ESG integration involves systematically incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into traditional financial analysis and investment decisions to enhance risk management and identify value opportunities. Sustainable investing, by contrast, prioritizes investments specifically aimed at generating positive social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. Explore further to understand how these strategies shape responsible finance.
Why it is important
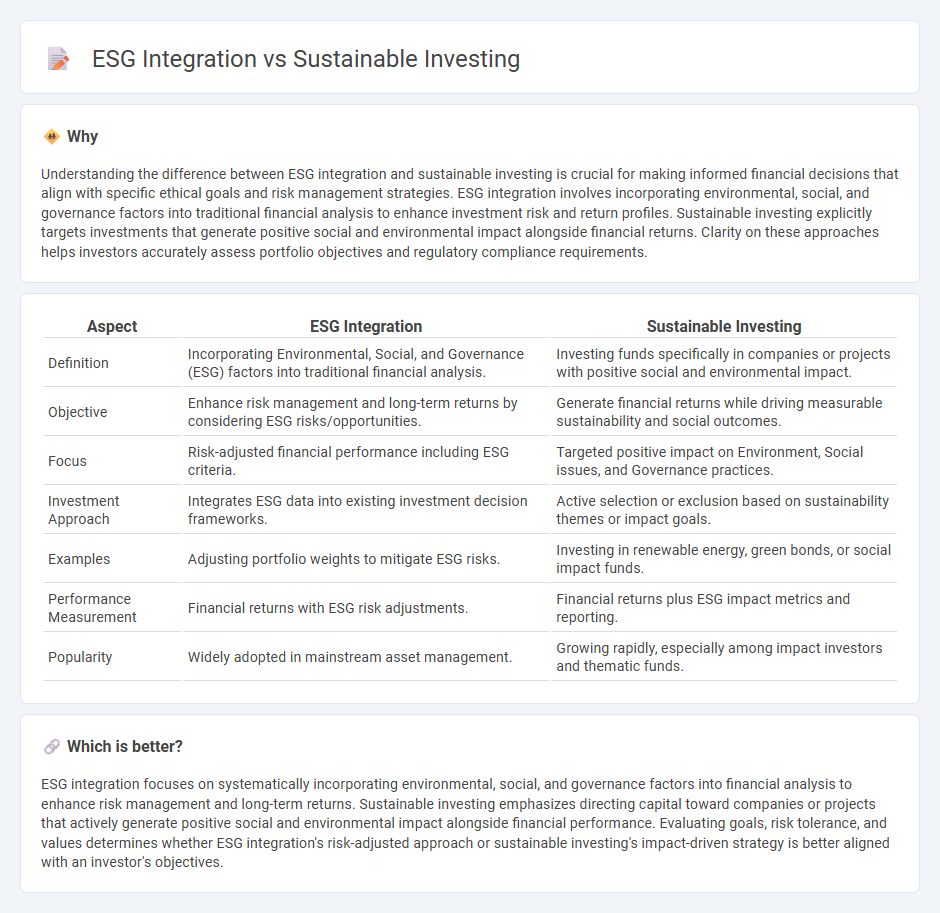
Understanding the difference between ESG integration and sustainable investing is crucial for making informed financial decisions that align with specific ethical goals and risk management strategies. ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into traditional financial analysis to enhance investment risk and return profiles. Sustainable investing explicitly targets investments that generate positive social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. Clarity on these approaches helps investors accurately assess portfolio objectives and regulatory compliance requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Integration | Sustainable Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into traditional financial analysis. | Investing funds specifically in companies or projects with positive social and environmental impact. |
| Objective | Enhance risk management and long-term returns by considering ESG risks/opportunities. | Generate financial returns while driving measurable sustainability and social outcomes. |
| Focus | Risk-adjusted financial performance including ESG criteria. | Targeted positive impact on Environment, Social issues, and Governance practices. |
| Investment Approach | Integrates ESG data into existing investment decision frameworks. | Active selection or exclusion based on sustainability themes or impact goals. |
| Examples | Adjusting portfolio weights to mitigate ESG risks. | Investing in renewable energy, green bonds, or social impact funds. |
| Performance Measurement | Financial returns with ESG risk adjustments. | Financial returns plus ESG impact metrics and reporting. |
| Popularity | Widely adopted in mainstream asset management. | Growing rapidly, especially among impact investors and thematic funds. |
Which is better?
ESG integration focuses on systematically incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into financial analysis to enhance risk management and long-term returns. Sustainable investing emphasizes directing capital toward companies or projects that actively generate positive social and environmental impact alongside financial performance. Evaluating goals, risk tolerance, and values determines whether ESG integration's risk-adjusted approach or sustainable investing's impact-driven strategy is better aligned with an investor's objectives.
Connection
ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into financial analysis to better assess risks and opportunities, which directly supports sustainable investing by promoting capital allocation to companies with responsible practices. Sustainable investing focuses on generating long-term financial returns while advancing positive environmental and social impacts, relying heavily on ESG data to guide investment decisions. This interconnected approach enhances portfolio resilience and drives the transition toward a more sustainable global economy.
Key Terms
Impact Investing
Sustainable investing prioritizes long-term environmental and social benefits by incorporating rigorous impact metrics, while ESG integration evaluates environmental, social, and governance factors primarily to mitigate risk and enhance financial returns. Impact investing specifically directs capital to projects delivering measurable positive social and environmental outcomes alongside financial gains, making it a targeted and strategic subset of sustainable finance. Explore how impact investing strategies transform portfolio management and drive meaningful change.
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Screening
ESG screening evaluates companies based on environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices to mitigate risks and enhance ethical investment outcomes. Sustainable investing incorporates ESG factors but emphasizes long-term value creation and positive societal impact through selective asset allocation. Explore deeper insights into ESG integration strategies to align investments with sustainability goals.
Risk-adjusted Return
Sustainable investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to generate positive societal impact alongside financial returns, whereas ESG integration systematically incorporates these criteria into traditional financial analysis to improve risk-adjusted returns. Studies show ESG integration can enhance portfolio resilience by reducing exposure to non-financial risks and improving long-term performance metrics such as Sharpe ratio and alpha. Discover how aligning investment strategies with ESG principles can maximize risk-adjusted returns and contribute to sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
What Is Sustainable Investing? | HBS Online - Sustainable investing is an investment strategy that considers environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) factors, aiming to drive positive social and environmental impact while providing competitive financial returns, reflecting growing investor demand and the triple bottom line approach.
Socially responsible investing - Socially responsible investing (SRI) integrates ethical, social, or environmental goals with financial returns, often involving screening out harmful industries and promoting corporate practices that advance environmental stewardship, consumer protection, and diversity.
Sustainable investing programs | CFA Institute - The CFA Institute offers education and credentials focused on integrating ESG factors into investment decisions, helping professionals meet client demand for sustainability and addressing climate risk, transition finance, and ethical investment practices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com