Upzoning increases allowable building density across broader areas, promoting urban growth and affordable housing development. Spot zoning targets specific parcels for zoning changes, often benefiting individual property owners but raising concerns about fairness and planning consistency. Discover the impacts of these zoning practices on real estate markets and community development.
Why it is important
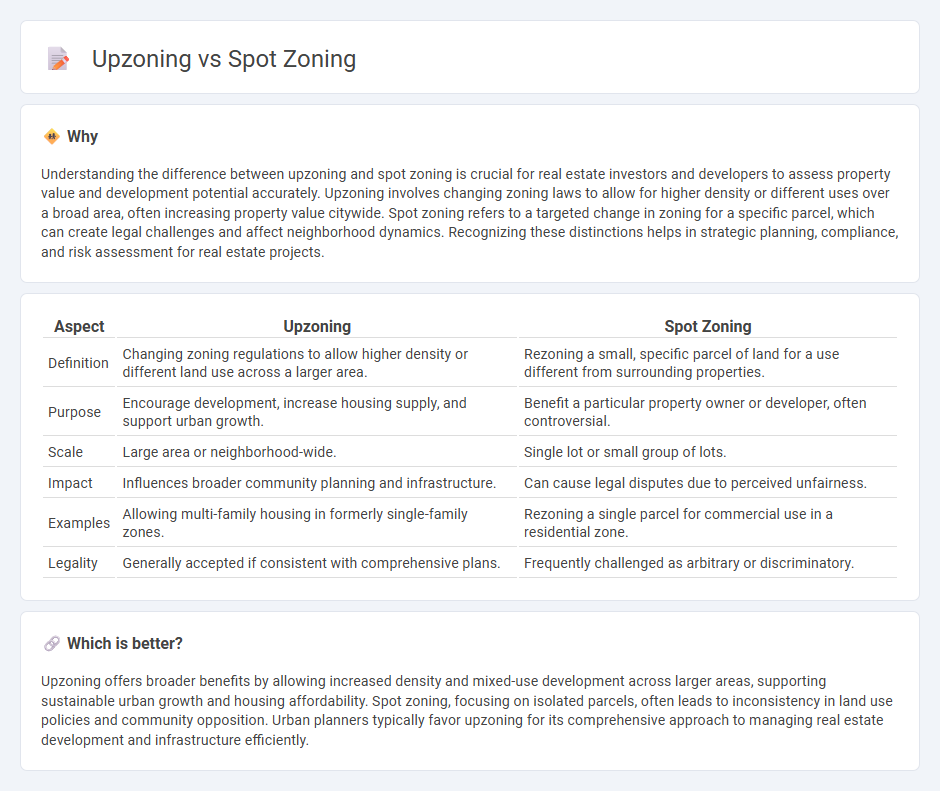
Understanding the difference between upzoning and spot zoning is crucial for real estate investors and developers to assess property value and development potential accurately. Upzoning involves changing zoning laws to allow for higher density or different uses over a broad area, often increasing property value citywide. Spot zoning refers to a targeted change in zoning for a specific parcel, which can create legal challenges and affect neighborhood dynamics. Recognizing these distinctions helps in strategic planning, compliance, and risk assessment for real estate projects.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Upzoning | Spot Zoning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changing zoning regulations to allow higher density or different land use across a larger area. | Rezoning a small, specific parcel of land for a use different from surrounding properties. |
| Purpose | Encourage development, increase housing supply, and support urban growth. | Benefit a particular property owner or developer, often controversial. |
| Scale | Large area or neighborhood-wide. | Single lot or small group of lots. |
| Impact | Influences broader community planning and infrastructure. | Can cause legal disputes due to perceived unfairness. |
| Examples | Allowing multi-family housing in formerly single-family zones. | Rezoning a single parcel for commercial use in a residential zone. |
| Legality | Generally accepted if consistent with comprehensive plans. | Frequently challenged as arbitrary or discriminatory. |
Which is better?
Upzoning offers broader benefits by allowing increased density and mixed-use development across larger areas, supporting sustainable urban growth and housing affordability. Spot zoning, focusing on isolated parcels, often leads to inconsistency in land use policies and community opposition. Urban planners typically favor upzoning for its comprehensive approach to managing real estate development and infrastructure efficiently.
Connection
Upzoning and spot zoning both involve changes to land use regulations that affect property development potential, with upzoning generally increasing allowable density or building height across a broader area. Spot zoning occurs when a small parcel of land is rezoned differently from surrounding properties, often creating conflicts or special exceptions within a community. These zoning practices influence real estate values by altering development opportunities and can lead to legal challenges based on fairness and planning consistency.
Key Terms
Land Use
Spot zoning refers to the practice of singling out a small parcel of land within a larger zoning area for a use that is inconsistent with the surrounding properties, potentially disrupting the planned land use pattern. Upzoning involves changing the zoning regulations to allow for higher density or more intensive land uses, often to promote urban development or accommodate population growth. Explore the implications and regulatory considerations of spot zoning versus upzoning to better understand their impact on land use planning.
Density
Spot zoning involves changing zoning laws for a specific parcel, often creating density inconsistencies with surrounding areas, while upzoning increases allowable building density across broader zones to promote urban growth. Spot zoning can lead to controversial density spikes, whereas upzoning supports planned density increases that align with city-wide development goals. Explore detailed impacts of zoning strategies on urban density to optimize land use and community planning.
Zoning Amendment
Spot zoning refers to the practice of changing zoning laws for a specific parcel of land in a way that differs from the surrounding area, often favoring private interests and raising legal concerns. Upzoning involves amending zoning regulations to allow for increased density or more intensive land use, promoting urban growth and development. Explore detailed distinctions and case studies to understand how zoning amendments impact urban planning and community dynamics.
Source and External Links
Spot zoning - Wikipedia - Spot zoning occurs when a city applies a different zoning classification to a specific parcel within a larger area, usually providing unjustified benefits to one property owner while conflicting with the city's master plan and potentially harming neighboring properties.
spot zoning | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - Spot zoning happens when special zoning laws are applied to certain properties (or a group of properties) that differ from those around them, sometimes allowing controversial or potentially illegal advantages to particular owners, and its legality depends on local ordinances and the public interest.
SPOT ZONING - Land Use and Sustainable Development Law Clinic - Spot zoning is the process of reclassifying a parcel (or parcels) for a land use inconsistent with and less restrictive than the surrounding area, often to benefit a specific property owner, which can be challenged if it works against the public interest and comprehensive planning.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com