Tokenization of real-world assets transforms physical or traditional financial instruments into digital tokens on blockchain, enhancing liquidity, transparency, and fractional ownership. Mortgage-backed securities pool home loans into tradable assets but often lack the immediate traceability and accessibility provided by tokenized assets. Discover how tokenization is revolutionizing asset management beyond conventional mortgage-backed securities.
Why it is important
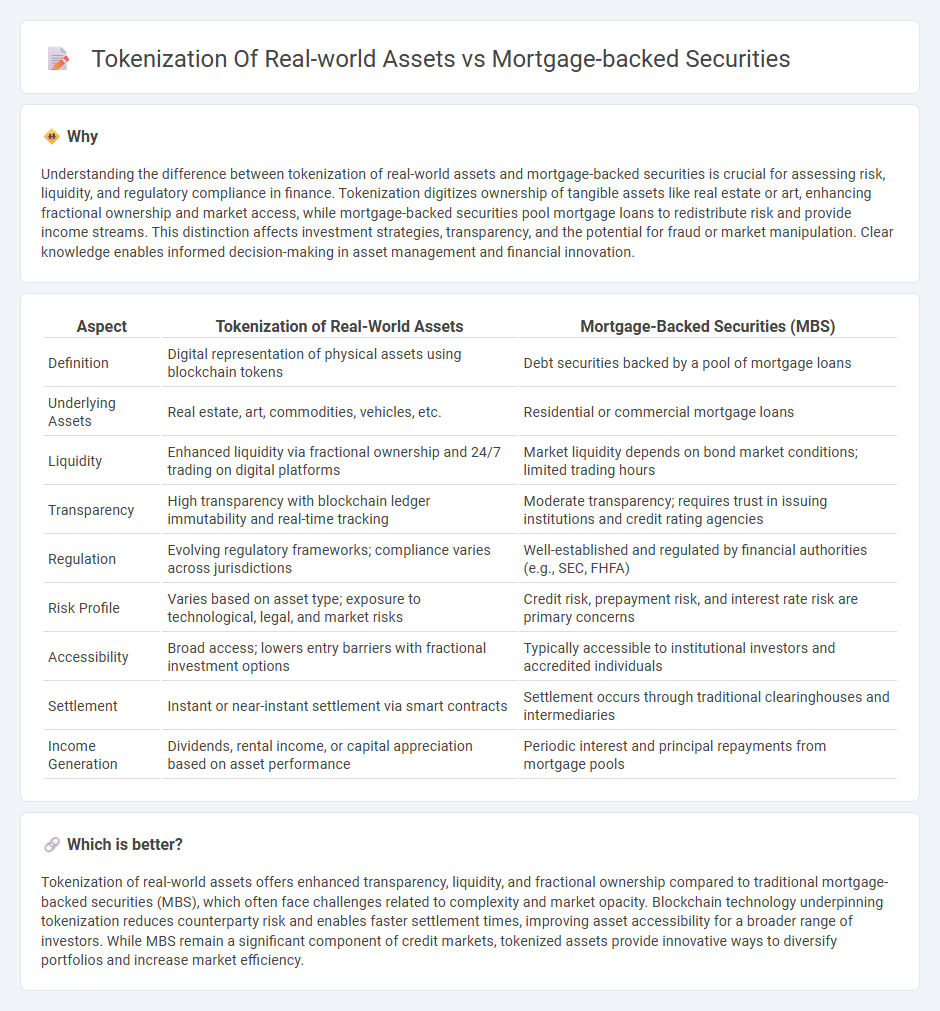
Understanding the difference between tokenization of real-world assets and mortgage-backed securities is crucial for assessing risk, liquidity, and regulatory compliance in finance. Tokenization digitizes ownership of tangible assets like real estate or art, enhancing fractional ownership and market access, while mortgage-backed securities pool mortgage loans to redistribute risk and provide income streams. This distinction affects investment strategies, transparency, and the potential for fraud or market manipulation. Clear knowledge enables informed decision-making in asset management and financial innovation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenization of Real-World Assets | Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital representation of physical assets using blockchain tokens | Debt securities backed by a pool of mortgage loans |
| Underlying Assets | Real estate, art, commodities, vehicles, etc. | Residential or commercial mortgage loans |
| Liquidity | Enhanced liquidity via fractional ownership and 24/7 trading on digital platforms | Market liquidity depends on bond market conditions; limited trading hours |
| Transparency | High transparency with blockchain ledger immutability and real-time tracking | Moderate transparency; requires trust in issuing institutions and credit rating agencies |
| Regulation | Evolving regulatory frameworks; compliance varies across jurisdictions | Well-established and regulated by financial authorities (e.g., SEC, FHFA) |
| Risk Profile | Varies based on asset type; exposure to technological, legal, and market risks | Credit risk, prepayment risk, and interest rate risk are primary concerns |
| Accessibility | Broad access; lowers entry barriers with fractional investment options | Typically accessible to institutional investors and accredited individuals |
| Settlement | Instant or near-instant settlement via smart contracts | Settlement occurs through traditional clearinghouses and intermediaries |
| Income Generation | Dividends, rental income, or capital appreciation based on asset performance | Periodic interest and principal repayments from mortgage pools |
Which is better?
Tokenization of real-world assets offers enhanced transparency, liquidity, and fractional ownership compared to traditional mortgage-backed securities (MBS), which often face challenges related to complexity and market opacity. Blockchain technology underpinning tokenization reduces counterparty risk and enables faster settlement times, improving asset accessibility for a broader range of investors. While MBS remain a significant component of credit markets, tokenized assets provide innovative ways to diversify portfolios and increase market efficiency.
