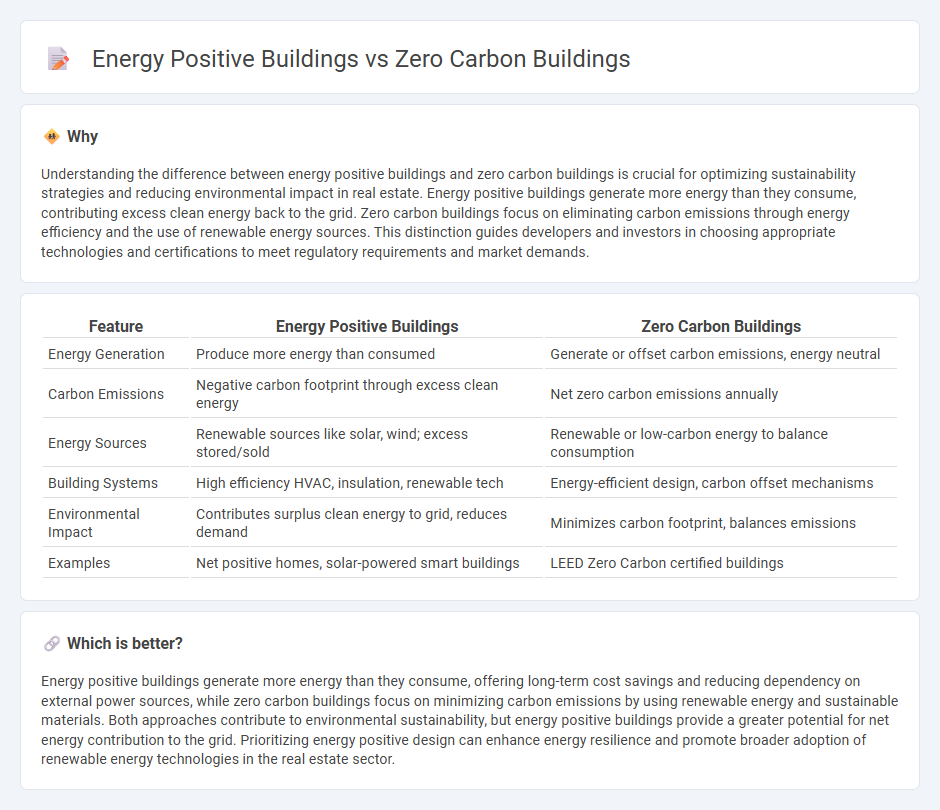
| Feature | Energy Positive Buildings | Zero Carbon Buildings |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Generation | Produce more energy than consumed | Generate or offset carbon emissions, energy neutral |
| Carbon Emissions | Negative carbon footprint through excess clean energy | Net zero carbon emissions annually |
| Energy Sources | Renewable sources like solar, wind; excess stored/sold | Renewable or low-carbon energy to balance consumption |
| Building Systems | High efficiency HVAC, insulation, renewable tech | Energy-efficient design, carbon offset mechanisms |
| Environmental Impact | Contributes surplus clean energy to grid, reduces demand | Minimizes carbon footprint, balances emissions |
| Examples | Net positive homes, solar-powered smart buildings | LEED Zero Carbon certified buildings |
Which is better?
Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, offering long-term cost savings and reducing dependency on external power sources, while zero carbon buildings focus on minimizing carbon emissions by using renewable energy and sustainable materials. Both approaches contribute to environmental sustainability, but energy positive buildings provide a greater potential for net energy contribution to the grid. Prioritizing energy positive design can enhance energy resilience and promote broader adoption of renewable energy technologies in the real estate sector.
Connection
Energy positive buildings produce more energy than they consume through renewable sources like solar panels and advanced insulation technologies, directly supporting zero carbon building goals by minimizing carbon emissions. Zero carbon buildings focus on eliminating net greenhouse gas emissions during their operation, relying heavily on energy positive designs to achieve this target efficiently. The integration of energy positive features in zero carbon buildings accelerates sustainable development in real estate by reducing environmental impact and enhancing energy efficiency.
Key Terms
Net Zero Carbon
Net Zero Carbon buildings are designed to balance the amount of carbon emitted and offset, achieving a net zero carbon footprint primarily through energy efficiency, renewable energy integration, and carbon offsetting strategies. Energy positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, contributing surplus clean energy back to the grid, accelerating decarbonization beyond carbon neutrality. Explore key innovations and strategies driving the shift towards truly sustainable built environments.
Energy Surplus
Energy Surplus highlights the fundamental difference between Zero Carbon buildings and energy positive buildings by emphasizing the generation of excess renewable energy beyond consumption. Zero Carbon buildings achieve net-zero emissions through balanced energy use and onsite renewable generation, while energy positive buildings produce a surplus of clean energy that can be exported to the grid. Explore the benefits and technologies behind these building standards to understand their critical role in sustainable urban development.
Building Performance
Zero Carbon buildings achieve net-zero carbon emissions through efficient energy use and renewable energy integration, minimizing the environmental impact of construction and operation. Energy Positive buildings generate more energy than they consume, often incorporating photovoltaic systems and advanced energy storage to supply surplus power to the grid. Explore the innovations driving high-performance building design to understand how these concepts transform sustainable architecture.
Source and External Links
Achieving Zero-Carbon Buildings - This report outlines how electric, efficient, and flexible solutions can decarbonize buildings, improving living standards and reducing energy bills.
Zero Carbon Certification - This certification program by the International Living Future Institute aims to create buildings that are energy-efficient, combustion-free, and powered by renewable sources.
Zero Carbon Building Standards - These standards, developed by CAGBC, provide a framework for Canadian buildings to be highly energy-efficient and minimize greenhouse gas emissions through operations and materials.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com