Tangible asset tokenization converts physical assets such as real estate, art, or commodities into digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity. Debt tokenization involves representing debt instruments like bonds or loans as blockchain-based tokens to improve transparency and ease of trading. Explore the key differences and benefits of these innovative investment methods to optimize your portfolio strategy.
Why it is important
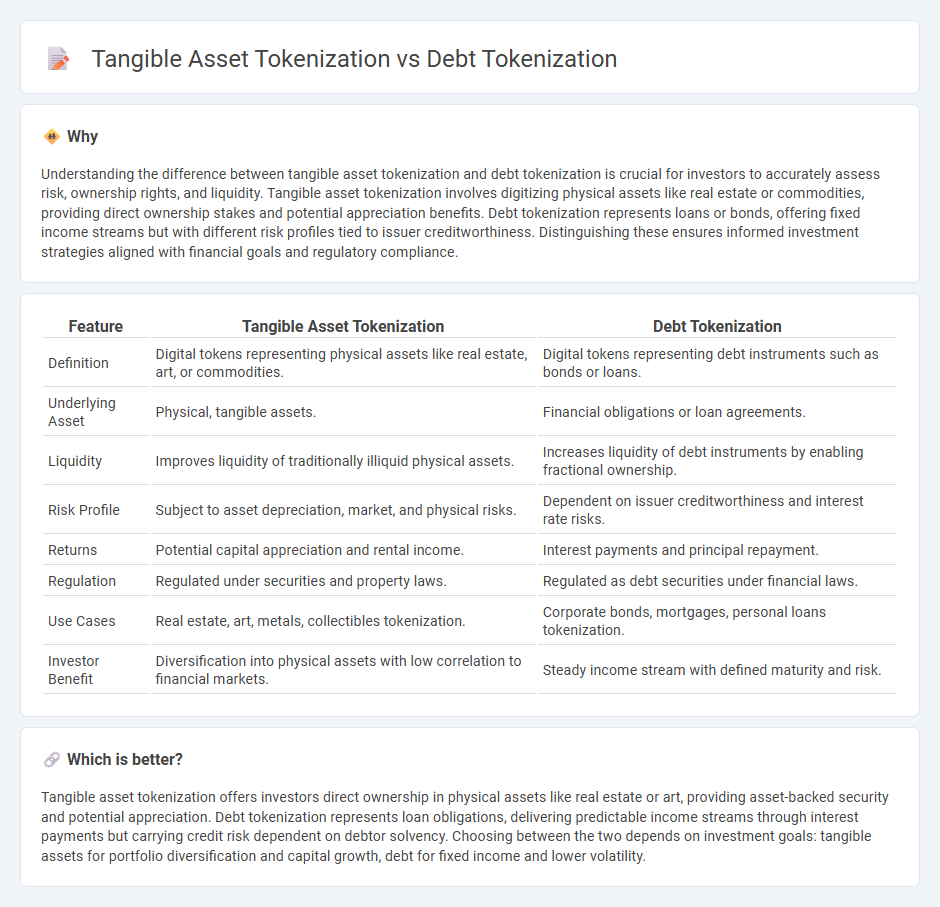
Understanding the difference between tangible asset tokenization and debt tokenization is crucial for investors to accurately assess risk, ownership rights, and liquidity. Tangible asset tokenization involves digitizing physical assets like real estate or commodities, providing direct ownership stakes and potential appreciation benefits. Debt tokenization represents loans or bonds, offering fixed income streams but with different risk profiles tied to issuer creditworthiness. Distinguishing these ensures informed investment strategies aligned with financial goals and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tangible Asset Tokenization | Debt Tokenization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital tokens representing physical assets like real estate, art, or commodities. | Digital tokens representing debt instruments such as bonds or loans. |
| Underlying Asset | Physical, tangible assets. | Financial obligations or loan agreements. |
| Liquidity | Improves liquidity of traditionally illiquid physical assets. | Increases liquidity of debt instruments by enabling fractional ownership. |
| Risk Profile | Subject to asset depreciation, market, and physical risks. | Dependent on issuer creditworthiness and interest rate risks. |
| Returns | Potential capital appreciation and rental income. | Interest payments and principal repayment. |
| Regulation | Regulated under securities and property laws. | Regulated as debt securities under financial laws. |
| Use Cases | Real estate, art, metals, collectibles tokenization. | Corporate bonds, mortgages, personal loans tokenization. |
| Investor Benefit | Diversification into physical assets with low correlation to financial markets. | Steady income stream with defined maturity and risk. |
Which is better?
Tangible asset tokenization offers investors direct ownership in physical assets like real estate or art, providing asset-backed security and potential appreciation. Debt tokenization represents loan obligations, delivering predictable income streams through interest payments but carrying credit risk dependent on debtor solvency. Choosing between the two depends on investment goals: tangible assets for portfolio diversification and capital growth, debt for fixed income and lower volatility.
Connection
Tangible asset tokenization transforms physical assets like real estate or commodities into digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity. Debt tokenization converts debt instruments such as bonds or loans into tradable tokens, facilitating easier transfer and increased market accessibility. Both processes leverage blockchain technology to streamline investment, reduce intermediaries, and improve transparency in asset management.
Key Terms
Securitization
Debt tokenization transforms loan obligations into digital tokens representing debt claims, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity within securitization markets. Tangible asset tokenization converts physical assets like real estate or commodities into blockchain-based tokens, facilitating asset-backed securities with improved transparency and accessibility. Explore how these tokenization methods revolutionize securitization by enhancing market efficiency and investor access.
Collateralization
Debt tokenization transforms traditional debt instruments into digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity. Tangible asset tokenization involves creating digital tokens backed by physical assets like real estate or commodities, providing direct collateralization through the asset's intrinsic value. Explore how collateralization mechanisms differ between these tokenization types to better understand risk management and investment strategies.
Asset-backed token
Debt tokenization converts debt instruments like loans or bonds into digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and easier trading on blockchain platforms. Tangible asset tokenization involves representing physical assets such as real estate, art, or commodities as digital tokens to enhance liquidity and accessibility. Explore in-depth comparisons and benefits of asset-backed tokens to understand their impact on modern finance.
Source and External Links
What are tokenized debt instruments? A beginner's guide - Tokenized debt instruments are digital representations of traditional loans or bonds issued as blockchain tokens, enabling fractional ownership, automated smart contract management, and increased liquidity and transparency, though they face regulatory and standardization challenges.
What are tokenized debt instruments? A beginner's guide - Tokenized debt instruments use blockchain technology to digitize traditional debt securities like bonds and loans, facilitating faster, lower-cost transactions and greater accessibility, with various forms including corporate bonds, mortgages, and peer-to-peer lending agreements.
Debt Tokenization: A New Way To Relieve Debt - Debt tokenization converts real-world debt into digital tokens, simplifying tracking and management of debt obligations while offering new opportunities for capital access and portfolio diversification for investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com