Adaptive reuse transforms obsolete buildings into functional spaces by preserving structural elements and integrating modern designs, enhancing sustainability and cultural value. Renovation focuses on upgrading existing structures to improve comfort, aesthetics, and market value, often involving repairs and modernization within the original framework. Discover how these approaches reshape real estate development by balancing innovation and preservation.
Why it is important
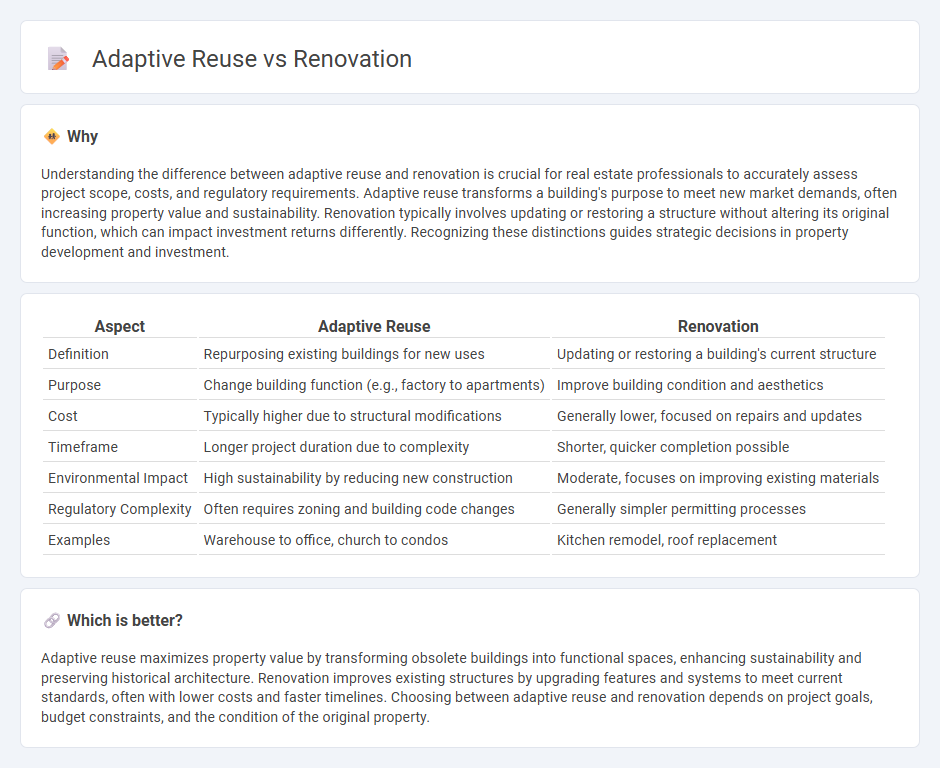
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse and renovation is crucial for real estate professionals to accurately assess project scope, costs, and regulatory requirements. Adaptive reuse transforms a building's purpose to meet new market demands, often increasing property value and sustainability. Renovation typically involves updating or restoring a structure without altering its original function, which can impact investment returns differently. Recognizing these distinctions guides strategic decisions in property development and investment.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse | Renovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses | Updating or restoring a building's current structure |
| Purpose | Change building function (e.g., factory to apartments) | Improve building condition and aesthetics |
| Cost | Typically higher due to structural modifications | Generally lower, focused on repairs and updates |
| Timeframe | Longer project duration due to complexity | Shorter, quicker completion possible |
| Environmental Impact | High sustainability by reducing new construction | Moderate, focuses on improving existing materials |
| Regulatory Complexity | Often requires zoning and building code changes | Generally simpler permitting processes |
| Examples | Warehouse to office, church to condos | Kitchen remodel, roof replacement |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse maximizes property value by transforming obsolete buildings into functional spaces, enhancing sustainability and preserving historical architecture. Renovation improves existing structures by upgrading features and systems to meet current standards, often with lower costs and faster timelines. Choosing between adaptive reuse and renovation depends on project goals, budget constraints, and the condition of the original property.
Connection
Adaptive reuse and renovation are interconnected in real estate as both involve transforming existing structures to meet new purposes or modern standards, enhancing property value and sustainability. Adaptive reuse focuses on repurposing buildings for different functions while renovation improves or restores current features without changing the building's fundamental use. Together, they optimize asset utilization, reduce construction waste, and preserve architectural heritage within urban development.
Key Terms
Retrofit
Renovation involves updating existing structures to improve functionality and aesthetics, while adaptive reuse transforms buildings for new purposes beyond their original design. Retrofit, a key aspect of both processes, enhances energy efficiency and structural performance through upgrades like insulation, HVAC improvements, and seismic reinforcement. Explore detailed strategies and benefits of retrofit to optimize building sustainability and value.
Historic Preservation
Renovation in historic preservation involves updating and repairing existing structures to restore their original appearance and function, often adhering to strict guidelines to maintain architectural integrity. Adaptive reuse, by contrast, transforms historic buildings for new purposes, balancing preservation with modern functionality to ensure sustainable use while retaining significant heritage elements. Explore more about how these approaches safeguard cultural value and extend the life of historic landmarks.
Zoning Compliance
Renovation projects must strictly adhere to existing zoning regulations, often requiring modifications to meet current standards for land use, building height, and density. Adaptive reuse projects leverage zoning flexibility, allowing for creative repurposing of structures while complying with zoning variances or overlays that encourage historic preservation and sustainability. Explore how zoning compliance influences the feasibility and design strategies of renovation versus adaptive reuse projects.
Source and External Links
Renovation - The process of improving broken, damaged, or outdated structures, typically involving several phases from project initiation to finalization.
Renovate vs. Remodel - Explains the differences between renovating and remodeling, including scope, cost, and complexity of projects.
Renovation vs. Remodel - Discusses how renovations are typically smaller, less expensive projects, while remodels involve major changes requiring professional assistance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com