Art flipping and real estate flipping both offer lucrative investment opportunities through buying undervalued assets and reselling at higher prices, yet they differ significantly in market liquidity and capital requirements. Art flipping relies on trends, artist reputation, and auction dynamics, while real estate flipping demands property renovations, local market knowledge, and navigating regulatory processes. Explore these strategies in depth to determine which investment aligns best with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Why it is important
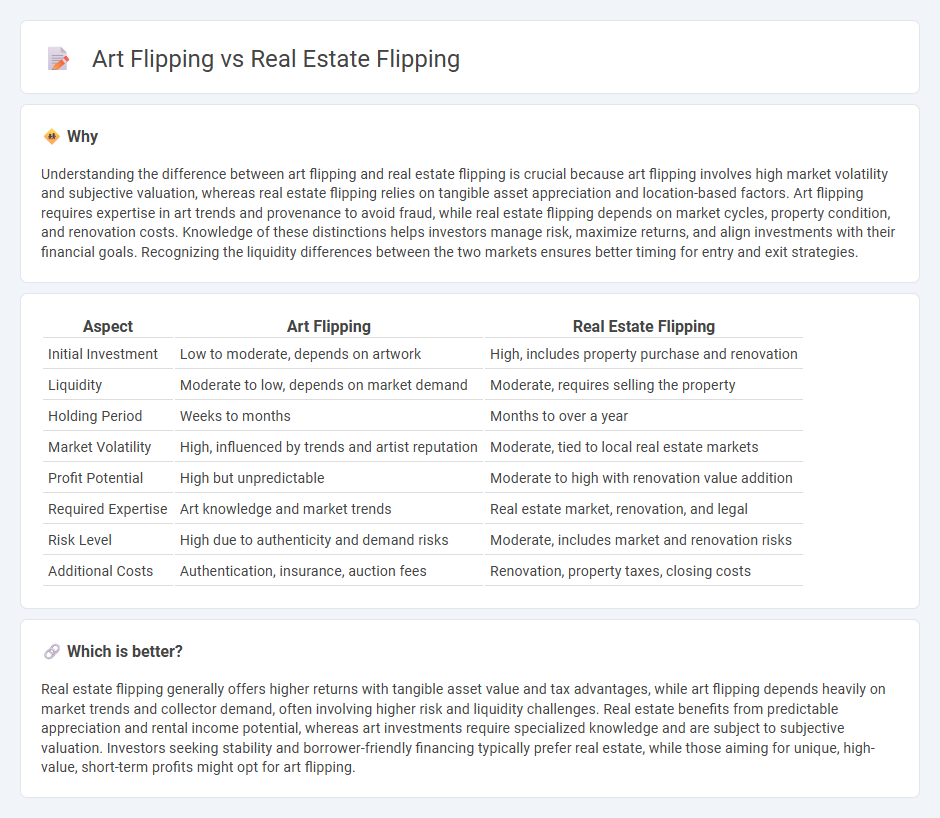
Understanding the difference between art flipping and real estate flipping is crucial because art flipping involves high market volatility and subjective valuation, whereas real estate flipping relies on tangible asset appreciation and location-based factors. Art flipping requires expertise in art trends and provenance to avoid fraud, while real estate flipping depends on market cycles, property condition, and renovation costs. Knowledge of these distinctions helps investors manage risk, maximize returns, and align investments with their financial goals. Recognizing the liquidity differences between the two markets ensures better timing for entry and exit strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Art Flipping | Real Estate Flipping |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low to moderate, depends on artwork | High, includes property purchase and renovation |
| Liquidity | Moderate to low, depends on market demand | Moderate, requires selling the property |
| Holding Period | Weeks to months | Months to over a year |
| Market Volatility | High, influenced by trends and artist reputation | Moderate, tied to local real estate markets |
| Profit Potential | High but unpredictable | Moderate to high with renovation value addition |
| Required Expertise | Art knowledge and market trends | Real estate market, renovation, and legal |
| Risk Level | High due to authenticity and demand risks | Moderate, includes market and renovation risks |
| Additional Costs | Authentication, insurance, auction fees | Renovation, property taxes, closing costs |
Which is better?
Real estate flipping generally offers higher returns with tangible asset value and tax advantages, while art flipping depends heavily on market trends and collector demand, often involving higher risk and liquidity challenges. Real estate benefits from predictable appreciation and rental income potential, whereas art investments require specialized knowledge and are subject to subjective valuation. Investors seeking stability and borrower-friendly financing typically prefer real estate, while those aiming for unique, high-value, short-term profits might opt for art flipping.
Connection
Art flipping and real estate flipping both involve purchasing undervalued assets, enhancing their appeal or condition, and selling them at a profit within a short timeframe. Investors leverage market trends, scarcity, and aesthetic or structural improvements to boost asset value, capitalizing on market demand cycles. Expertise in valuation, timing, and negotiation is crucial in maximizing returns in both flipping strategies.
Key Terms
**Real Estate Flipping:**
Real estate flipping involves purchasing properties at a lower market value, renovating them, and selling at a higher price to generate substantial profits. Key factors for success include location analysis, renovation costs, market trends, and timing the sale to maximize return on investment. Discover more insights on how to effectively navigate the real estate flipping market and boost your investment success.
Renovation
Renovation in real estate flipping involves structural improvements such as repairing foundations, updating electrical systems, and enhancing curb appeal to significantly increase property value. In contrast, art flipping relies on restoration techniques that preserve or enhance artwork integrity, focusing on cleaning, repairing damages, and sometimes reframing to boost market appeal. Explore detailed strategies and key renovation differences in real estate and art flipping to maximize your investment returns.
Market Value
Real estate flipping involves purchasing properties below market value, renovating them, and selling at a higher price to capitalize on increased market demand and location-based appreciation. Art flipping focuses on acquiring artworks with potential for value growth driven by artist reputation, rarity, and market trends within the fine art sector. Explore deeper insights into how market value dynamics influence these investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Flipping - Wikipedia - Real estate flipping is the process where investors buy, rehab, and sell properties quickly for a profit, with 207,088 houses flipped in the US in 2017 representing 5.9% of single-family home sales that year.
What is the 70% rule in house flipping? - Rocket Mortgage - The 70% rule advises investors to pay no more than 70% of a property's after-repair value (ARV) minus repair costs to ensure profitability when flipping homes, although it has limitations like estimation challenges and excluding additional expenses.
Illegal Property Flipping - FBI - Illegal property flipping schemes involve artificially inflating a property's price with minor repairs and using straw buyers and false appraisals to defraud lenders, which is a criminal offense distinct from legal flipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com