Tokenized treasury bills leverage blockchain technology to offer enhanced liquidity and transparency compared to traditional Certificates of Deposit (CDs), which typically have fixed terms and limited marketability. Treasury bills are short-term government securities that, when tokenized, facilitate fractional ownership and seamless trading, whereas CDs are bank-issued products that lock funds for a specified period with a fixed interest rate. Explore the key differences between tokenized treasury bills and CDs to optimize your investment strategy.
Why it is important
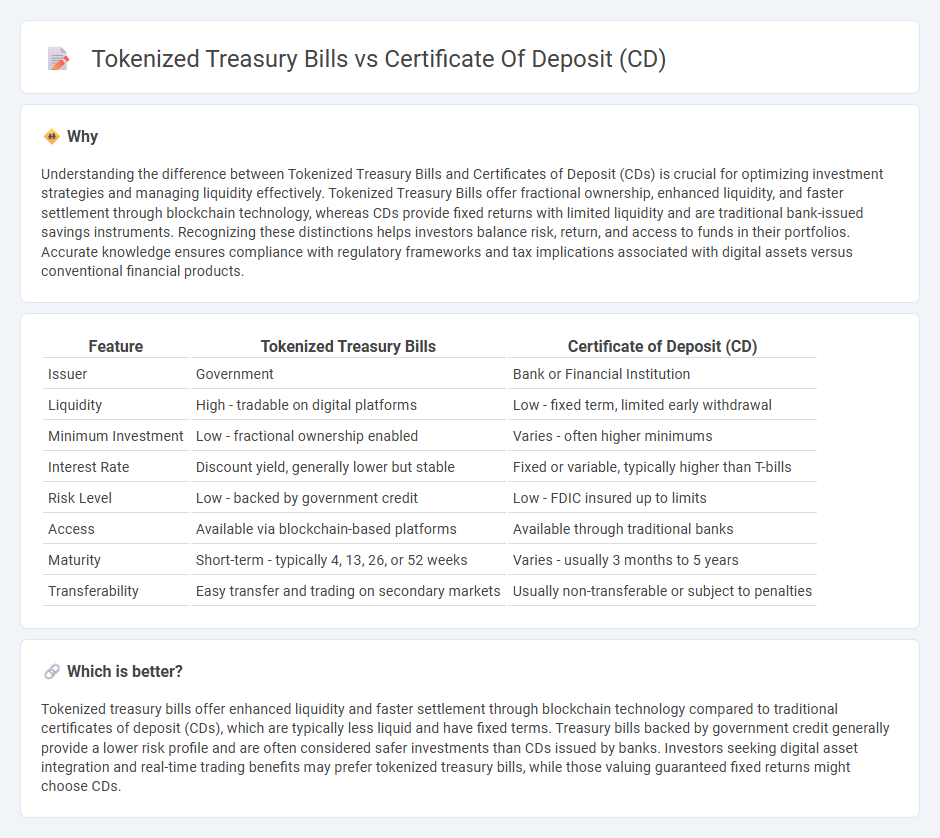
Understanding the difference between Tokenized Treasury Bills and Certificates of Deposit (CDs) is crucial for optimizing investment strategies and managing liquidity effectively. Tokenized Treasury Bills offer fractional ownership, enhanced liquidity, and faster settlement through blockchain technology, whereas CDs provide fixed returns with limited liquidity and are traditional bank-issued savings instruments. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors balance risk, return, and access to funds in their portfolios. Accurate knowledge ensures compliance with regulatory frameworks and tax implications associated with digital assets versus conventional financial products.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tokenized Treasury Bills | Certificate of Deposit (CD) |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Government | Bank or Financial Institution |
| Liquidity | High - tradable on digital platforms | Low - fixed term, limited early withdrawal |
| Minimum Investment | Low - fractional ownership enabled | Varies - often higher minimums |
| Interest Rate | Discount yield, generally lower but stable | Fixed or variable, typically higher than T-bills |
| Risk Level | Low - backed by government credit | Low - FDIC insured up to limits |
| Access | Available via blockchain-based platforms | Available through traditional banks |
| Maturity | Short-term - typically 4, 13, 26, or 52 weeks | Varies - usually 3 months to 5 years |
| Transferability | Easy transfer and trading on secondary markets | Usually non-transferable or subject to penalties |
Which is better?
Tokenized treasury bills offer enhanced liquidity and faster settlement through blockchain technology compared to traditional certificates of deposit (CDs), which are typically less liquid and have fixed terms. Treasury bills backed by government credit generally provide a lower risk profile and are often considered safer investments than CDs issued by banks. Investors seeking digital asset integration and real-time trading benefits may prefer tokenized treasury bills, while those valuing guaranteed fixed returns might choose CDs.
Connection
Tokenized treasury bills and Certificates of Deposit (CDs) both represent digital financial instruments that provide fixed-income investment opportunities through blockchain technology, enhancing transparency and liquidity. Tokenized treasury bills are government-backed short-term securities issued on a blockchain, while tokenized CDs are bank-issued deposits with fixed maturities and interest, transformed into tradable digital tokens. Both instruments enable fractional ownership and seamless trading on digital platforms, bridging traditional finance with decentralized asset management.
Key Terms
Interest Rate
Certificate of deposit (CD) interest rates typically range from 0.5% to 4%, depending on the term length and issuing bank's policies. Tokenized treasury bills leverage blockchain technology and offer competitive yields often tied closely to government bond rates, generally around 3% to 5%, reflecting lower risk and enhanced liquidity. Explore how these financial instruments compare in interest returns and investment flexibility to make informed decisions.
Liquidity
Certificate of deposit (CD) typically offers fixed interest rates but comes with limited liquidity due to early withdrawal penalties, making access to funds restrictive. Tokenized treasury bills, traded on blockchain platforms, provide enhanced liquidity by enabling fractional ownership and near-instant secondary market transactions. Explore the benefits of tokenized treasury bills to better understand their liquidity advantages over traditional CDs.
Counterparty Risk
Certificates of deposit (CDs) expose investors to counterparty risk since banks may default on interest or principal payments during financial stress. Tokenized treasury bills mitigate this risk by representing government-backed securities on a blockchain platform, ensuring transparency and reducing reliance on intermediaries. Explore how these financial instruments compare in managing counterparty risk and safeguarding your investments.
Source and External Links
What is a certificate of deposit (CD)? - A certificate of deposit, or CD, is a type of savings account offered by banks and credit unions where you agree to keep your money deposited for a fixed time in exchange for interest, with early withdrawals subject to penalties and the principal insured up to $250,000 by the FDIC or NCUA.
Certificate of Deposit- Fixed Income Products - Charles Schwab - CDs are bank deposits paying a fixed interest rate over a set term, considered safe and federally insured, with risks including early withdrawal penalties and potential callable features by issuers.
Open a Certificate of Deposit (CD) Account Online | Wells Fargo - A CD offers a secure way to grow savings with a fixed interest rate for a specified term, serving goals for short-to-medium-term saving with FDIC insurance protecting your principal if held until maturity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com