Alternative data offers unique, non-traditional insights derived from sources such as social media, satellite imagery, and transaction records, which can enhance investment decision-making beyond conventional datasets. Big data encompasses massive volumes of structured and unstructured information generated at high velocity, enabling complex analytics to identify market trends and risks. Explore how integrating alternative data with big data transforms financial strategies for better accuracy and competitive advantage.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between alternative data and big data is crucial for making informed financial decisions and gaining competitive advantages. Alternative data, such as social media trends or satellite imagery, provides non-traditional insights that can enhance predictive models beyond conventional big data sources like transaction records or market data. Differentiating these data types enables financial analysts to tailor strategies, optimize investment portfolios, and mitigate risks effectively. Knowledge of their distinct characteristics supports compliance with data privacy regulations and improves data-driven financial innovation.
Comparison Table
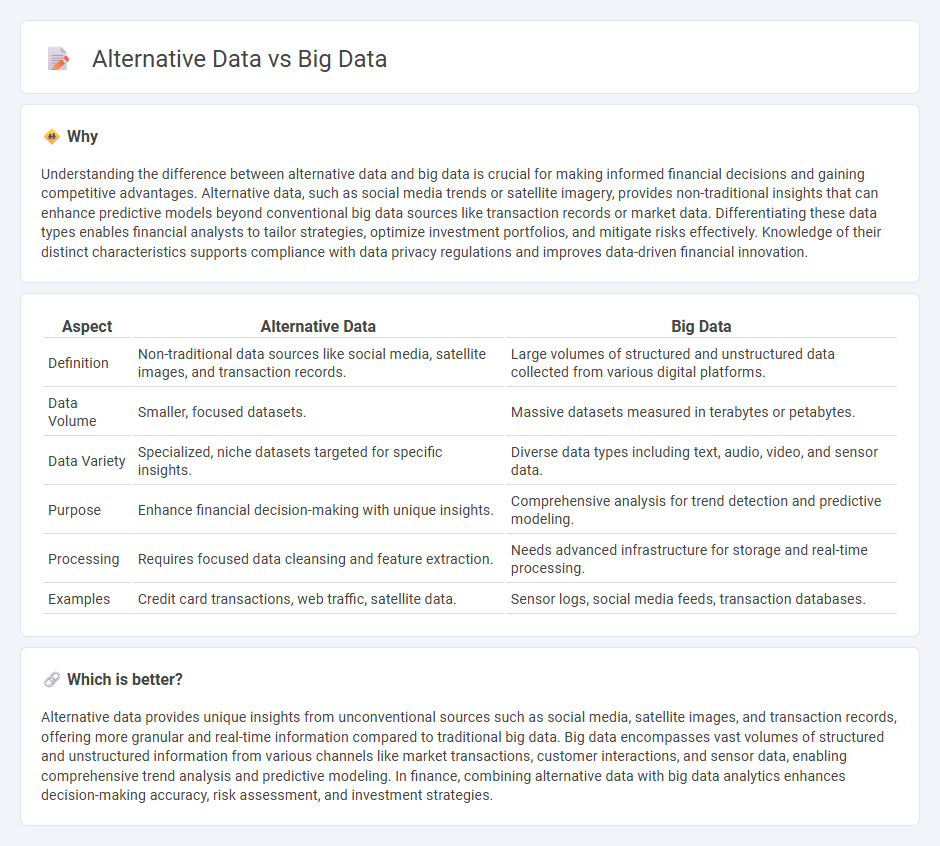
| Aspect | Alternative Data | Big Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-traditional data sources like social media, satellite images, and transaction records. | Large volumes of structured and unstructured data collected from various digital platforms. |
| Data Volume | Smaller, focused datasets. | Massive datasets measured in terabytes or petabytes. |
| Data Variety | Specialized, niche datasets targeted for specific insights. | Diverse data types including text, audio, video, and sensor data. |
| Purpose | Enhance financial decision-making with unique insights. | Comprehensive analysis for trend detection and predictive modeling. |
| Processing | Requires focused data cleansing and feature extraction. | Needs advanced infrastructure for storage and real-time processing. |
| Examples | Credit card transactions, web traffic, satellite data. | Sensor logs, social media feeds, transaction databases. |
Which is better?
Alternative data provides unique insights from unconventional sources such as social media, satellite images, and transaction records, offering more granular and real-time information compared to traditional big data. Big data encompasses vast volumes of structured and unstructured information from various channels like market transactions, customer interactions, and sensor data, enabling comprehensive trend analysis and predictive modeling. In finance, combining alternative data with big data analytics enhances decision-making accuracy, risk assessment, and investment strategies.
Connection
Alternative data and big data intersect by providing expansive, non-traditional information sources that enhance financial analysis beyond classic datasets. Big data's vast volume, velocity, and variety enable the processing of alternative data types such as social media sentiment, satellite imagery, and transactional records to uncover investment insights. Integrating these datasets improves predictive modeling, risk assessment, and decision-making in finance through advanced analytics and machine learning techniques.
Key Terms
Data Sources
Big data primarily originates from traditional structured sources such as transactional databases, social media platforms, sensors, and log files, capturing vast volumes of information generated at high velocity. Alternative data encompasses non-traditional sources including satellite imagery, credit card transactions, web scraping, and social media sentiment, offering unique insights beyond conventional datasets. Explore how integrating these diverse data sources can enhance predictive analytics and strategic decision-making.
Predictive Analytics
Big data encompasses vast and diverse datasets that enable predictive analytics to identify patterns and trends across industries, while alternative data refers to non-traditional data sources like social media, satellite images, and web traffic, enhancing prediction accuracy by providing unique insights. Predictive analytics leverages machine learning algorithms on both big and alternative data to forecast market movements, customer behavior, and operational risks with higher precision. Explore our detailed analysis on harnessing big and alternative data for cutting-edge predictive analytics solutions.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data constitutes over 80% of big data, encompassing text, images, and videos that lack a predefined format, posing significant challenges for traditional data processing tools. Alternative data, often sourced from social media, satellite imagery, and sensor networks, is predominantly unstructured and requires advanced analytics like natural language processing and machine learning for extraction of actionable insights. Explore deeper methodologies to harness unstructured alternative data and transform it into competitive business intelligence.
Source and External Links
What is Big Data? | IBM - Big data refers to massive, complex data sets that traditional data management systems cannot handle, and when properly collected and analyzed, it helps organizations discover new insights and make better decisions.
Big Data Defined: Examples and Benefits | Google Cloud - Big data is extremely large, diverse collections of structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data that grows exponentially and requires advanced tools to store, process, and analyze for business insights.
What Is Big Data? - Oracle - Big data is defined by the "five Vs"--volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value--and is used across industries like healthcare, retail, and finance to drive data-informed decisions and innovation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com