Pre-existing condition coverage determines the extent to which insurance policies cover illnesses or conditions present before the policy start date, often impacting eligibility and premiums. Underwriting is the comprehensive risk assessment process insurers use to evaluate applicants' health, lifestyle, and medical history to establish policy terms and pricing. Explore the nuances between pre-existing condition coverage and underwriting to make informed insurance decisions.
Why it is important
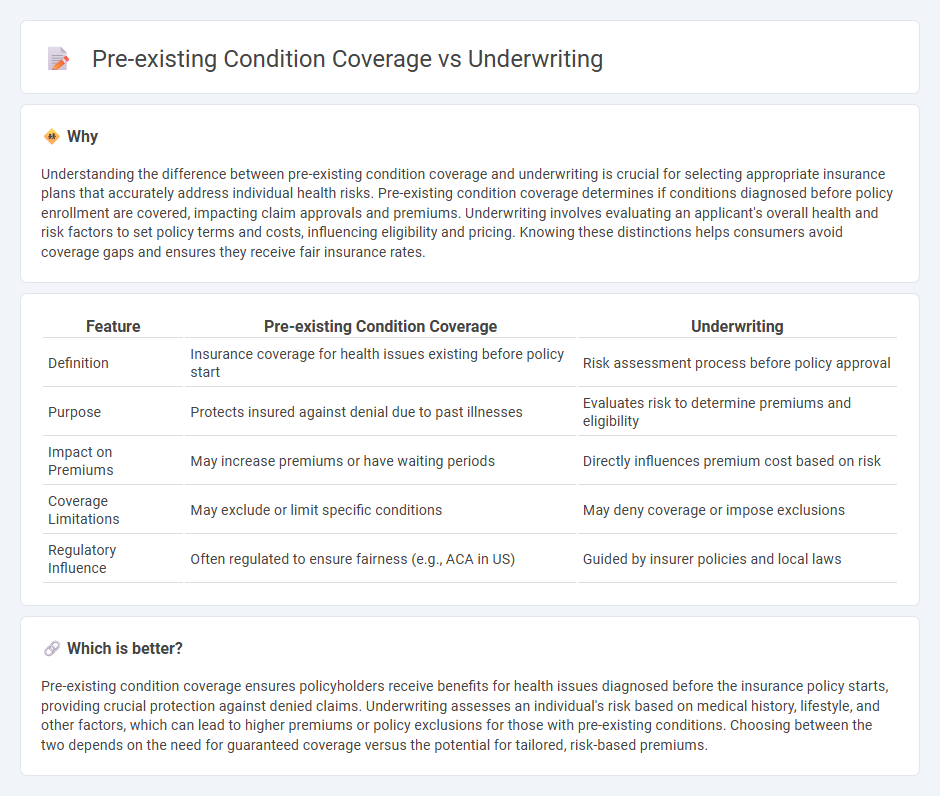
Understanding the difference between pre-existing condition coverage and underwriting is crucial for selecting appropriate insurance plans that accurately address individual health risks. Pre-existing condition coverage determines if conditions diagnosed before policy enrollment are covered, impacting claim approvals and premiums. Underwriting involves evaluating an applicant's overall health and risk factors to set policy terms and costs, influencing eligibility and pricing. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers avoid coverage gaps and ensures they receive fair insurance rates.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Pre-existing Condition Coverage | Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insurance coverage for health issues existing before policy start | Risk assessment process before policy approval |
| Purpose | Protects insured against denial due to past illnesses | Evaluates risk to determine premiums and eligibility |
| Impact on Premiums | May increase premiums or have waiting periods | Directly influences premium cost based on risk |
| Coverage Limitations | May exclude or limit specific conditions | May deny coverage or impose exclusions |
| Regulatory Influence | Often regulated to ensure fairness (e.g., ACA in US) | Guided by insurer policies and local laws |
Which is better?
Pre-existing condition coverage ensures policyholders receive benefits for health issues diagnosed before the insurance policy starts, providing crucial protection against denied claims. Underwriting assesses an individual's risk based on medical history, lifestyle, and other factors, which can lead to higher premiums or policy exclusions for those with pre-existing conditions. Choosing between the two depends on the need for guaranteed coverage versus the potential for tailored, risk-based premiums.
Connection
Pre-existing condition coverage directly impacts underwriting by requiring insurers to assess the health history of applicants to determine risk levels accurately. Underwriting processes integrate medical records and prior diagnoses to establish coverage terms and premiums, ensuring that potential risks associated with pre-existing conditions are appropriately managed. This connection allows insurers to balance policy affordability while protecting their financial pool from unforeseen high-cost claims.
Key Terms
Risk Assessment
Underwriting involves evaluating an applicant's health, lifestyle, and medical history to determine insurance premiums and coverage eligibility, while pre-existing condition coverage specifically addresses conditions diagnosed before policy initiation. Risk assessment in underwriting calculates the probability and potential cost of claims, influencing policy terms and exclusions related to pre-existing conditions. Explore more to understand how insurers balance risk and coverage options for better protection.
Exclusions
Underwriting in health insurance assesses risk factors before policy approval, often leading to exclusions related to pre-existing conditions such as chronic illnesses or prior treatments, impacting coverage availability and cost. Pre-existing condition coverage specifically addresses these health issues by defining terms that limit or exclude benefits based on medical history. Explore further to understand how exclusions vary between underwriting processes and pre-existing condition policies.
Medical History
Underwriting evaluates an applicant's medical history, lifestyle, and risks to determine insurance premium rates and coverage eligibility, while pre-existing condition coverage specifically addresses illnesses or conditions present before policy issuance. Insurance providers often apply stricter terms or exclusions based on historical health data during underwriting to mitigate risk. Explore how underwriting criteria impact pre-existing condition coverage to make informed insurance decisions.
Source and External Links
What Is Underwriting? Definition, Types and How It Works - Underwriting is the process of evaluating and quantifying financial risks involved in loans, investments, or insurance policies to protect banks, investors, and insurance companies, with underwriters assessing creditworthiness and setting appropriate terms and rates.
What Is Underwriting? | PNC Insights - In real estate, underwriting evaluates potential risks before loan approval or insurance issuance, analyzing borrower ability, property value, and market conditions to tailor terms and mitigate risks.
Underwriting - Securities underwriting involves investment banks guaranteeing a price on securities issued by companies or governments, then selling them to the public while managing risk and earning a profit from the price spread.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com