Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to offer transparent, permissionless financial services without traditional intermediaries, enabling access to lending, borrowing, and trading globally. Microfinance focuses on providing small loans, savings, and financial services to underserved populations, fostering economic development in low-income communities. Explore the key differences and unique advantages of DeFi and microfinance in transforming financial inclusion.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between decentralized finance (DeFi) and microfinance is crucial for making informed investment decisions and accessing appropriate financial tools. DeFi leverages blockchain technology to create transparent, permissionless financial services without intermediaries, while microfinance provides small loans and financial services to underserved populations to promote economic development. Knowing these distinctions helps individuals and institutions optimize resource allocation, risk management, and financial inclusion strategies effectively. This knowledge empowers users to choose platforms aligned with their financial goals and regulatory preferences.
Comparison Table
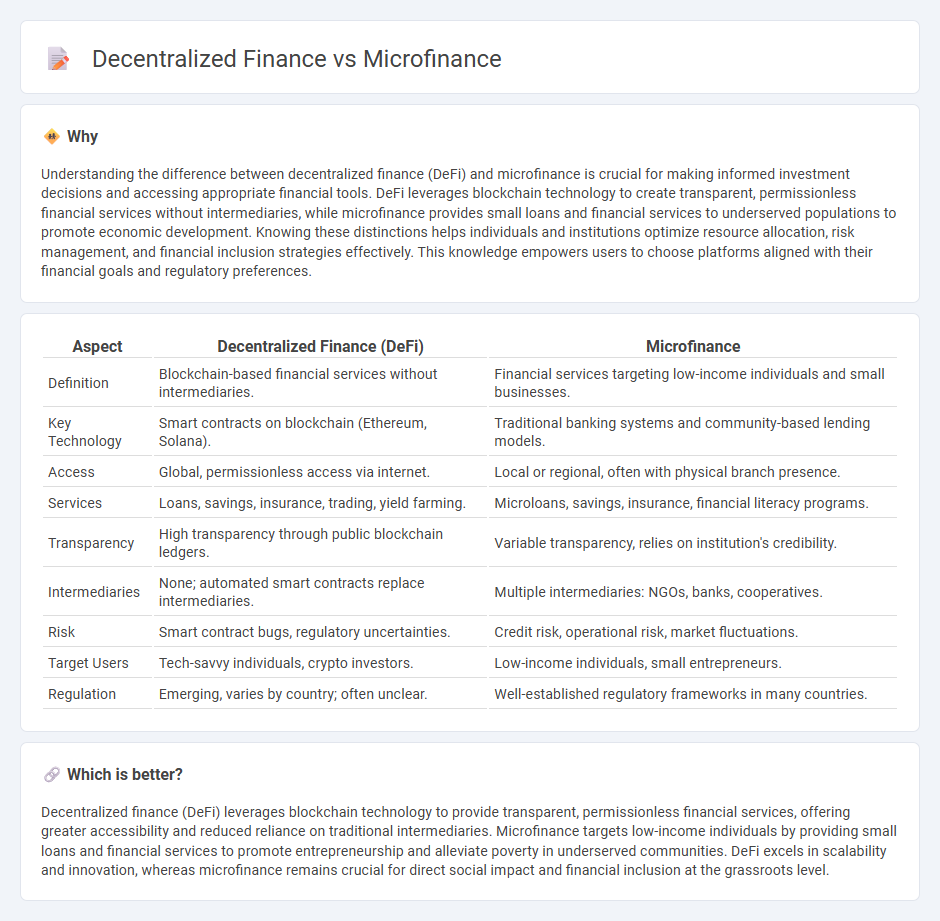
| Aspect | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Microfinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blockchain-based financial services without intermediaries. | Financial services targeting low-income individuals and small businesses. |
| Key Technology | Smart contracts on blockchain (Ethereum, Solana). | Traditional banking systems and community-based lending models. |
| Access | Global, permissionless access via internet. | Local or regional, often with physical branch presence. |
| Services | Loans, savings, insurance, trading, yield farming. | Microloans, savings, insurance, financial literacy programs. |
| Transparency | High transparency through public blockchain ledgers. | Variable transparency, relies on institution's credibility. |
| Intermediaries | None; automated smart contracts replace intermediaries. | Multiple intermediaries: NGOs, banks, cooperatives. |
| Risk | Smart contract bugs, regulatory uncertainties. | Credit risk, operational risk, market fluctuations. |
| Target Users | Tech-savvy individuals, crypto investors. | Low-income individuals, small entrepreneurs. |
| Regulation | Emerging, varies by country; often unclear. | Well-established regulatory frameworks in many countries. |
Which is better?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to provide transparent, permissionless financial services, offering greater accessibility and reduced reliance on traditional intermediaries. Microfinance targets low-income individuals by providing small loans and financial services to promote entrepreneurship and alleviate poverty in underserved communities. DeFi excels in scalability and innovation, whereas microfinance remains crucial for direct social impact and financial inclusion at the grassroots level.
Connection
Decentralized finance (DeFi) and microfinance both aim to increase financial inclusion by providing accessible financial services to underserved populations. DeFi leverages blockchain technology to create transparent, permissionless platforms for lending, borrowing, and investing, which aligns with microfinance's goal of offering small loans and financial products to low-income individuals. The integration of DeFi into microfinance can reduce transaction costs, enhance trust, and enable secure, efficient access to capital for millions in emerging markets.
Key Terms
Financial Inclusion
Microfinance institutions provide small loans and financial services to underserved populations, fostering financial inclusion by targeting low-income individuals without access to traditional banking. Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to offer transparent, permissionless financial tools, removing intermediaries and reducing barriers, thus broadening access to credit, savings, and investment opportunities for marginalized groups. Explore how these innovations are reshaping financial inclusion on a global scale.
Smart Contracts
Microfinance traditionally offers small loans to underserved populations through centralized institutions, whereas decentralized finance (DeFi) utilizes blockchain technology and smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer financial services without intermediaries. Smart contracts automate loan issuance, repayments, and collateral management transparently and securely, reducing operational costs and increasing accessibility in DeFi platforms. Explore the transformative potential of smart contracts in bridging financial inclusivity and efficiency by learning more about their applications in microfinance and DeFi systems.
Peer-to-Peer Lending
Peer-to-peer lending in microfinance leverages direct loans between individuals facilitated by regulated institutions, targeting underserved borrowers with minimal collateral and fixed interest rates, supporting financial inclusion. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms use blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer lending without intermediaries, offering greater transparency, liquidity, and programmable smart contracts, often featuring variable interest rates based on market dynamics. Explore how these innovative lending models reshape access to capital and revolutionize global financial ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Microfinance - Definition, Benefits, Drawbacks, Models - Microfinance offers financial services like microcredit, savings, microinsurance, and fund transfers to individuals of lower socioeconomic status who lack access to traditional banking, aiming to promote economic development and entrepreneurship in impoverished areas.
Microfinance 101: All you need to know - Kiva - Microfinance provides financial services to underserved individuals and small businesses who are often unbanked due to poverty, lack of documentation, geographic barriers, and systemic inequalities, helping increase economic opportunity and financial inclusion worldwide.
Microfinancing Basics - My Own Business Institute - Microfinance is the provision of small loans and other financial services to entrepreneurs who cannot access traditional funding, often involving both institution-centered and client-centered models to support small business growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com