Carbon credit arbitrage leverages price differences between carbon markets to generate profit by buying low in one market and selling high in another, whereas emissions trading involves regulated entities buying and selling emissions allowances to comply with environmental targets. Arbitrage opportunities arise from discrepancies in carbon credit valuation, market liquidity, and regulatory frameworks across regions, offering strategic investment advantages in the evolving climate economy. Explore the dynamics and strategies behind these carbon market mechanisms to optimize your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
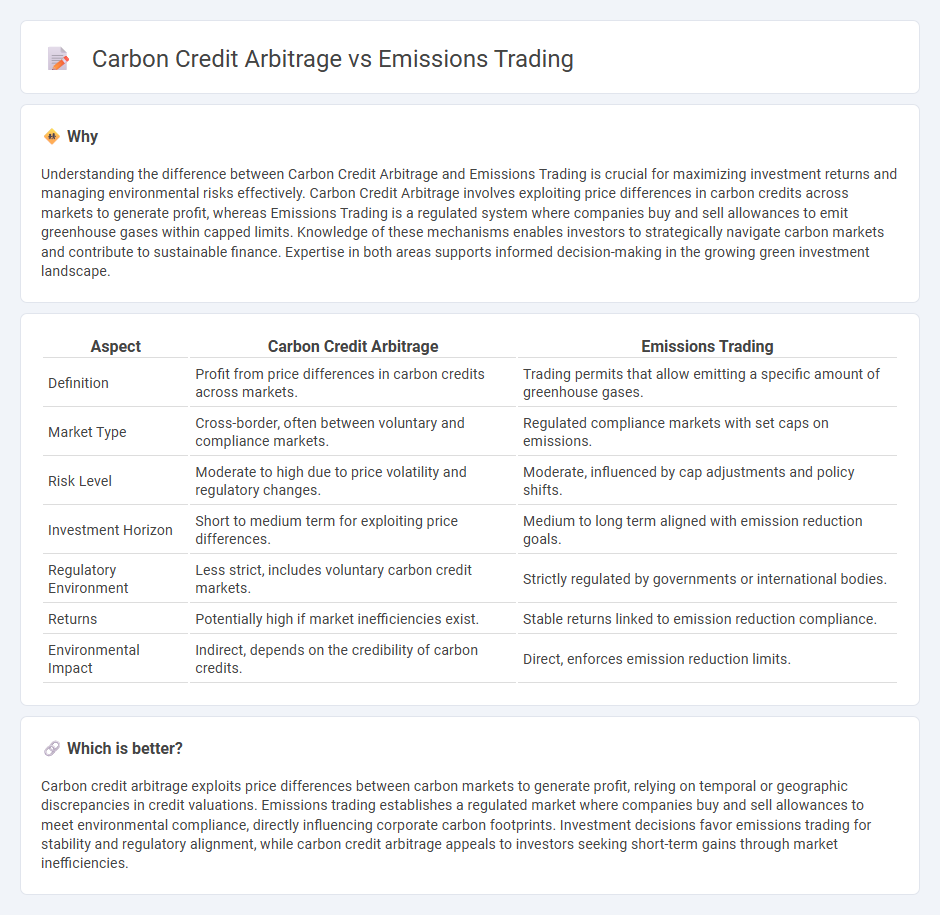
Understanding the difference between Carbon Credit Arbitrage and Emissions Trading is crucial for maximizing investment returns and managing environmental risks effectively. Carbon Credit Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences in carbon credits across markets to generate profit, whereas Emissions Trading is a regulated system where companies buy and sell allowances to emit greenhouse gases within capped limits. Knowledge of these mechanisms enables investors to strategically navigate carbon markets and contribute to sustainable finance. Expertise in both areas supports informed decision-making in the growing green investment landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credit Arbitrage | Emissions Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profit from price differences in carbon credits across markets. | Trading permits that allow emitting a specific amount of greenhouse gases. |
| Market Type | Cross-border, often between voluntary and compliance markets. | Regulated compliance markets with set caps on emissions. |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high due to price volatility and regulatory changes. | Moderate, influenced by cap adjustments and policy shifts. |
| Investment Horizon | Short to medium term for exploiting price differences. | Medium to long term aligned with emission reduction goals. |
| Regulatory Environment | Less strict, includes voluntary carbon credit markets. | Strictly regulated by governments or international bodies. |
| Returns | Potentially high if market inefficiencies exist. | Stable returns linked to emission reduction compliance. |
| Environmental Impact | Indirect, depends on the credibility of carbon credits. | Direct, enforces emission reduction limits. |
Which is better?
Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price differences between carbon markets to generate profit, relying on temporal or geographic discrepancies in credit valuations. Emissions trading establishes a regulated market where companies buy and sell allowances to meet environmental compliance, directly influencing corporate carbon footprints. Investment decisions favor emissions trading for stability and regulatory alignment, while carbon credit arbitrage appeals to investors seeking short-term gains through market inefficiencies.
Connection
Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price differences between regional emissions trading systems (ETS) to buy low-cost credits and sell them in higher-priced markets, maximizing profits. Emissions trading creates regulatory frameworks that assign economic value to carbon allowances, enabling arbitrage opportunities through market linkage or lack of price harmonization. This interconnected dynamic incentivizes efficient carbon reduction while influencing international climate policy and investment flows.
Key Terms
Cap-and-trade
Emissions trading under cap-and-trade programs sets a regulatory limit on total greenhouse gas emissions, allowing companies to buy and sell allowances to meet their caps efficiently. Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price differences between various carbon credit markets, seeking profit across regional or compliance schemes without necessarily reducing emissions. Explore in-depth how cap-and-trade mechanisms function and the strategic role of carbon credit arbitrage in climate finance.
Allowance price
Emissions trading markets establish allowance prices based on supply and demand dynamics, with prices reflecting the cost of emitting one ton of CO2 equivalent under regulatory caps. Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between different carbon markets or project standards, aiming to profit from buying low in one market and selling high in another, thus impacting allowance price volatility. Explore how allowance pricing mechanisms drive market efficiency and arbitrage opportunities in carbon finance.
Compliance market
Emissions trading in the compliance market involves companies buying and selling government-mandated allowances to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases, ensuring adherence to regulatory limits. Carbon credit arbitrage exploits price differentials between various carbon credit markets or instruments, aiming for profit without necessarily contributing to emissions reduction. Explore the intricate dynamics between emissions trading and carbon credit arbitrage to enhance your compliance market strategies.
Source and External Links
Emissions trading - Wikipedia - Emissions trading, also called cap and trade, is a market-oriented approach that sets a pollution cap and allows companies to buy and sell emission permits, incentivizing pollution reduction economically.
What Is Emissions Trading? | US EPA - Emissions trading programs set a pollution cap and allocate tradable allowances, giving sources flexibility to meet goals and have successfully reduced emissions like acid rain pollutants over decades.
EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) - EU Climate Action - The EU ETS, launched in 2005 as the world's first international emissions trading system, limits emissions across multiple sectors and phases in stronger reductions with a 'polluter pays' principle.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com