Cold chain traceability ensures the consistent monitoring of temperature-sensitive products during transportation and storage, reducing spoilage risks and maintaining quality. Perishable goods management involves optimizing inventory, handling, and delivery processes to extend shelf life and meet safety standards. Discover how integrating advanced traceability technologies enhances the efficiency of perishable goods management.
Why it is important
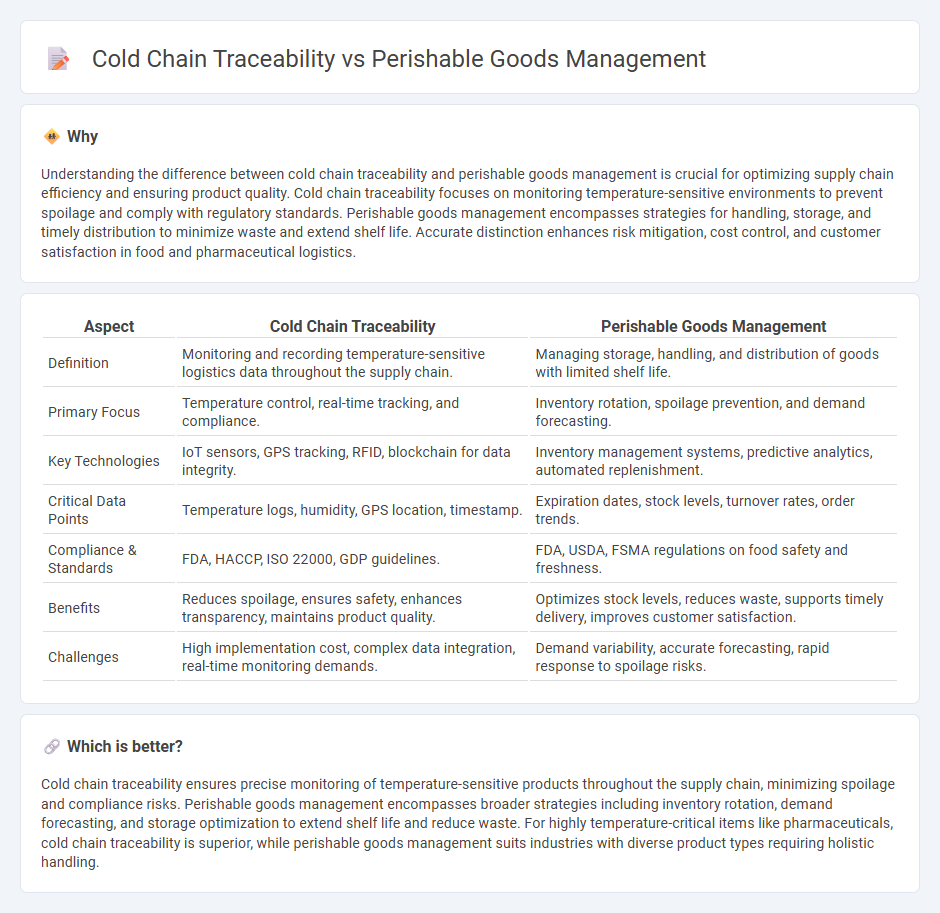
Understanding the difference between cold chain traceability and perishable goods management is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and ensuring product quality. Cold chain traceability focuses on monitoring temperature-sensitive environments to prevent spoilage and comply with regulatory standards. Perishable goods management encompasses strategies for handling, storage, and timely distribution to minimize waste and extend shelf life. Accurate distinction enhances risk mitigation, cost control, and customer satisfaction in food and pharmaceutical logistics.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Traceability | Perishable Goods Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monitoring and recording temperature-sensitive logistics data throughout the supply chain. | Managing storage, handling, and distribution of goods with limited shelf life. |
| Primary Focus | Temperature control, real-time tracking, and compliance. | Inventory rotation, spoilage prevention, and demand forecasting. |
| Key Technologies | IoT sensors, GPS tracking, RFID, blockchain for data integrity. | Inventory management systems, predictive analytics, automated replenishment. |
| Critical Data Points | Temperature logs, humidity, GPS location, timestamp. | Expiration dates, stock levels, turnover rates, order trends. |
| Compliance & Standards | FDA, HACCP, ISO 22000, GDP guidelines. | FDA, USDA, FSMA regulations on food safety and freshness. |
| Benefits | Reduces spoilage, ensures safety, enhances transparency, maintains product quality. | Optimizes stock levels, reduces waste, supports timely delivery, improves customer satisfaction. |
| Challenges | High implementation cost, complex data integration, real-time monitoring demands. | Demand variability, accurate forecasting, rapid response to spoilage risks. |
Which is better?
Cold chain traceability ensures precise monitoring of temperature-sensitive products throughout the supply chain, minimizing spoilage and compliance risks. Perishable goods management encompasses broader strategies including inventory rotation, demand forecasting, and storage optimization to extend shelf life and reduce waste. For highly temperature-critical items like pharmaceuticals, cold chain traceability is superior, while perishable goods management suits industries with diverse product types requiring holistic handling.
Connection
Cold chain traceability ensures real-time monitoring of temperature-sensitive perishable goods, maintaining product quality from origin to destination. Effective perishable goods management relies on detailed cold chain data to prevent spoilage, reduce waste, and comply with safety regulations. Integrating IoT sensors and blockchain technology enhances transparency and accountability throughout the cold supply chain.
Key Terms
**Perishable goods management:**
Perishable goods management involves overseeing the storage, transportation, and handling of items such as fresh produce, dairy, and pharmaceuticals to minimize spoilage and ensure safety. Effective temperature control, inventory rotation, and real-time monitoring are critical components to extend shelf life and reduce waste. Discover more about advanced strategies and technologies enhancing perishable goods management.
Shelf life
Effective perishable goods management relies heavily on controlling temperature and humidity to extend shelf life, reducing spoilage and waste. Cold chain traceability enhances this process by providing real-time data monitoring, ensuring optimal storage conditions throughout the supply chain. Explore how integrating advanced cold chain technologies can revolutionize your perishable goods management and maximize shelf life.
FIFO (First In, First Out)
Perishable goods management demands strict adherence to FIFO (First In, First Out) principles to minimize spoilage and ensure product freshness. Cold chain traceability enhances FIFO implementation by providing real-time monitoring of temperature and handling conditions throughout the supply chain. Explore advanced cold chain solutions to optimize FIFO processes and reduce waste effectively.
Source and External Links
Perishability and Freshness Management in Supply Chain - Umbrex - Focuses on improving inventory management and logistics for perishable goods, emphasizing cold chain maintenance, monitoring inventory turnover, transportation lead times, temperature control, and aligning delivery schedules with demand to reduce spoilage and increase efficiency.
Perishable Goods Inventory Management Guide - Unleashed - Recommends best practices such as measuring inventory turnover, strengthening supplier relationships, automating processes, minimizing waste through repurposing or discounts, and maximizing product shelf life with proper packaging and storage conditions.
A Guide to Managing Perishable Inventory - Sortly - Highlights operational procedures for managing perishable inventory, including creating a detailed standard operating procedure (SOP) and implementing the FIFO (first-in, first-out) method to ensure older stock is used or sold first, minimizing waste and spoilage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com