Cold chain management ensures the integrity of temperature-sensitive products through controlled storage and transportation, preventing spoilage and maintaining quality in pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals. Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient return, recycling, and disposal of goods, optimizing sustainability and cost-effectiveness in supply chains. Discover how these critical logistics strategies enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cold chain management and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and product integrity. Cold chain management focuses on maintaining temperature-sensitive goods from production to delivery, ensuring quality and safety. Reverse logistics involves the process of returning, recycling, or disposing of products, which helps reduce waste and recover value. Properly distinguishing these logistics types supports compliance with industry regulations and enhances customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Management | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
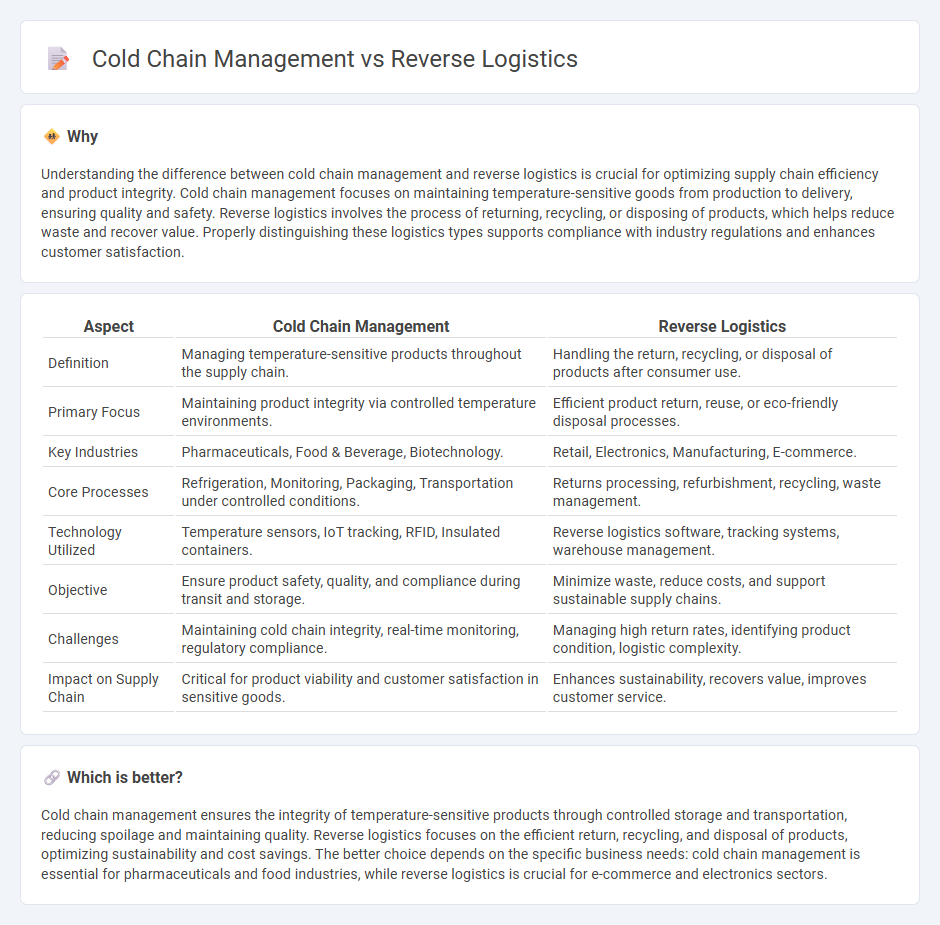
| Definition | Managing temperature-sensitive products throughout the supply chain. | Handling the return, recycling, or disposal of products after consumer use. |
| Primary Focus | Maintaining product integrity via controlled temperature environments. | Efficient product return, reuse, or eco-friendly disposal processes. |
| Key Industries | Pharmaceuticals, Food & Beverage, Biotechnology. | Retail, Electronics, Manufacturing, E-commerce. |
| Core Processes | Refrigeration, Monitoring, Packaging, Transportation under controlled conditions. | Returns processing, refurbishment, recycling, waste management. |
| Technology Utilized | Temperature sensors, IoT tracking, RFID, Insulated containers. | Reverse logistics software, tracking systems, warehouse management. |
| Objective | Ensure product safety, quality, and compliance during transit and storage. | Minimize waste, reduce costs, and support sustainable supply chains. |
| Challenges | Maintaining cold chain integrity, real-time monitoring, regulatory compliance. | Managing high return rates, identifying product condition, logistic complexity. |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Critical for product viability and customer satisfaction in sensitive goods. | Enhances sustainability, recovers value, improves customer service. |
Which is better?
Cold chain management ensures the integrity of temperature-sensitive products through controlled storage and transportation, reducing spoilage and maintaining quality. Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient return, recycling, and disposal of products, optimizing sustainability and cost savings. The better choice depends on the specific business needs: cold chain management is essential for pharmaceuticals and food industries, while reverse logistics is crucial for e-commerce and electronics sectors.
Connection
Cold chain management ensures the temperature-sensitive goods maintain optimal conditions from origin to delivery, preventing spoilage and quality loss. Reverse logistics involves the efficient return, recycling, or disposal of products, including spoiled or expired items from the cold chain. Integrating cold chain management with reverse logistics minimizes waste, enhances sustainability, and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
Key Terms
**Reverse Logistics:**
Reverse logistics involves the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or distributor for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal, emphasizing cost reduction and sustainability. It manages product returns, remanufacturing, refurbishing, and waste management while optimizing transportation and storage to minimize environmental impact. Explore how reverse logistics enhances supply chain efficiency and supports circular economy initiatives.
Returns Processing
Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient handling of product returns, refurbishments, and recycling to minimize waste and recover value, while cold chain management ensures temperature-sensitive goods are stored and transported within strict thermal guidelines to maintain product integrity. Returns processing in reverse logistics involves inspecting, sorting, and restocking or disposing of returned items, a process that requires close coordination with cold chain protocols to prevent spoilage of perishable goods. Explore our detailed analysis to understand the critical differences and overlaps between reverse logistics and cold chain management in returns processing.
Refurbishment
Reverse logistics in refurbishment involves the collection, inspection, and reconditioning of used products to restore them for resale or reuse, optimizing resource efficiency and reducing waste. Cold chain management ensures temperature-sensitive goods remain within required cold storage conditions during reverse logistics processes, preserving quality and safety. Explore how integrating reverse logistics and cold chain management enhances refurbishment outcomes and sustainability.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or distributor for return, repair, remanufacture, recycling, or disposal, aimed at recapturing value and enhancing supply chain efficiency through lean principles.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics manages returns and surplus goods, involving processes like return authorization, transportation planning, and refurbishment across various industries to reduce waste and recover value.
Reverse logistics - Wikipedia - Reverse logistics involves the upstream movement of goods for value recovery or proper disposal, including remanufacturing and refurbishing, and it represents a growing global market with increased focus on sustainability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com