Connection
Tokenization of real-world assets enables the transformation of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) into digital tokens, enhancing liquidity and transparency in the financial markets. This process allows fractional ownership of MBS, making it easier for investors to buy, sell, and trade these securities on blockchain platforms. By integrating tokenization with mortgage-backed securities, financial institutions can reduce settlement times and lower transaction costs, driving greater efficiency and accessibility in asset management.
Key Terms
Securitization
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are traditional financial instruments where loans are pooled and sold to investors, offering predictable cash flows derived from real estate debt. Tokenization of real-world assets leverages blockchain technology to create digital tokens representing ownership in physical assets, enhancing liquidity, transparency, and fractional ownership. Explore how these innovations transform securitization by increasing accessibility and efficiency in asset-backed investments.
Asset-backed tokens
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are traditional financial instruments that bundle home loans into tradeable assets, providing liquidity but often suffering from opacity and complex valuation. Tokenization of real-world assets, particularly asset-backed tokens, leverages blockchain technology to create transparent, liquid, and divisible tokens representing ownership in physical or financial assets, including mortgages, offering enhanced accessibility and efficiency. Discover more about how asset-backed tokens are revolutionizing investment strategies and transforming asset liquidity.
Liquidity
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) provide liquidity by pooling mortgages and issuing tradable securities, allowing investors to buy shares in real estate debt. Tokenization of real-world assets leverages blockchain technology to create fractional ownership tokens, offering enhanced liquidity through 24/7 trading and reduced transaction barriers. Explore how these innovations reshape asset liquidity and investment accessibility.
Source and External Links
Mortgage-Backed Securities and Collateralized ... - Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are debt obligations backed by pools of residential mortgage loans, issued by government agencies like Ginnie Mae or GSEs such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, and structured into varying classes (tranches) with different risk and payment priorities.
Mortgage-Backed Securities: A Guide - MBS are investments in bundled home mortgages sold by lenders, appealing to investors by diversifying risk across many borrowers, with types including pass-throughs, collateralized mortgage obligations, and stripped MBS.
Mortgage-backed security - An MBS is an asset-backed security secured by a mortgage or collection of mortgages, often structured into tranches differing in risk and yield, and was a central factor in the 2008 subprime mortgage crisis.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com