Impact investing directs capital to projects and companies generating measurable social or environmental benefits alongside financial returns, emphasizing proactive change. Socially responsible investing (SRI) involves selecting or excluding investments based on ethical guidelines, often avoiding industries like tobacco or fossil fuels to align with personal or institutional values. Explore the nuances and strategies of impact investing versus SRI to make informed financial decisions.
Why it is important
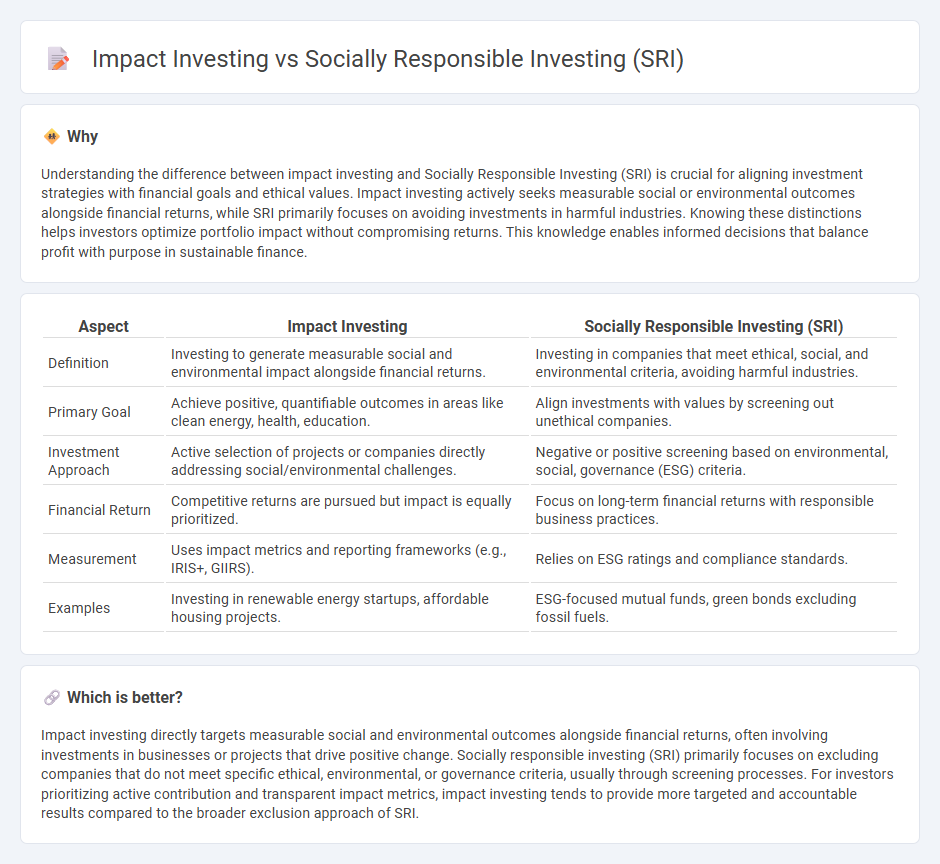
Understanding the difference between impact investing and Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) is crucial for aligning investment strategies with financial goals and ethical values. Impact investing actively seeks measurable social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, while SRI primarily focuses on avoiding investments in harmful industries. Knowing these distinctions helps investors optimize portfolio impact without compromising returns. This knowledge enables informed decisions that balance profit with purpose in sustainable finance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Impact Investing | Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing to generate measurable social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. | Investing in companies that meet ethical, social, and environmental criteria, avoiding harmful industries. |
| Primary Goal | Achieve positive, quantifiable outcomes in areas like clean energy, health, education. | Align investments with values by screening out unethical companies. |
| Investment Approach | Active selection of projects or companies directly addressing social/environmental challenges. | Negative or positive screening based on environmental, social, governance (ESG) criteria. |
| Financial Return | Competitive returns are pursued but impact is equally prioritized. | Focus on long-term financial returns with responsible business practices. |
| Measurement | Uses impact metrics and reporting frameworks (e.g., IRIS+, GIIRS). | Relies on ESG ratings and compliance standards. |
| Examples | Investing in renewable energy startups, affordable housing projects. | ESG-focused mutual funds, green bonds excluding fossil fuels. |
Which is better?
Impact investing directly targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, often involving investments in businesses or projects that drive positive change. Socially responsible investing (SRI) primarily focuses on excluding companies that do not meet specific ethical, environmental, or governance criteria, usually through screening processes. For investors prioritizing active contribution and transparent impact metrics, impact investing tends to provide more targeted and accountable results compared to the broader exclusion approach of SRI.
Connection
Impact investing and Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) are connected through their shared goal of generating positive social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. Impact investing targets measurable, intentional impacts in sectors like renewable energy or affordable housing, while SRI integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to avoid harmful industries. Both strategies attract investors aiming to align capital deployment with ethical values and long-term sustainability performance.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Socially responsible investing (SRI) prioritizes avoiding companies with poor ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices to align portfolios with ethical values. Impact investing actively seeks investments generating measurable positive social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. Discover more about how SRI and impact investing shape sustainable finance strategies.
Intentionality
Socially responsible investing (SRI) emphasizes screening investments based on ethical criteria to avoid harm, while impact investing prioritizes intentionality by seeking measurable positive social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. Impact investors actively target projects and companies that address global challenges such as climate change, clean energy, and social equity, differentiating this approach from the broader values-based exclusions found in SRI. Explore deeper insights into how intentionality shapes investment strategies and drives sustainable impact.
Measurable impact
Socially responsible investing (SRI) emphasizes avoiding investments in companies with negative social or environmental impacts, while impact investing prioritizes funding ventures that generate measurable, positive social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. Impact investing employs specific metrics, such as the Global Impact Investing Network's IRIS+ system, to quantify social or environmental benefits, ensuring transparency and accountability. Explore the distinctions and methodologies that define these investment strategies to optimize your portfolio's societal influence.
Source and External Links
Socially responsible investing - Wikipedia - Socially responsible investing (SRI) is any investment strategy that seeks financial returns alongside ethical, social, or environmental goals, often focusing on ESG factors and encouraging corporate practices promoting environmental stewardship, human rights, and diversity, while avoiding industries with negative social effects.
What Is Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) and How to Get Started - SRI aims to generate both social change and financial returns, including investments in companies with positive sustainable or social impacts and excluding those with negative impacts, often guided by environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
Socially Responsible Investing | Green America - SRI integrates values with investment decisions, encouraging investments in transparent, community-oriented, and environmentally responsible companies while avoiding firms lacking in these areas, and offers tools to screen investments based on personal values related to ESG performance and shareholder activism.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com