Cyber risk underwriting involves assessing digital threats such as data breaches, ransomware, and cyber-attacks, focusing on IT infrastructure vulnerabilities and regulatory compliance. Property underwriting centers on evaluating physical assets like buildings, equipment, and inventory for risks including fire, theft, and natural disasters. Explore these underwriting approaches to understand their unique risk factors and coverage scopes.
Why it is important
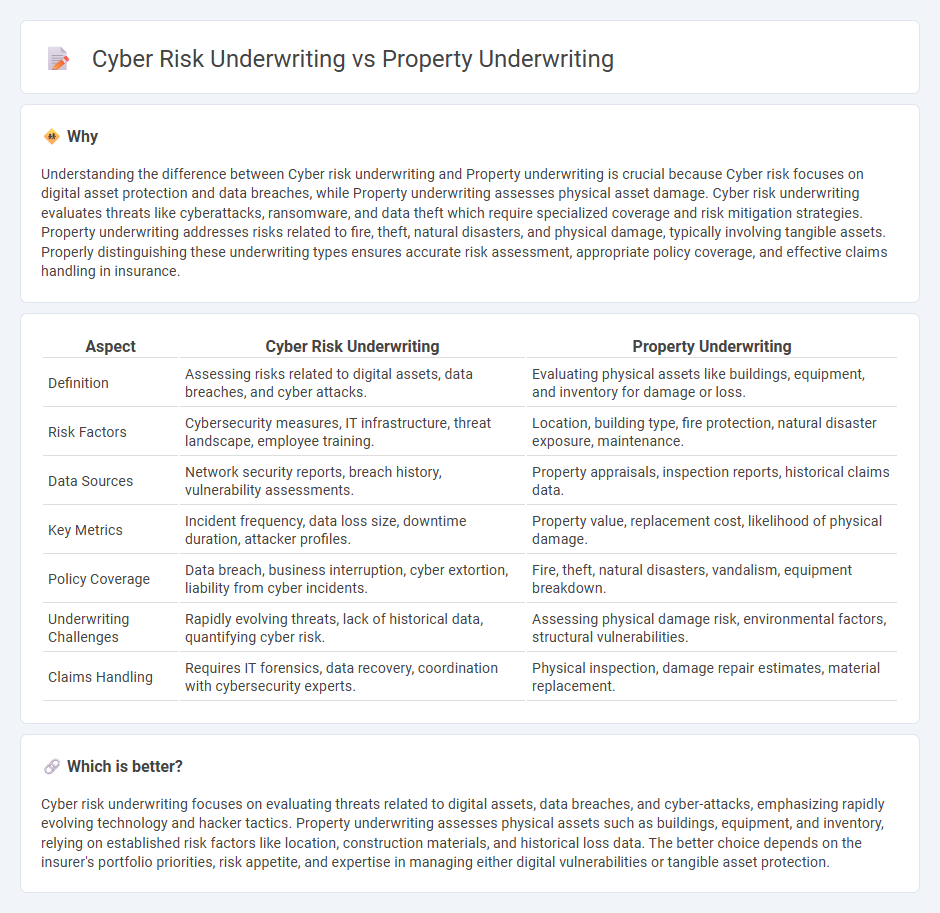
Understanding the difference between Cyber risk underwriting and Property underwriting is crucial because Cyber risk focuses on digital asset protection and data breaches, while Property underwriting assesses physical asset damage. Cyber risk underwriting evaluates threats like cyberattacks, ransomware, and data theft which require specialized coverage and risk mitigation strategies. Property underwriting addresses risks related to fire, theft, natural disasters, and physical damage, typically involving tangible assets. Properly distinguishing these underwriting types ensures accurate risk assessment, appropriate policy coverage, and effective claims handling in insurance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cyber Risk Underwriting | Property Underwriting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessing risks related to digital assets, data breaches, and cyber attacks. | Evaluating physical assets like buildings, equipment, and inventory for damage or loss. |
| Risk Factors | Cybersecurity measures, IT infrastructure, threat landscape, employee training. | Location, building type, fire protection, natural disaster exposure, maintenance. |
| Data Sources | Network security reports, breach history, vulnerability assessments. | Property appraisals, inspection reports, historical claims data. |
| Key Metrics | Incident frequency, data loss size, downtime duration, attacker profiles. | Property value, replacement cost, likelihood of physical damage. |
| Policy Coverage | Data breach, business interruption, cyber extortion, liability from cyber incidents. | Fire, theft, natural disasters, vandalism, equipment breakdown. |
| Underwriting Challenges | Rapidly evolving threats, lack of historical data, quantifying cyber risk. | Assessing physical damage risk, environmental factors, structural vulnerabilities. |
| Claims Handling | Requires IT forensics, data recovery, coordination with cybersecurity experts. | Physical inspection, damage repair estimates, material replacement. |
Which is better?
Cyber risk underwriting focuses on evaluating threats related to digital assets, data breaches, and cyber-attacks, emphasizing rapidly evolving technology and hacker tactics. Property underwriting assesses physical assets such as buildings, equipment, and inventory, relying on established risk factors like location, construction materials, and historical loss data. The better choice depends on the insurer's portfolio priorities, risk appetite, and expertise in managing either digital vulnerabilities or tangible asset protection.
Connection
Cyber risk underwriting and property underwriting intersect through the evaluation of physical and digital asset vulnerabilities, where cyber threats can directly impact property operations and cause tangible property damage. Underwriters assess the risks of cyberattacks causing interruptions, such as ransomware affecting building management systems or IoT device breaches leading to physical damage. Integrating cyber risk data with property underwriting enhances accuracy in predicting losses and developing comprehensive insurance solutions.
Key Terms
**Property Underwriting:**
Property underwriting involves assessing risks related to physical assets such as buildings, equipment, and inventory to determine coverage terms and premium rates. It requires analyzing location, construction quality, occupancy, and potential hazards like fire or natural disasters to minimize losses. Explore more to understand how property underwriting protects valuable assets against unforeseen events.
Replacement Cost
Property underwriting primarily evaluates replacement cost to determine the expense of repairing or rebuilding physical assets after a loss, ensuring coverage aligns with current market values and construction standards. Cyber risk underwriting, by contrast, focuses on assessing potential financial impacts from data breaches or cyberattacks, where replacement cost may involve digital asset recovery and business interruption costs rather than tangible rebuilding. Explore further to understand how replacement cost considerations vary significantly between property and cyber risk underwriting.
Loss History
Property underwriting emphasizes analyzing loss history by examining past claims related to physical damages such as fire, theft, or natural disasters to assess risk exposure and set premiums. Cyber risk underwriting, however, relies on a more complex evaluation of loss history that includes data breaches, ransomware incidents, and system outages, reflecting the evolving nature of cyber threats and their financial impacts. Explore further to understand how these distinct loss history assessments influence underwriting strategies and risk management approaches.
Source and External Links
What Is Underwriting? | PNC Insights - This webpage explains how underwriting in real estate involves assessing potential risks and tailoring agreements to mitigate them, particularly in mortgage lending.
What Is Underwriting in Real Estate? Key Concept Explained - This article discusses how underwriting evaluates financial and risk aspects of real estate investments, including market analysis and due diligence.
Subpart B4, Underwriting Property - This guide outlines property underwriting and appraisal requirements for conventional loans, covering property assessment and valuation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com