Song catalog purchases involve acquiring the rights to a collection of songs, granting the buyer control over licensing, distribution, and revenue streams. Music royalties, on the other hand, represent ongoing income generated from the public use and performance of individual songs or catalogs. Explore the key differences and investment potential between these two revenue models.
Why it is important
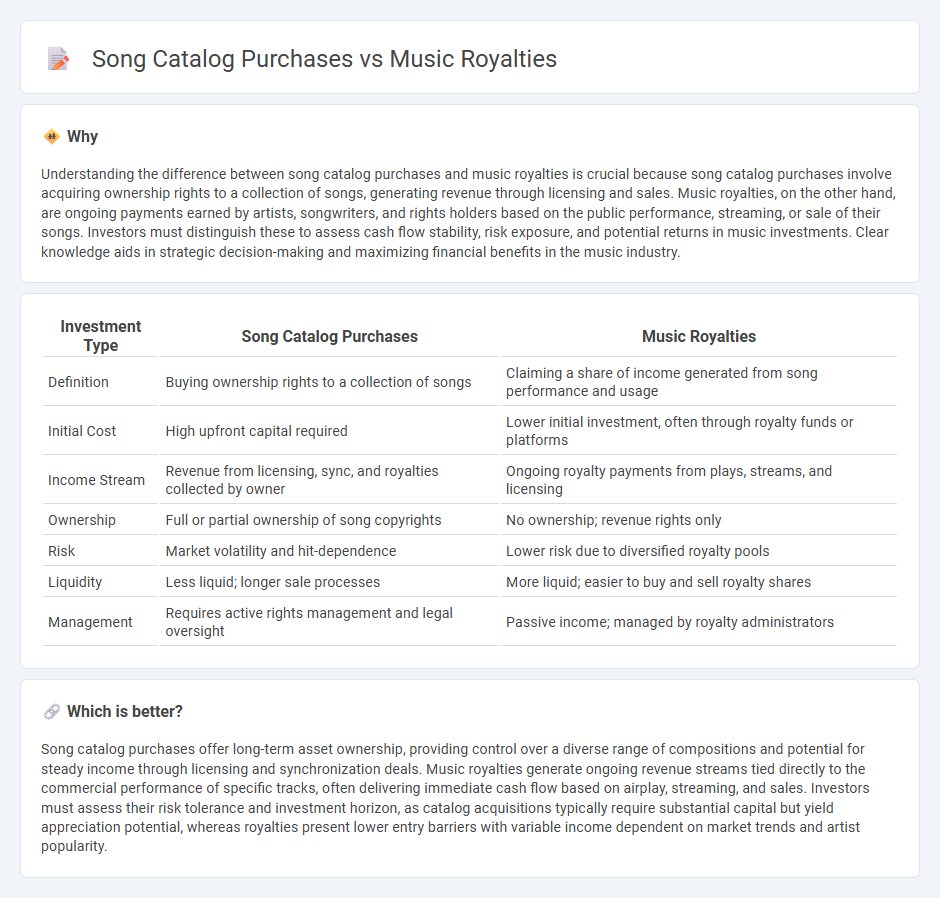
Understanding the difference between song catalog purchases and music royalties is crucial because song catalog purchases involve acquiring ownership rights to a collection of songs, generating revenue through licensing and sales. Music royalties, on the other hand, are ongoing payments earned by artists, songwriters, and rights holders based on the public performance, streaming, or sale of their songs. Investors must distinguish these to assess cash flow stability, risk exposure, and potential returns in music investments. Clear knowledge aids in strategic decision-making and maximizing financial benefits in the music industry.
Comparison Table
| Investment Type | Song Catalog Purchases | Music Royalties |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying ownership rights to a collection of songs | Claiming a share of income generated from song performance and usage |
| Initial Cost | High upfront capital required | Lower initial investment, often through royalty funds or platforms |
| Income Stream | Revenue from licensing, sync, and royalties collected by owner | Ongoing royalty payments from plays, streams, and licensing |
| Ownership | Full or partial ownership of song copyrights | No ownership; revenue rights only |
| Risk | Market volatility and hit-dependence | Lower risk due to diversified royalty pools |
| Liquidity | Less liquid; longer sale processes | More liquid; easier to buy and sell royalty shares |
| Management | Requires active rights management and legal oversight | Passive income; managed by royalty administrators |
Which is better?
Song catalog purchases offer long-term asset ownership, providing control over a diverse range of compositions and potential for steady income through licensing and synchronization deals. Music royalties generate ongoing revenue streams tied directly to the commercial performance of specific tracks, often delivering immediate cash flow based on airplay, streaming, and sales. Investors must assess their risk tolerance and investment horizon, as catalog acquisitions typically require substantial capital but yield appreciation potential, whereas royalties present lower entry barriers with variable income dependent on market trends and artist popularity.
Connection
Investment in song catalog purchases involves acquiring rights to music royalties, enabling investors to earn income from streams, downloads, and licensing deals. These music royalties generate consistent cash flow, making song catalogs attractive assets in the entertainment investment sector. The value of song catalogs often appreciates over time due to increasing royalty revenue and growing demand for music content.
Key Terms
Revenue Streams
Music royalties generate ongoing revenue streams through public performances, mechanical licenses, and synchronization deals, providing artists and rights holders with consistent income based on usage. Song catalog purchases offer a lump sum upfront payment, transferring ownership of multiple tracks and their future royalty earnings to the buyer. Explore detailed insights on how these revenue models impact the music industry's financial landscape.
Intellectual Property Rights
Music royalties represent ongoing income generated by the performance, reproduction, and distribution rights of a song, directly tied to the songwriter or copyright holder's intellectual property rights. Song catalog purchases involve acquiring the full ownership of a collection of songs' copyrighted material, granting control over licensing, royalties, and usage rights. Explore deeper insights into intellectual property strategies and revenue optimization in the music industry.
Asset Valuation
Music royalties provide ongoing revenue streams based on performance, mechanical, and synchronization rights, with valuation heavily influenced by historical earnings and projected future cash flows. Song catalog purchases involve acquiring ownership of a collection of compositions, where asset valuation depends on factors such as the catalog's size, hit frequency, genre diversity, and market demand. Explore our detailed analysis on accurately valuing music assets to maximize investment potential.
Source and External Links
Music Royalties Inc. - A company that acquires song royalties from top artists and distributes dividends to investors, offering direct exposure to music revenues from streaming and other platforms.
Music Royalties Explained - Explains the different types of music royalties, how they are collected, and the roles of artists, producers, and session musicians in receiving payments.
How Music Royalties Work - Describes the roles of songwriters, publishers, and record labels in receiving and distributing royalties, and how ownership percentages are determined among contributors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com