Quick commerce focuses on delivering products within minutes using centralized micro-fulfillment centers to ensure rapid order processing and last-mile execution. Hyperlocal delivery emphasizes serving customers within a specific geographic area by leveraging nearby stores and local couriers to reduce delivery time and enhance customer experience. Explore the nuances and operational advantages of both models to optimize your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
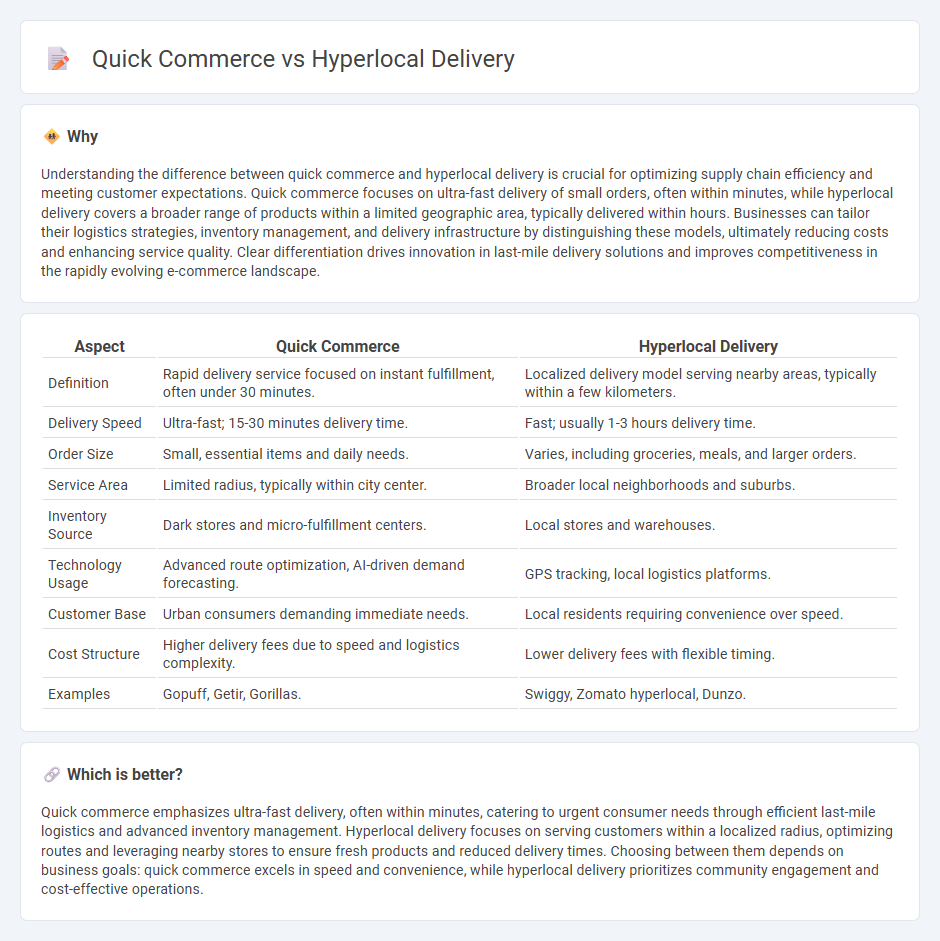
Understanding the difference between quick commerce and hyperlocal delivery is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting customer expectations. Quick commerce focuses on ultra-fast delivery of small orders, often within minutes, while hyperlocal delivery covers a broader range of products within a limited geographic area, typically delivered within hours. Businesses can tailor their logistics strategies, inventory management, and delivery infrastructure by distinguishing these models, ultimately reducing costs and enhancing service quality. Clear differentiation drives innovation in last-mile delivery solutions and improves competitiveness in the rapidly evolving e-commerce landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quick Commerce | Hyperlocal Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid delivery service focused on instant fulfillment, often under 30 minutes. | Localized delivery model serving nearby areas, typically within a few kilometers. |
| Delivery Speed | Ultra-fast; 15-30 minutes delivery time. | Fast; usually 1-3 hours delivery time. |
| Order Size | Small, essential items and daily needs. | Varies, including groceries, meals, and larger orders. |
| Service Area | Limited radius, typically within city center. | Broader local neighborhoods and suburbs. |
| Inventory Source | Dark stores and micro-fulfillment centers. | Local stores and warehouses. |
| Technology Usage | Advanced route optimization, AI-driven demand forecasting. | GPS tracking, local logistics platforms. |
| Customer Base | Urban consumers demanding immediate needs. | Local residents requiring convenience over speed. |
| Cost Structure | Higher delivery fees due to speed and logistics complexity. | Lower delivery fees with flexible timing. |
| Examples | Gopuff, Getir, Gorillas. | Swiggy, Zomato hyperlocal, Dunzo. |
Which is better?
Quick commerce emphasizes ultra-fast delivery, often within minutes, catering to urgent consumer needs through efficient last-mile logistics and advanced inventory management. Hyperlocal delivery focuses on serving customers within a localized radius, optimizing routes and leveraging nearby stores to ensure fresh products and reduced delivery times. Choosing between them depends on business goals: quick commerce excels in speed and convenience, while hyperlocal delivery prioritizes community engagement and cost-effective operations.
Connection
Quick commerce relies heavily on hyperlocal delivery to fulfill orders within minutes by sourcing products from nearby stores, reducing transportation time and costs. Hyperlocal delivery networks optimize last-mile logistics through advanced route planning and real-time tracking, ensuring rapid and reliable order fulfillment. This synergy enhances customer satisfaction and drives efficiency in urban e-commerce ecosystems.
Key Terms
Last-Mile Fulfillment
Hyperlocal delivery specializes in sourcing and delivering products within a limited geographic area, ensuring faster local order fulfillment and reduced delivery times. Quick commerce, or q-commerce, emphasizes ultra-fast delivery often within 30 minutes, leveraging advanced logistics, dark stores, and real-time inventory systems for immediate last-mile fulfillment. Explore more to understand how these models revolutionize urban logistics and customer experience.
Dark Stores
Dark stores serve as essential hubs in both hyperlocal delivery and quick commerce models, optimizing inventory management and reducing delivery times by locating products closer to consumers. These fulfillment centers leverage advanced logistics and data analytics to ensure rapid order processing, catering to the growing demand for immediate product availability. Explore how dark stores are revolutionizing urban retail and transforming customer expectations for speed and convenience.
Order Aggregation
Order aggregation in hyperlocal delivery consolidates multiple customer orders from a specific geographic area, optimizing delivery routes and reducing costs while maintaining speed and freshness. In quick commerce, order aggregation is less common due to the emphasis on ultra-fast, often single-item deliveries within minutes, prioritizing speed over batch processing. Explore how different aggregation strategies impact delivery efficiency and customer satisfaction in these evolving retail models.
Source and External Links
Hyperlocal Delivery for the Hyperconnected Consumer - Hyperlocal delivery is a logistics model that facilitates fast home delivery of products from local businesses, often within the same neighborhood or city.
Hyperlocal Delivery Model and How Does it Work - This delivery model emphasizes rapid delivery, typically within 45 minutes to 4 hours, and utilizes technology for efficient order tracking and management.
Hyperlocal Delivery - Hyperlocal delivery boosts opportunities for local vendors by providing them with a wider customer base and improved flexibility for customers through customizable delivery options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com