Greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds, driven by growing demand for sustainable investments and environmental impact considerations. Conventional bonds typically offer higher yields reflecting greater risk or less market enthusiasm for non-green projects. Explore the evolving dynamics and implications of greenium in bond markets to better understand sustainable finance trends.
Why it is important
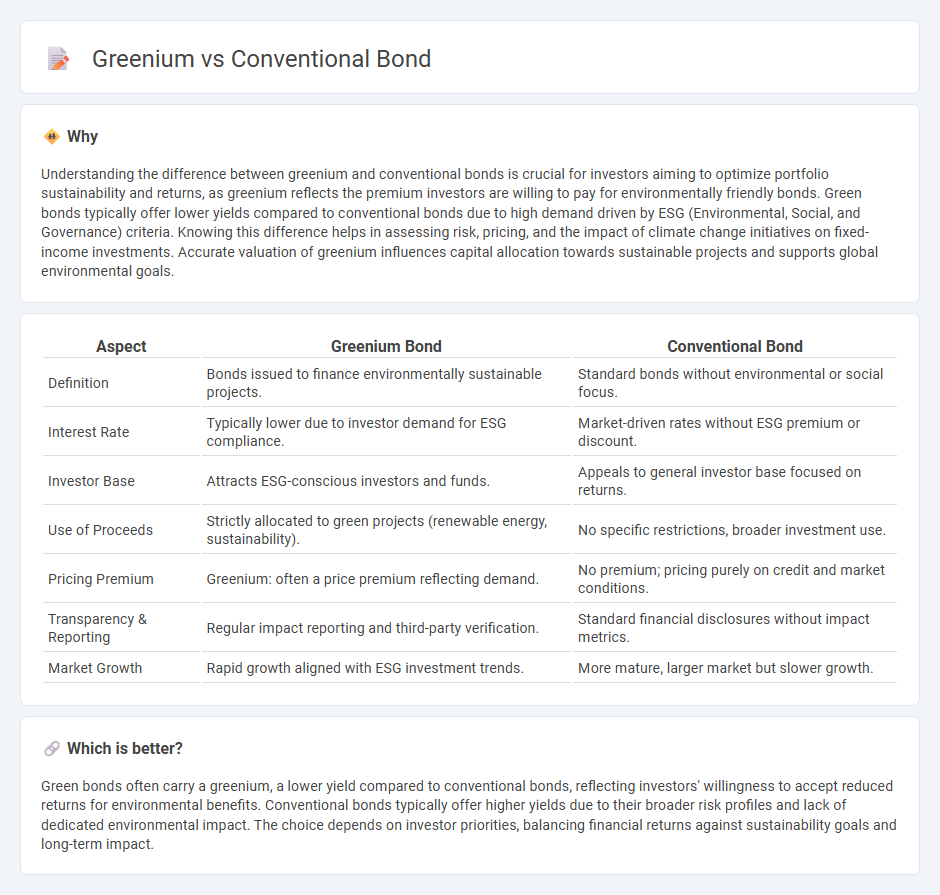
Understanding the difference between greenium and conventional bonds is crucial for investors aiming to optimize portfolio sustainability and returns, as greenium reflects the premium investors are willing to pay for environmentally friendly bonds. Green bonds typically offer lower yields compared to conventional bonds due to high demand driven by ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria. Knowing this difference helps in assessing risk, pricing, and the impact of climate change initiatives on fixed-income investments. Accurate valuation of greenium influences capital allocation towards sustainable projects and supports global environmental goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenium Bond | Conventional Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bonds issued to finance environmentally sustainable projects. | Standard bonds without environmental or social focus. |
| Interest Rate | Typically lower due to investor demand for ESG compliance. | Market-driven rates without ESG premium or discount. |
| Investor Base | Attracts ESG-conscious investors and funds. | Appeals to general investor base focused on returns. |
| Use of Proceeds | Strictly allocated to green projects (renewable energy, sustainability). | No specific restrictions, broader investment use. |
| Pricing Premium | Greenium: often a price premium reflecting demand. | No premium; pricing purely on credit and market conditions. |
| Transparency & Reporting | Regular impact reporting and third-party verification. | Standard financial disclosures without impact metrics. |
| Market Growth | Rapid growth aligned with ESG investment trends. | More mature, larger market but slower growth. |
Which is better?
Green bonds often carry a greenium, a lower yield compared to conventional bonds, reflecting investors' willingness to accept reduced returns for environmental benefits. Conventional bonds typically offer higher yields due to their broader risk profiles and lack of dedicated environmental impact. The choice depends on investor priorities, balancing financial returns against sustainability goals and long-term impact.
Connection
Greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds due to their environmental benefits. This price difference reflects lower yields on green bonds, signaling strong demand driven by sustainable investing commitments and regulatory support. The connection between greenium and conventional bonds highlights the growing integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into fixed-income markets.
Key Terms
Yield
Conventional bonds typically offer stable yields reflecting general market conditions, while greenium bonds often exhibit slightly lower yields due to increased demand for environmentally sustainable investments. This yield differential, known as the "greenium," reflects investors' willingness to accept reduced returns in exchange for positive environmental impact and enhanced ESG credentials. Explore deeper insights into how greenium influences bond valuation and investor behavior.
Coupon
Conventional bonds typically offer fixed coupon rates reflecting general market interest rates and credit risk, while green bonds often carry a "greenium," a yield discount due to high demand for environmentally sustainable investments. This greenium manifests as slightly lower coupons on green bonds compared to comparable conventional bonds, incentivizing investors to finance eco-friendly projects at reduced costs. Explore further to understand how greenium influences portfolio diversification and sustainability-driven investment strategies.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Conventional bonds typically prioritize financial returns without specific environmental or social criteria, while greenium bonds incorporate ESG factors by offering favorable pricing due to investor demand for sustainable projects. Green bonds, characterized by certified use of proceeds for environmentally friendly projects, often exhibit a "greenium," a pricing premium reflecting lower yields compared to conventional debt. Explore how integrating ESG metrics influences bond valuation and investor decision-making for more sustainable finance options.
Source and External Links
Statutory vs. Conventional Bonds: What's the Difference? - A conventional bond is governed by the specific language and intention of the bond documents, allowing it to be qualified, conditioned, or limited in lawful ways, unlike a statutory bond which must follow the requirements set by statute exactly.
Conventional bonds - Conventional bonds, also called nominal bonds (not indexed to inflation), are debt instruments issued by governments and companies, entitling investors to specific interest and principal payments on set dates, and often secured against assets.
Compare and Contrast Sukuk (Islamic Bonds) with Conventional Bonds - Conventional bonds are long-term debt instruments where income comes from the debt promised, with predetermined interest and principal repayments, contrasting with asset-backed Sukuk which indicate asset ownership.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com