Greenium represents the premium investors pay for environmentally friendly assets, reflecting increased demand for green bonds and sustainable stocks. Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to achieve financial returns while promoting ethical impact. Explore further to understand how greenium influences portfolio performance and drives the growth of sustainable finance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between greenium and sustainable investing is crucial for accurately assessing investment risks and returns. Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for green bonds compared to conventional ones, reflecting market demand for environmentally friendly assets. Sustainable investing encompasses a broader strategy that integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term value creation. Differentiating these concepts ensures informed decision-making aligned with financial goals and ethical considerations.
Comparison Table
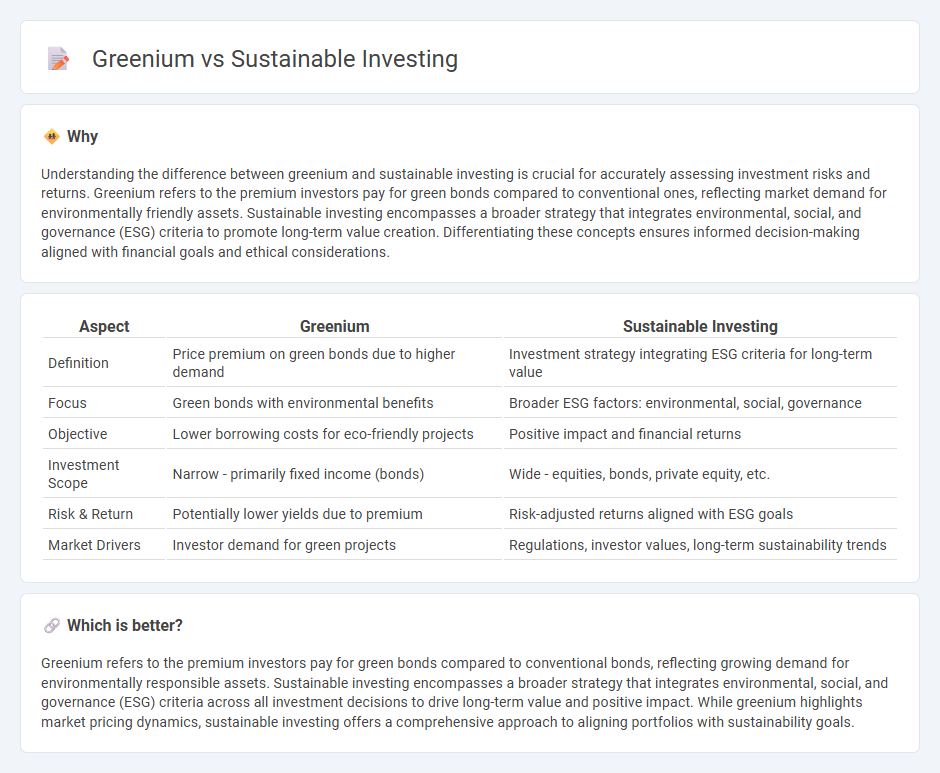
| Aspect | Greenium | Sustainable Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price premium on green bonds due to higher demand | Investment strategy integrating ESG criteria for long-term value |
| Focus | Green bonds with environmental benefits | Broader ESG factors: environmental, social, governance |
| Objective | Lower borrowing costs for eco-friendly projects | Positive impact and financial returns |
| Investment Scope | Narrow - primarily fixed income (bonds) | Wide - equities, bonds, private equity, etc. |
| Risk & Return | Potentially lower yields due to premium | Risk-adjusted returns aligned with ESG goals |
| Market Drivers | Investor demand for green projects | Regulations, investor values, long-term sustainability trends |
Which is better?
Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds, reflecting growing demand for environmentally responsible assets. Sustainable investing encompasses a broader strategy that integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria across all investment decisions to drive long-term value and positive impact. While greenium highlights market pricing dynamics, sustainable investing offers a comprehensive approach to aligning portfolios with sustainability goals.
Connection
Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds, reflecting demand-driven price advantages in sustainable investing markets. Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, attracting capital flows that increase the liquidity and valuation of green assets, thus contributing to the greenium effect. This connection incentivizes issuers to adopt eco-friendly projects while offering investors financial returns aligned with sustainability goals.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Sustainable investing integrates Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term financial returns while promoting positive societal impact. Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for assets with strong ESG profiles, reflecting growing demand for environmentally responsible investments. Explore how ESG factors shape responsible investing strategies and market dynamics by learning more about sustainable investing and greenium.
Green Bonds
Green bonds represent a crucial segment of sustainable investing by funding environmentally focused projects, offering investors both financial returns and positive ecological impact. The greenium, or green bond premium, reflects the often lower yield investors accept due to high demand for these eco-friendly securities compared to conventional bonds. Explore how the greenium influences investment strategies and market dynamics for a deeper understanding.
Risk-Adjusted Return
Sustainable investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term value while minimizing risks associated with non-compliance and reputational damage. Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for securities with strong sustainability credentials, impacting risk-adjusted returns by potentially lowering volatility and downside risk. Explore how these concepts influence portfolio performance and investment strategies in today's evolving financial landscape.
Source and External Links
What Is Sustainable Investing? | HBS Online - Sustainable investing is an investment strategy that integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to achieve financial returns while promoting long-term social and environmental value, reshaping how investors assess companies beyond short-term financial gains.
Socially responsible investing - Socially responsible investing (SRI) considers financial return alongside ethical, social, or environmental goals and often involves avoiding businesses with negative social impacts and actively fostering corporate practices that support environmental stewardship, human rights, and diversity.
SUSTAINABLE INVESTING - Major Sustainability - Penn State - Sustainable investing, also called ESG finance, involves various strategies such as negative and positive screening, ESG integration, and impact investing to balance financial returns with social and environmental outcomes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com