Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on restoring soil health and enhancing ecosystem biodiversity to create long-term environmental and financial benefits. Sustainable forestry investment involves managing forest resources responsibly to ensure continuous timber production while preserving wildlife habitats and reducing carbon footprints. Explore the distinct advantages and impact of each approach to make informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
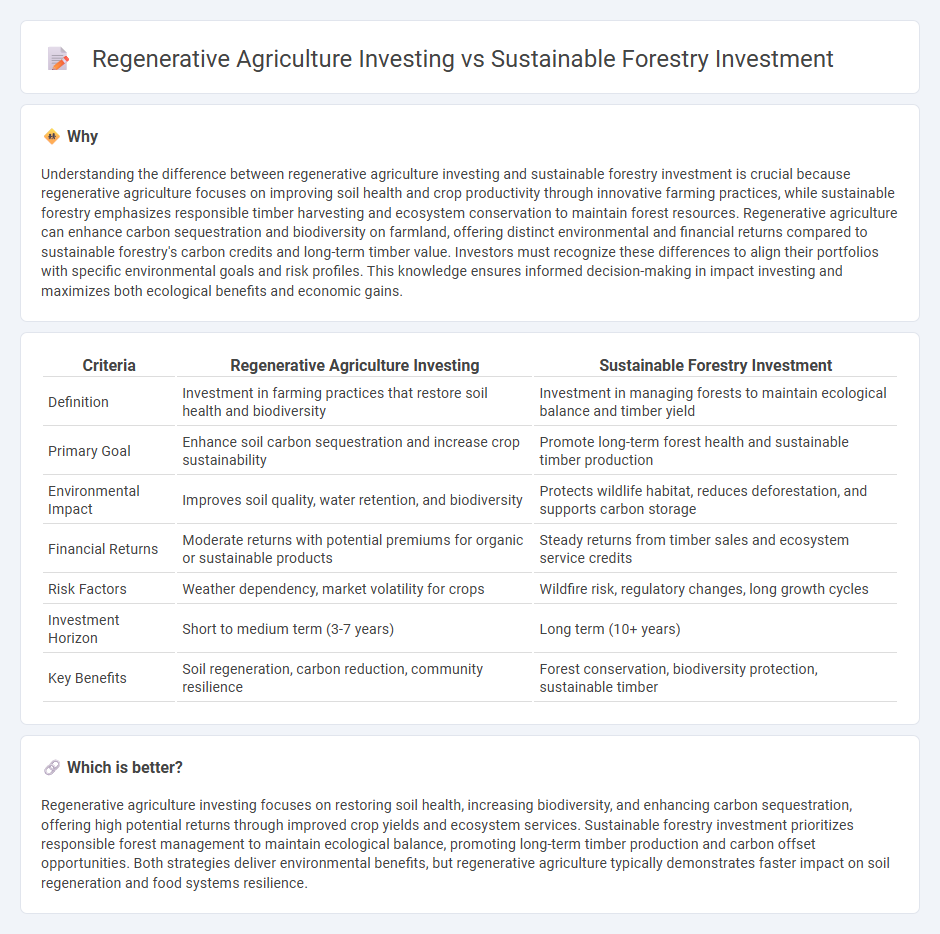
Understanding the difference between regenerative agriculture investing and sustainable forestry investment is crucial because regenerative agriculture focuses on improving soil health and crop productivity through innovative farming practices, while sustainable forestry emphasizes responsible timber harvesting and ecosystem conservation to maintain forest resources. Regenerative agriculture can enhance carbon sequestration and biodiversity on farmland, offering distinct environmental and financial returns compared to sustainable forestry's carbon credits and long-term timber value. Investors must recognize these differences to align their portfolios with specific environmental goals and risk profiles. This knowledge ensures informed decision-making in impact investing and maximizes both ecological benefits and economic gains.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Regenerative Agriculture Investing | Sustainable Forestry Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in farming practices that restore soil health and biodiversity | Investment in managing forests to maintain ecological balance and timber yield |
| Primary Goal | Enhance soil carbon sequestration and increase crop sustainability | Promote long-term forest health and sustainable timber production |
| Environmental Impact | Improves soil quality, water retention, and biodiversity | Protects wildlife habitat, reduces deforestation, and supports carbon storage |
| Financial Returns | Moderate returns with potential premiums for organic or sustainable products | Steady returns from timber sales and ecosystem service credits |
| Risk Factors | Weather dependency, market volatility for crops | Wildfire risk, regulatory changes, long growth cycles |
| Investment Horizon | Short to medium term (3-7 years) | Long term (10+ years) |
| Key Benefits | Soil regeneration, carbon reduction, community resilience | Forest conservation, biodiversity protection, sustainable timber |
Which is better?
Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on restoring soil health, increasing biodiversity, and enhancing carbon sequestration, offering high potential returns through improved crop yields and ecosystem services. Sustainable forestry investment prioritizes responsible forest management to maintain ecological balance, promoting long-term timber production and carbon offset opportunities. Both strategies deliver environmental benefits, but regenerative agriculture typically demonstrates faster impact on soil regeneration and food systems resilience.
Connection
Regenerative agriculture investing and sustainable forestry investment both focus on restoring ecosystems and enhancing carbon sequestration to combat climate change. These investment strategies prioritize long-term soil health and biodiversity, promoting resilient landscapes that support sustainable food systems and timber production. By integrating environmental stewardship with economic returns, they attract impact investors seeking measurable ecological benefits alongside financial growth.
Key Terms
Sustainable forestry investment:
Sustainable forestry investment emphasizes the responsible management of forest resources to ensure long-term ecological balance, enhanced carbon sequestration, and biodiversity preservation. This approach supports economic growth by promoting renewable timber products and maintaining ecosystem services critical for climate resilience. Explore more about the benefits and strategies of sustainable forestry investment to align your portfolio with environmental sustainability goals.
FSC Certification
Sustainable forestry investment, aligned with FSC certification, ensures responsible management of forest resources promoting biodiversity and long-term ecological balance. Regenerative agriculture investing emphasizes soil health and ecosystem restoration, often complementing FSC principles by enhancing carbon sequestration and water retention. Explore how integrating FSC certification into your investment strategy fosters environmental resilience and sustainable returns.
Carbon Sequestration
Sustainable forestry investments enhance carbon sequestration by preserving existing forests and promoting responsible timber harvesting practices, leading to long-term carbon storage in biomass and soil. Regenerative agriculture investing focuses on rebuilding soil organic matter and improving biodiversity, which increases carbon capture in agricultural lands and boosts ecosystem resilience. Explore the comparative benefits and methodologies of these investment strategies to make an informed decision on maximizing carbon sequestration impact.
Source and External Links
Climate Initiatives - Exemplary Forestry Investment Fund - The Exemplary Forestry Investment Fund is a for-profit, long-term timber investment focused on acquiring and conserving 100,000 acres of Maine forests, offering returns from conservation easements and carbon credits while ensuring sustainable, climate-positive forest management.
Investing in forestry: A path to sustainable returns - Sustainable forestry investments provide environmental benefits such as carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation, align with ESG criteria, and offer financial returns by meeting growing demand for responsibly sourced forest products.
Forestry Funds: The Emerging Star of Alternative Investments - EY - Forestry funds are gaining traction as resilient, ESG-compliant alternative assets with dual financial and environmental benefits, increasingly favored by investors seeking long-term growth and positive climate impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com