Bucket investing segments assets into distinct categories based on risk tolerance and investment horizons, enabling targeted allocation for short-, medium-, and long-term goals. Factor investing focuses on systematic strategies by exploiting specific drivers of returns such as value, momentum, size, and quality across various securities. Explore these investment methodologies to identify which aligns best with your financial objectives and risk profile.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between bucket investing and factor investing is crucial for optimizing portfolio strategy and risk management. Bucket investing segments assets into separate pools for specific time horizons, reducing short-term volatility impact. Factor investing targets specific drivers of return such as value, momentum, and quality to enhance performance and diversification. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their approach with financial goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
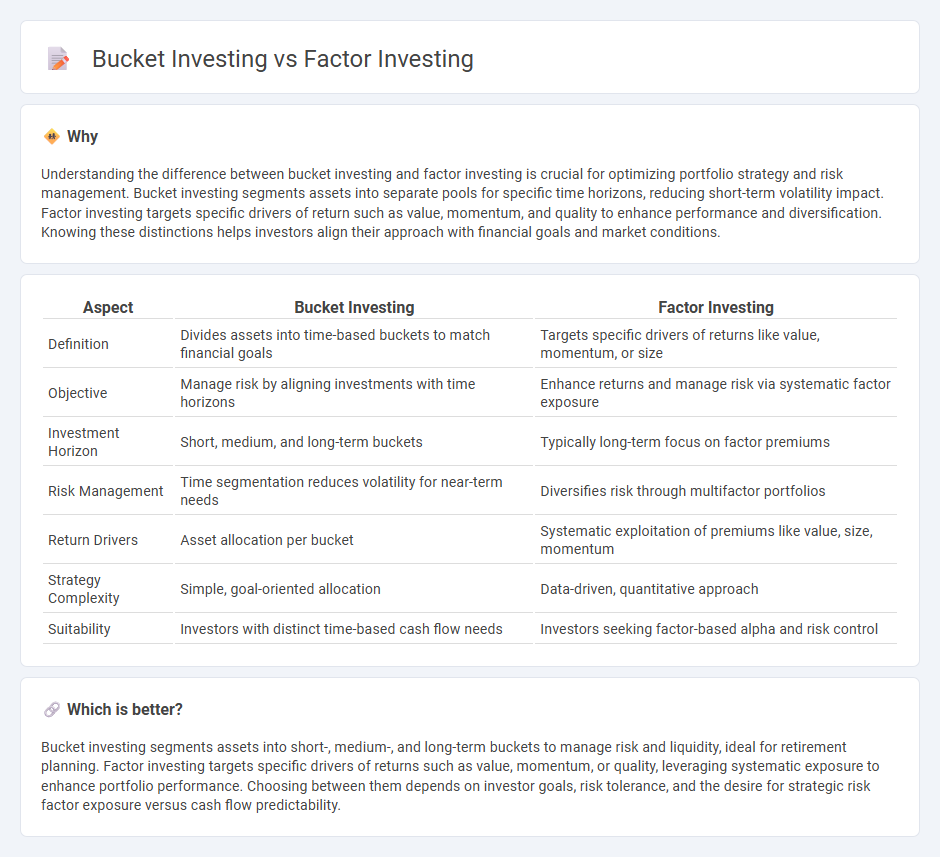
| Aspect | Bucket Investing | Factor Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Divides assets into time-based buckets to match financial goals | Targets specific drivers of returns like value, momentum, or size |
| Objective | Manage risk by aligning investments with time horizons | Enhance returns and manage risk via systematic factor exposure |
| Investment Horizon | Short, medium, and long-term buckets | Typically long-term focus on factor premiums |
| Risk Management | Time segmentation reduces volatility for near-term needs | Diversifies risk through multifactor portfolios |
| Return Drivers | Asset allocation per bucket | Systematic exploitation of premiums like value, size, momentum |
| Strategy Complexity | Simple, goal-oriented allocation | Data-driven, quantitative approach |
| Suitability | Investors with distinct time-based cash flow needs | Investors seeking factor-based alpha and risk control |
Which is better?
Bucket investing segments assets into short-, medium-, and long-term buckets to manage risk and liquidity, ideal for retirement planning. Factor investing targets specific drivers of returns such as value, momentum, or quality, leveraging systematic exposure to enhance portfolio performance. Choosing between them depends on investor goals, risk tolerance, and the desire for strategic risk factor exposure versus cash flow predictability.
Connection
Bucket investing and factor investing both aim to optimize portfolio allocation by targeting specific risk-return profiles. Bucket investing segments assets into distinct time horizons or goals, while factor investing focuses on underlying drivers like value, momentum, or size to enhance returns and manage risk. Integrating factor investing within bucket strategies enables investors to systematically capture style premia aligned with each bucket's investment objective.
Key Terms
Risk Factors
Factor investing targets specific risk factors like value, momentum, and size to tailor portfolio returns and manage systemic risks more efficiently. Bucket investing diversifies assets across different time horizons and risk levels to meet cash flow needs and reduce reinvestment risk. Explore detailed strategies and performance comparisons to determine which approach best suits your financial goals.
Diversification
Factor investing targets specific drivers of returns such as value, momentum, or quality to enhance portfolio diversification by capturing distinct risk premiums. Bucket investing spreads assets into separate "buckets" based on time horizons or risk tolerance, aiming to balance income and growth through varied strategies within each segment. Explore how each method optimizes diversification dynamics by learning more about their tailored approaches.
Asset Allocation
Factor investing emphasizes systematic exposure to specific drivers of returns such as value, momentum, and size to achieve superior risk-adjusted performance compared to traditional approaches. Bucket investing segregates assets into distinct categories based on time horizons or risk tolerance, aiming to match investment goals with liquidity needs and reduce behavioral biases. Explore the nuances of these strategies and how tailored asset allocation can optimize your portfolio's resilience and growth potential.
Source and External Links
What is factor investing? - BlackRock - Factor investing is an approach targeting specific drivers of return (factors) across asset classes to improve portfolio outcomes, reduce volatility, and enhance diversification, using strategies like smart beta and enhanced factor approaches that leverage technology and data.
Guide to factor investing in equity markets - Robeco - Factor investing involves selecting market segments with characteristics (factors) shown historically to deliver higher risk-adjusted returns than the market, such as value, momentum, low volatility, and quality, dating back to the 1970s.
What is Factor Investing? - NEPC - Factor investing seeks to capture premiums associated with specific risks like value, size, momentum, low volatility, dividend yield, and quality to enhance portfolio risk/return, diversification, and the ability to express investment views.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com