Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods maintain strict environmental controls throughout transportation, preserving quality and safety. Intermodal transport combines multiple modes of transportation, such as rail, truck, and sea, to optimize efficiency and reduce costs in the supply chain. Explore the advantages and applications of cold chain and intermodal transport to enhance your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
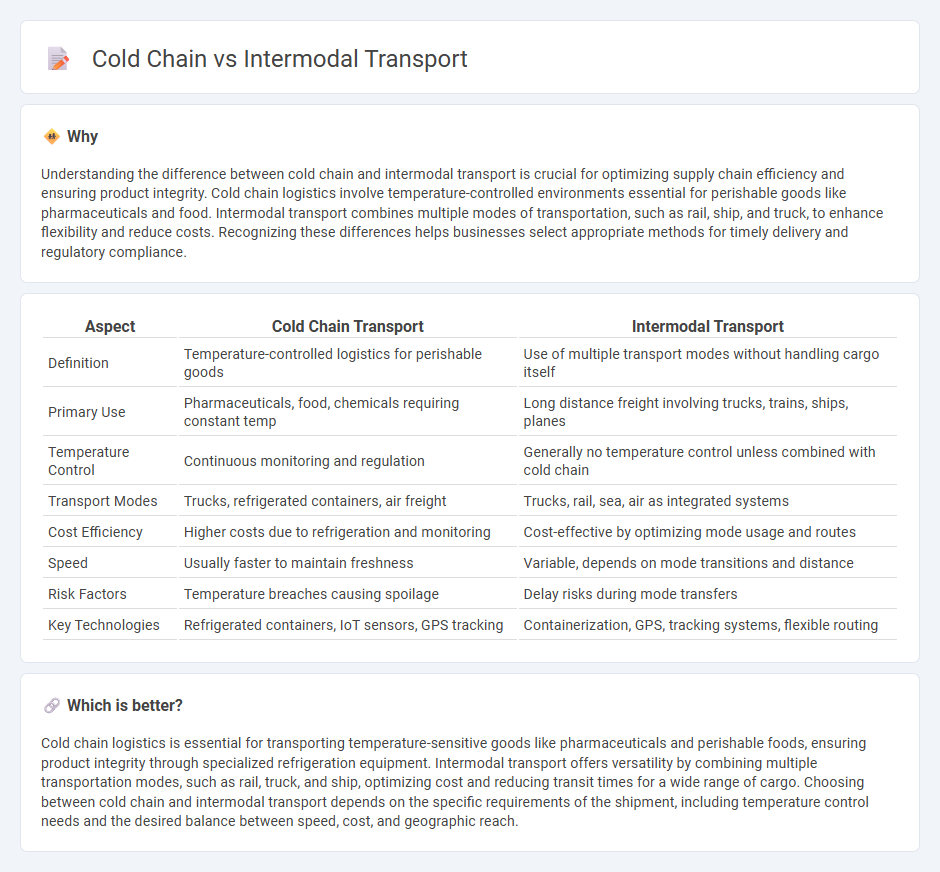
Understanding the difference between cold chain and intermodal transport is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and ensuring product integrity. Cold chain logistics involve temperature-controlled environments essential for perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food. Intermodal transport combines multiple modes of transportation, such as rail, ship, and truck, to enhance flexibility and reduce costs. Recognizing these differences helps businesses select appropriate methods for timely delivery and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Transport | Intermodal Transport |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled logistics for perishable goods | Use of multiple transport modes without handling cargo itself |
| Primary Use | Pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals requiring constant temp | Long distance freight involving trucks, trains, ships, planes |
| Temperature Control | Continuous monitoring and regulation | Generally no temperature control unless combined with cold chain |
| Transport Modes | Trucks, refrigerated containers, air freight | Trucks, rail, sea, air as integrated systems |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher costs due to refrigeration and monitoring | Cost-effective by optimizing mode usage and routes |
| Speed | Usually faster to maintain freshness | Variable, depends on mode transitions and distance |
| Risk Factors | Temperature breaches causing spoilage | Delay risks during mode transfers |
| Key Technologies | Refrigerated containers, IoT sensors, GPS tracking | Containerization, GPS, tracking systems, flexible routing |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics is essential for transporting temperature-sensitive goods like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods, ensuring product integrity through specialized refrigeration equipment. Intermodal transport offers versatility by combining multiple transportation modes, such as rail, truck, and ship, optimizing cost and reducing transit times for a wide range of cargo. Choosing between cold chain and intermodal transport depends on the specific requirements of the shipment, including temperature control needs and the desired balance between speed, cost, and geographic reach.
Connection
Cold chain logistics rely heavily on intermodal transport to maintain temperature-sensitive goods' integrity across various transit points, combining refrigerated trucks, rail cars, and shipping containers. Utilizing seamless transfers between transportation modes minimizes spoilage risk by ensuring consistent temperature control throughout the supply chain. Efficient coordination between cold storage equipment and intermodal infrastructure enhances product quality for pharmaceuticals, perishable foods, and other temperature-sensitive commodities.
Key Terms
Intermodal Transport:
Intermodal transport involves moving goods using multiple modes of transportation, such as rail, truck, and ship, optimizing efficiency and minimizing logistics costs. This approach enhances supply chain flexibility, reduces transit times, and lowers carbon emissions compared to single-mode transport. Discover how intermodal transport can revolutionize your logistics strategy by exploring detailed benefits and implementation techniques.
Containerization
Intermodal transport leverages containerization to facilitate seamless transfer of goods across multiple transportation modes, enhancing efficiency and reducing handling risks. In cold chain logistics, containerization plays a critical role by maintaining temperature-controlled environments essential for perishable products during transit. Explore the advantages of containerization in optimizing both intermodal transport and cold chain management for your supply chain needs.
Transshipment
Intermodal transport integrates multiple modes of transportation, improving efficiency in moving goods, while cold chain emphasizes temperature-controlled handling critical for perishable items during storage and transit. Transshipment plays a pivotal role in both systems, enabling seamless transfer of cargo between vehicles without compromising temperature integrity in cold chain logistics. Discover how optimized transshipment techniques enhance reliability and reduce spoilage in global supply chains.
Source and External Links
What Is Intermodal Transportation? History, Benefits, Examples - Intermodal transportation involves moving goods in a steel container using two or more modes of transportation such as ships, rail, aircraft, and trucks, enabling efficient and versatile freight movement internationally and domestically.
Intermodal freight transport - Wikipedia - Intermodal freight transport uses multiple transport modes (rail, ship, truck, aircraft) to move containers without handling the freight itself during transfers, improving security, reducing damage, and lowering costs especially for long-distance shipments.
Intermodal transport: what it is and benefits | Savino Del Bene - It is a method of transporting goods in the same container through two or more transport methods without unloading the cargo, providing a seamless and flexible solution that enhances supply chain efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com