Lease-to-own models allow tenants to rent a property with the option to purchase it later, often applying a portion of rent payments toward the down payment. Equity sharing arrangements involve multiple parties co-owning a property, sharing both the investment costs and future profits or losses. Explore the advantages and challenges of these innovative real estate financing options to determine which suits your investment goals.
Why it is important
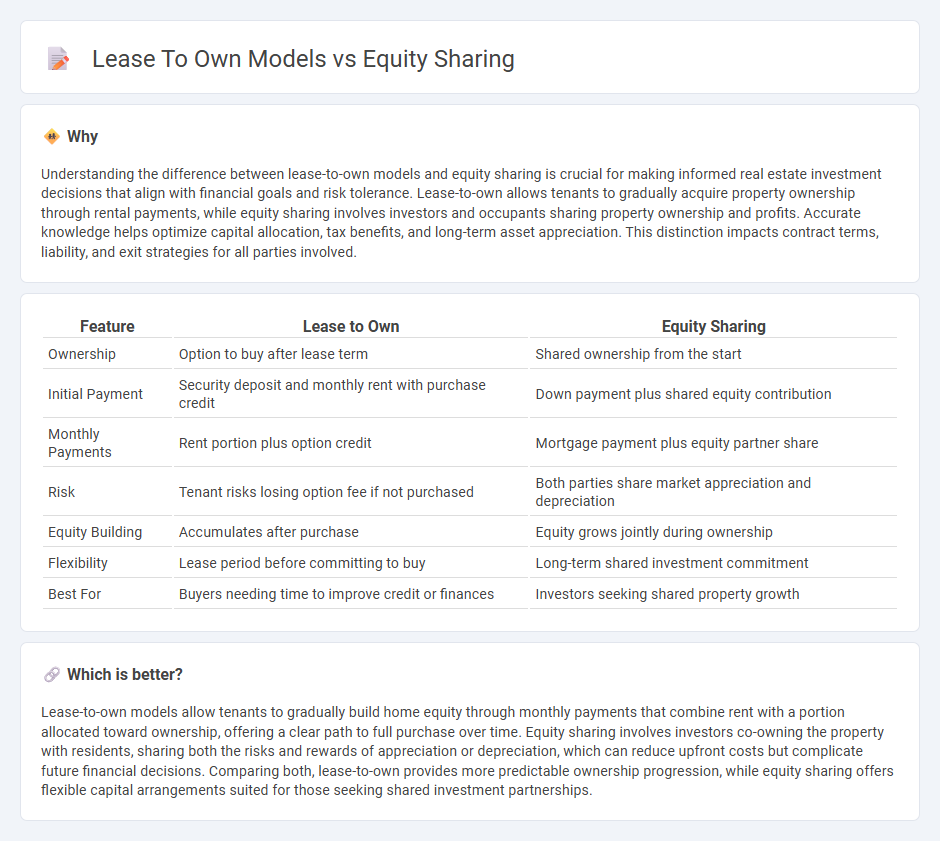
Understanding the difference between lease-to-own models and equity sharing is crucial for making informed real estate investment decisions that align with financial goals and risk tolerance. Lease-to-own allows tenants to gradually acquire property ownership through rental payments, while equity sharing involves investors and occupants sharing property ownership and profits. Accurate knowledge helps optimize capital allocation, tax benefits, and long-term asset appreciation. This distinction impacts contract terms, liability, and exit strategies for all parties involved.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lease to Own | Equity Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Option to buy after lease term | Shared ownership from the start |
| Initial Payment | Security deposit and monthly rent with purchase credit | Down payment plus shared equity contribution |
| Monthly Payments | Rent portion plus option credit | Mortgage payment plus equity partner share |
| Risk | Tenant risks losing option fee if not purchased | Both parties share market appreciation and depreciation |
| Equity Building | Accumulates after purchase | Equity grows jointly during ownership |
| Flexibility | Lease period before committing to buy | Long-term shared investment commitment |
| Best For | Buyers needing time to improve credit or finances | Investors seeking shared property growth |
Which is better?
Lease-to-own models allow tenants to gradually build home equity through monthly payments that combine rent with a portion allocated toward ownership, offering a clear path to full purchase over time. Equity sharing involves investors co-owning the property with residents, sharing both the risks and rewards of appreciation or depreciation, which can reduce upfront costs but complicate future financial decisions. Comparing both, lease-to-own provides more predictable ownership progression, while equity sharing offers flexible capital arrangements suited for those seeking shared investment partnerships.
Connection
Lease to own models and equity sharing intersect by allowing tenants to build ownership stakes through rental payments, which are partially credited toward future purchase of the property. This hybrid approach enables tenants to accumulate equity over time while occupying the property, bridging the gap between renting and buying. Real estate investors leverage these models to attract long-term occupants and create shared financial interests in property value appreciation.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Equity sharing involves multiple parties owning a percentage of the property, aligning financial interests and risks among co-owners, while lease-to-own models grant occupants the right to lease with an option to purchase later, retaining ownership with the original landlord until the option is exercised. Equity sharing commonly requires joint decision-making and shared equity appreciation or depreciation, contrasting with lease-to-own's fixed lease terms and potential purchase price agreements. Explore detailed comparisons of ownership structures to determine which model suits your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Down Payment
Equity sharing models typically require a lower down payment compared to traditional home purchases, as buyers and investors jointly share the property equity. Lease-to-own agreements often involve an upfront option fee or rent premium that functions like a down payment, making home entry more accessible for those without substantial savings. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which model best suits your financial situation and homeownership goals.
Rent Credits
Equity sharing models allow tenants to accumulate rent credits that contribute directly toward homeownership by converting a portion of their rent into equity in the property. Lease to own agreements typically offer rent credits that can be applied to the purchase price, enabling tenants to build a financial stake over time. Explore the differences in rent credit allocation and benefits to determine which model best suits your path to homeownership.
Source and External Links
Equity Sharing - Collins Law Corporation - Equity sharing is a home ownership arrangement where parties share ownership and benefits, often involving investors providing down payments and residents covering expenses.
Equity Sharing - Wikipedia - Equity sharing involves multiple owners of a property, blending ownership to maximize profit and tax benefits, often with investors providing funding in exchange for equity stakes.
Shared Equity Housing | NeighborWorks America - Shared equity housing models create affordable homes, build family wealth, and foster community involvement by limiting home sale prices and sharing appreciation gains.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com