Industrial Internet integrates advanced sensors and data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Lean Manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and improving workflow efficiency through continuous improvement and value stream mapping. Explore how these methodologies transform production efficiency and drive innovation in the manufacturing sector.
Why it is important
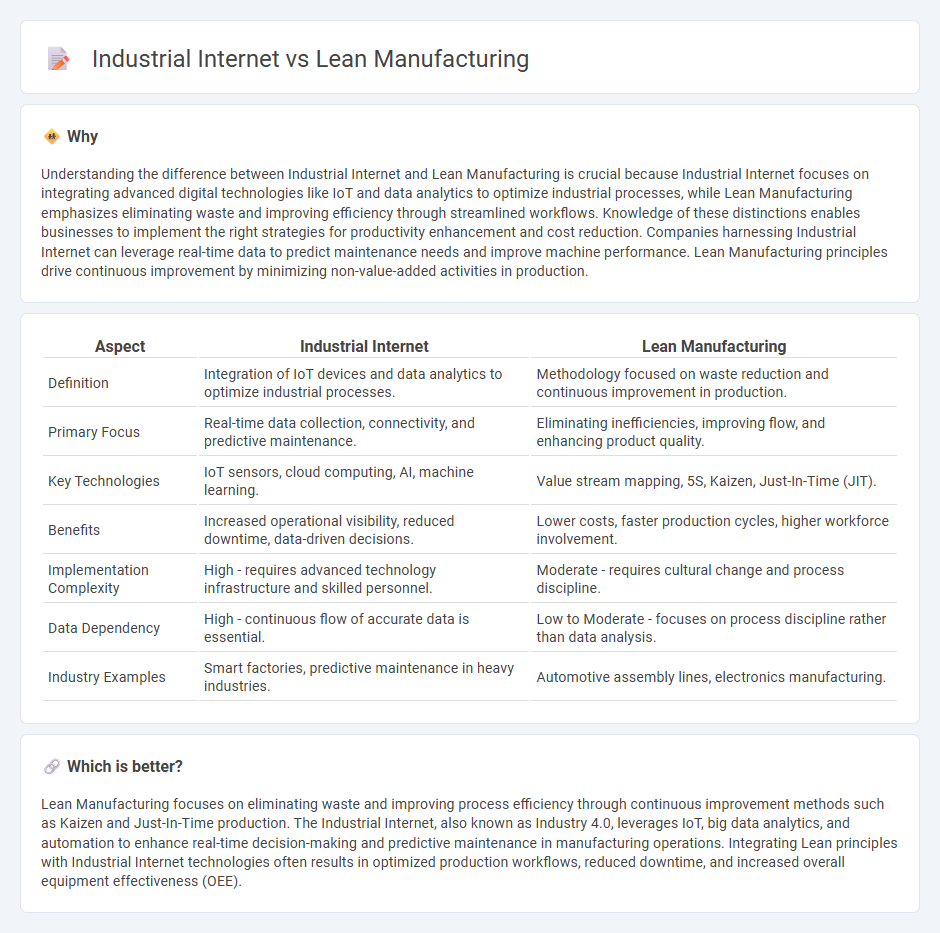
Understanding the difference between Industrial Internet and Lean Manufacturing is crucial because Industrial Internet focuses on integrating advanced digital technologies like IoT and data analytics to optimize industrial processes, while Lean Manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste and improving efficiency through streamlined workflows. Knowledge of these distinctions enables businesses to implement the right strategies for productivity enhancement and cost reduction. Companies harnessing Industrial Internet can leverage real-time data to predict maintenance needs and improve machine performance. Lean Manufacturing principles drive continuous improvement by minimizing non-value-added activities in production.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Internet | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of IoT devices and data analytics to optimize industrial processes. | Methodology focused on waste reduction and continuous improvement in production. |
| Primary Focus | Real-time data collection, connectivity, and predictive maintenance. | Eliminating inefficiencies, improving flow, and enhancing product quality. |
| Key Technologies | IoT sensors, cloud computing, AI, machine learning. | Value stream mapping, 5S, Kaizen, Just-In-Time (JIT). |
| Benefits | Increased operational visibility, reduced downtime, data-driven decisions. | Lower costs, faster production cycles, higher workforce involvement. |
| Implementation Complexity | High - requires advanced technology infrastructure and skilled personnel. | Moderate - requires cultural change and process discipline. |
| Data Dependency | High - continuous flow of accurate data is essential. | Low to Moderate - focuses on process discipline rather than data analysis. |
| Industry Examples | Smart factories, predictive maintenance in heavy industries. | Automotive assembly lines, electronics manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and improving process efficiency through continuous improvement methods such as Kaizen and Just-In-Time production. The Industrial Internet, also known as Industry 4.0, leverages IoT, big data analytics, and automation to enhance real-time decision-making and predictive maintenance in manufacturing operations. Integrating Lean principles with Industrial Internet technologies often results in optimized production workflows, reduced downtime, and increased overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Connection
The Industrial Internet integrates IoT sensors and real-time data analytics within manufacturing processes to enhance productivity and reduce downtime. Lean Manufacturing principles leverage this connected data to identify waste, streamline workflows, and optimize resource utilization efficiently. Together, they create a data-driven environment that accelerates continuous improvement and operational excellence in industrial production.
Key Terms
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) in Lean Manufacturing identifies and eliminates waste within production processes, enhancing operational efficiency by visualizing material and information flows. The Industrial Internet integrates real-time data, IoT sensors, and advanced analytics into VSM to provide dynamic insights, enabling proactive decision-making and continuous improvement. Explore how combining Lean VSM with Industrial Internet technologies drives superior value creation and process optimization.
IoT Sensors
Lean Manufacturing enhances operational efficiency by minimizing waste and optimizing processes, while the Industrial Internet leverages IoT sensors to enable real-time data collection and predictive maintenance. IoT sensors provide critical insights into equipment performance, environmental conditions, and supply chain status, driving smarter decision-making in industrial settings. Explore how integrating Lean Manufacturing with IoT sensors revolutionizes production systems for maximum productivity and reduced downtime.
Continuous Improvement
Lean Manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process optimization through continuous improvement techniques like Kaizen and value stream mapping, enhancing operational efficiency on the factory floor. The Industrial Internet integrates real-time data analytics and IoT sensors to monitor machines and workflows, enabling predictive maintenance and rapid feedback loops for continuous improvement. Explore how combining Lean principles with Industrial Internet technologies can drive smarter manufacturing processes and boost overall productivity.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production and supplier response times, closely linked to just-in-time manufacturing, emphasizing eliminating seven types of waste to improve efficiency and value for customers, originally developed as the Toyota Production System.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology aimed at minimizing waste and maximizing productivity based on Toyota's system, bringing benefits like reduced lead times, lower costs, and improved quality through principles such as continuous improvement (Kaizen).
What is Lean Manufacturing? - Planview - Lean manufacturing applies Lean principles and tools to physical product development, focusing on waste elimination and sustainable value delivery through methods like value stream mapping, pull systems, continuous improvement, and performance visualization.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com