Forestry investment offers long-term sustainable returns through the management of timberland assets, benefiting from natural growth cycles and carbon credit opportunities. Private equity focuses on acquiring equity stakes in private companies with potential for high financial gains through active business management and eventual exit strategies. Discover how these distinct investment avenues align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Why it is important
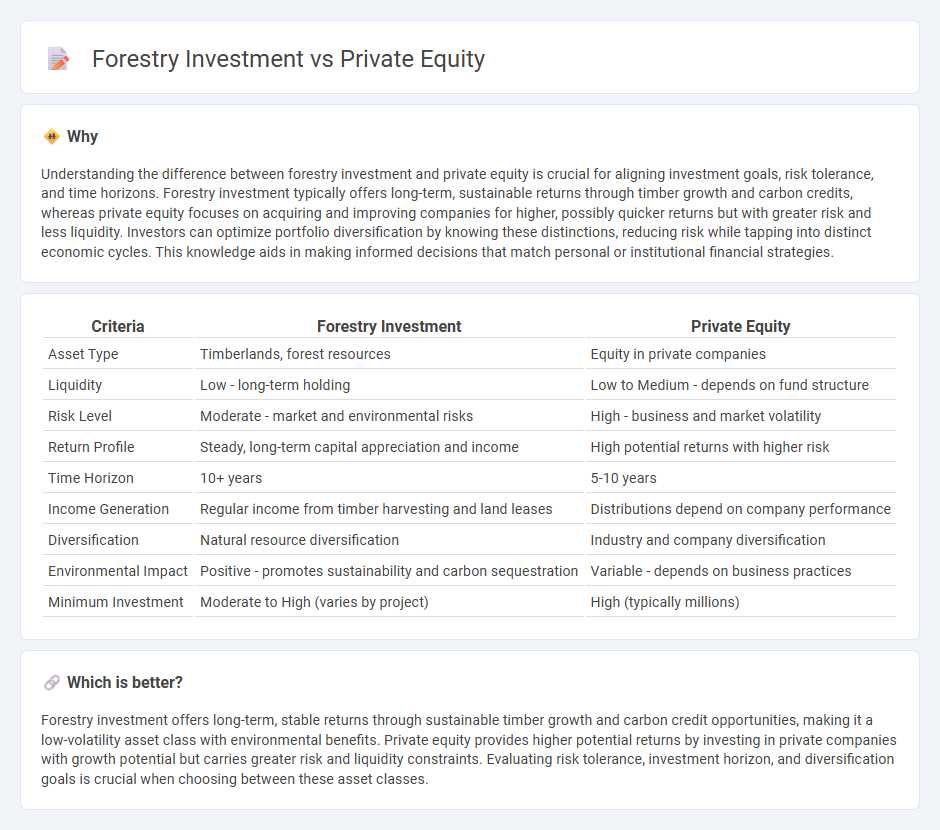
Understanding the difference between forestry investment and private equity is crucial for aligning investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizons. Forestry investment typically offers long-term, sustainable returns through timber growth and carbon credits, whereas private equity focuses on acquiring and improving companies for higher, possibly quicker returns but with greater risk and less liquidity. Investors can optimize portfolio diversification by knowing these distinctions, reducing risk while tapping into distinct economic cycles. This knowledge aids in making informed decisions that match personal or institutional financial strategies.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Forestry Investment | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Timberlands, forest resources | Equity in private companies |
| Liquidity | Low - long-term holding | Low to Medium - depends on fund structure |
| Risk Level | Moderate - market and environmental risks | High - business and market volatility |
| Return Profile | Steady, long-term capital appreciation and income | High potential returns with higher risk |
| Time Horizon | 10+ years | 5-10 years |
| Income Generation | Regular income from timber harvesting and land leases | Distributions depend on company performance |
| Diversification | Natural resource diversification | Industry and company diversification |
| Environmental Impact | Positive - promotes sustainability and carbon sequestration | Variable - depends on business practices |
| Minimum Investment | Moderate to High (varies by project) | High (typically millions) |
Which is better?
Forestry investment offers long-term, stable returns through sustainable timber growth and carbon credit opportunities, making it a low-volatility asset class with environmental benefits. Private equity provides higher potential returns by investing in private companies with growth potential but carries greater risk and liquidity constraints. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and diversification goals is crucial when choosing between these asset classes.
Connection
Forestry investment and private equity intersect through specialized funds that acquire, manage, and develop timberland assets to generate long-term returns. Private equity firms leverage capital to enhance forestry operations, optimizing sustainable timber production and carbon sequestration value. These investments benefit from stable cash flows, portfolio diversification, and increasing global demand for renewable resources.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Private equity investments often involve longer lock-up periods with limited liquidity, as funds are typically committed for five to ten years with restricted secondary market options. In contrast, forestry investments can offer varying liquidity levels depending on the asset type, such as timberland properties or forestry funds, with some providing periodic cash flows from timber sales. Explore detailed comparative data on liquidity profiles to make informed decisions between private equity and forestry investment opportunities.
Return profile
Private equity investments typically offer high potential returns with substantial risk due to market volatility and illiquidity, often yielding annualized returns between 15% to 25%. Forestry investments provide more stable, long-term returns driven by timber growth, carbon credits, and land appreciation, generally ranging from 5% to 8% annually with lower correlation to economic cycles. Explore the detailed return profiles and risk factors to determine which investment aligns best with your financial goals.
Asset management
Private equity asset management centers on active portfolio oversight, leveraging financial restructuring, operational improvements, and strategic exits to maximize returns. Forestry investment asset management prioritizes sustainable growth, carbon sequestration, and long-term yield through ecological stewardship and timber market analysis. Explore detailed strategies and performance metrics to understand the distinct asset management approaches in these sectors.
Source and External Links
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity involves investment in private companies through specialized funds, aiming to generate returns via strategies like revenue growth, margin expansion, and governance restructuring, typically over 4-7 years.
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity is medium to long-term finance given for equity stakes in high-growth unquoted companies, emphasizing active ownership and close collaboration with management to create lasting business value.
Private Equity: What You Need to Know - KKR - Private equity strategies focus on improving unlisted companies by strengthening management, refining strategy, and optimizing operations to drive growth and returns, distinct from public market investments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com