Digital real estate offers investors a unique opportunity to acquire virtual properties within online platforms and metaverses, providing potential for appreciation and rental income. Commodities, such as gold, oil, and agricultural products, serve as tangible assets that hedge against inflation and market volatility. Explore the advantages and risks of digital real estate versus traditional commodities to make informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital real estate and commodities is crucial for investment strategy, as digital real estate represents virtual assets like domain names and metaverse land, while commodities are physical goods like gold and oil with intrinsic value. Digital real estate offers scalability and potential for high returns through digital platforms, whereas commodities provide stability and act as a hedge against inflation. Recognizing these distinctions allows investors to diversify portfolios effectively and manage risks aligned with market volatility and liquidity. This knowledge helps optimize asset allocation tailored to financial goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
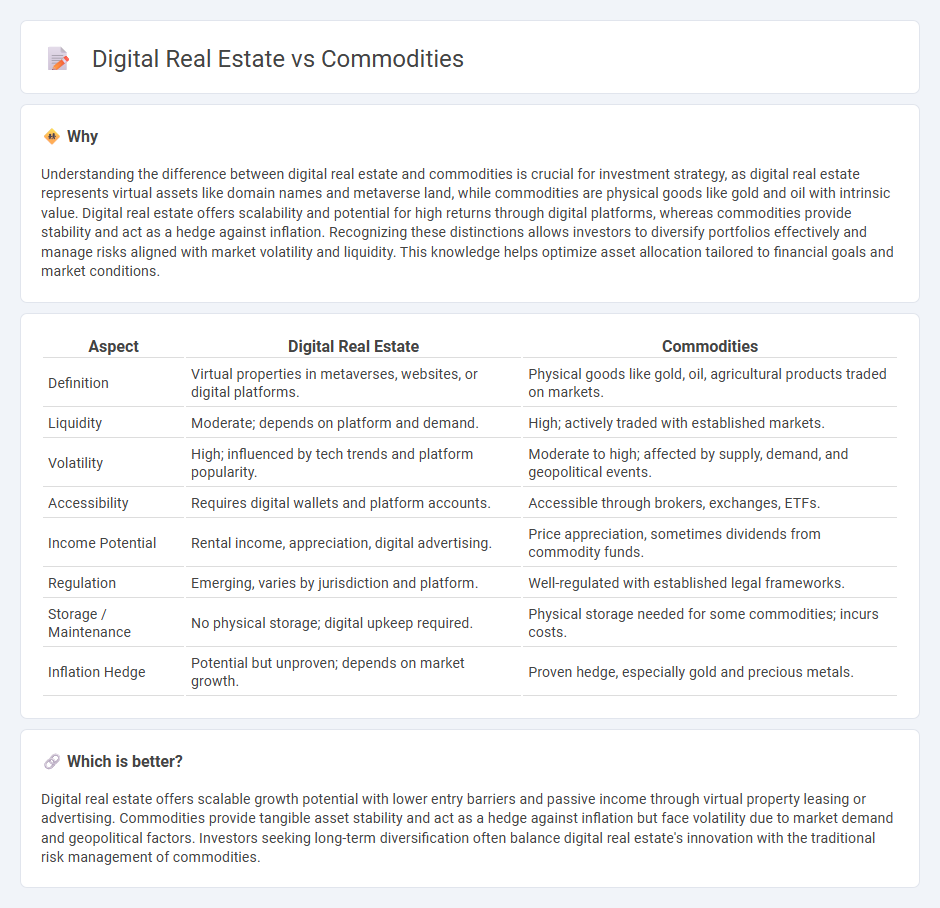
| Aspect | Digital Real Estate | Commodities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual properties in metaverses, websites, or digital platforms. | Physical goods like gold, oil, agricultural products traded on markets. |
| Liquidity | Moderate; depends on platform and demand. | High; actively traded with established markets. |
| Volatility | High; influenced by tech trends and platform popularity. | Moderate to high; affected by supply, demand, and geopolitical events. |
| Accessibility | Requires digital wallets and platform accounts. | Accessible through brokers, exchanges, ETFs. |
| Income Potential | Rental income, appreciation, digital advertising. | Price appreciation, sometimes dividends from commodity funds. |
| Regulation | Emerging, varies by jurisdiction and platform. | Well-regulated with established legal frameworks. |
| Storage / Maintenance | No physical storage; digital upkeep required. | Physical storage needed for some commodities; incurs costs. |
| Inflation Hedge | Potential but unproven; depends on market growth. | Proven hedge, especially gold and precious metals. |
Which is better?
Digital real estate offers scalable growth potential with lower entry barriers and passive income through virtual property leasing or advertising. Commodities provide tangible asset stability and act as a hedge against inflation but face volatility due to market demand and geopolitical factors. Investors seeking long-term diversification often balance digital real estate's innovation with the traditional risk management of commodities.
Connection
Digital real estate and commodities intersect through tokenization, which enables tradable digital assets representing physical commodities or virtual properties on blockchain platforms. This connection enhances liquidity and accessibility, allowing investors to diversify portfolios with fractional ownership in both real estate and commodity markets. The integration of smart contracts further streamlines transactions, ensuring transparency and security in digital asset investments.
Key Terms
Tangible Assets
Commodities such as gold, oil, and agricultural products represent tangible assets with physical presence and intrinsic value, offering investors a hedge against inflation and market volatility. Digital real estate, including virtual land in metaverse platforms, lacks physical form but provides opportunities for innovative revenue streams and capital appreciation in a rapidly growing digital economy. Explore the evolving landscape of tangible assets versus digital investments to understand their unique benefits and risks.
Scarcity
Commodities such as gold, oil, and agricultural products are valued for their physical scarcity and finite supply, which drives demand and price stability. Digital real estate, including virtual land in metaverse platforms, offers scarcity through blockchain-enforced ownership and limited virtual parcels, creating a novel asset class with potential growth. Explore how scarcity dynamics differ between tangible commodities and evolving digital real estate markets to enhance your investment strategy.
Liquidity
Commodities like gold and oil typically offer high liquidity due to well-established global markets and continuous trading volume, allowing quick conversions to cash. Digital real estate, such as virtual land and NFTs, often faces lower liquidity because it depends on niche platforms and fluctuating demand, making sales potentially slower and prices more volatile. Explore detailed insights on liquidity factors influencing both commodities and digital real estate markets.
Source and External Links
Understanding Commodities - Commodities are raw materials like agricultural products, energy, and metals, traded globally via futures contracts as an asset class offering diversification, inflation hedging, and return potential but come with risks related to economic cycles and volatility.
Commodities Versus Differentiated Products | Ag Decision Maker - Commodities are fungible products identical across producers, such as corn or crude oil, traded on futures markets, where producers are price takers with no influence over market price.
Commodities | U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission - Commodity futures contracts involve agreements to buy/sell standardized quantities of goods at fixed prices in the future, regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, with trading occurring on commodity exchanges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com