Adaptive reuse transforms existing properties into functional spaces, preserving architectural history while reducing environmental impact. Tear-down involves demolishing old structures to make way for new construction, often increasing property value but generating more waste. Explore these strategies to understand which best suits your real estate investment goals.
Why it is important
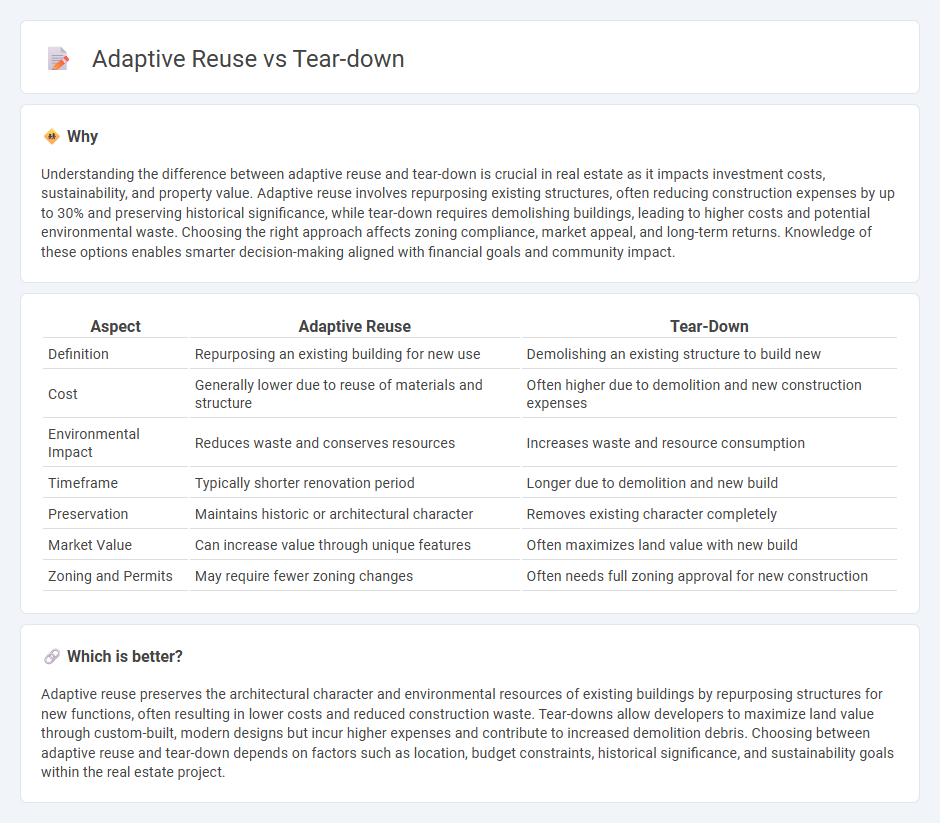
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse and tear-down is crucial in real estate as it impacts investment costs, sustainability, and property value. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing structures, often reducing construction expenses by up to 30% and preserving historical significance, while tear-down requires demolishing buildings, leading to higher costs and potential environmental waste. Choosing the right approach affects zoning compliance, market appeal, and long-term returns. Knowledge of these options enables smarter decision-making aligned with financial goals and community impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse | Tear-Down |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing an existing building for new use | Demolishing an existing structure to build new |
| Cost | Generally lower due to reuse of materials and structure | Often higher due to demolition and new construction expenses |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and conserves resources | Increases waste and resource consumption |
| Timeframe | Typically shorter renovation period | Longer due to demolition and new build |
| Preservation | Maintains historic or architectural character | Removes existing character completely |
| Market Value | Can increase value through unique features | Often maximizes land value with new build |
| Zoning and Permits | May require fewer zoning changes | Often needs full zoning approval for new construction |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse preserves the architectural character and environmental resources of existing buildings by repurposing structures for new functions, often resulting in lower costs and reduced construction waste. Tear-downs allow developers to maximize land value through custom-built, modern designs but incur higher expenses and contribute to increased demolition debris. Choosing between adaptive reuse and tear-down depends on factors such as location, budget constraints, historical significance, and sustainability goals within the real estate project.
Connection
Adaptive reuse and tear-down are connected through their approach to property redevelopment and urban revitalization. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings for new functions, preserving architectural heritage while reducing construction waste, whereas tear-down entails demolishing structures to build anew, often to maximize land value in high-demand real estate markets. Both strategies address changing market needs and zoning regulations, impacting sustainability and investment returns in real estate development.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a critical role in determining whether a property undergoes tear-down or adaptive reuse, with many municipalities imposing restrictions on building height, floor area ratio (FAR), and land use that can limit new construction but favor renovations. Adaptive reuse projects often benefit from zoning incentives such as variances, overlays, or historic district allowances that encourage preservation and sustainability while maintaining neighborhood character. Explore zoning strategies and case studies to understand how regulatory frameworks influence redevelopment decisions.
Historic Preservation
Historic preservation prioritizes adaptive reuse by repurposing buildings to retain architectural integrity and cultural significance while minimizing environmental impact compared to tear-down methods. Adaptive reuse extends the lifecycle of historic structures, preserving original materials and craftsmanship that represent heritage values. Discover how adaptive reuse strategies contribute to sustainable urban development and heritage conservation.
Building Code Compliance
Building code compliance differs significantly between tear-down and adaptive reuse projects, with tear-downs often requiring adherence to current codes for new construction, ensuring modern safety and accessibility standards. Adaptive reuse must reconcile existing structures with updated codes, addressing challenges such as fire safety, structural integrity, and accessibility while preserving historical elements. Explore detailed strategies to navigate building code compliance in both tear-down and adaptive reuse scenarios.
Source and External Links
Teardown (video game) - A 2022 sandbox-puzzle game focusing on demolition and heists, developed by Tuxedo Labs.
Teardown - A game featuring a fully destructible environment, creative problem-solving, and extensive mod support.
Haunted Cars Chase Me - A YouTube video showcasing Teardown gameplay with haunted cars in a survival scenario.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com